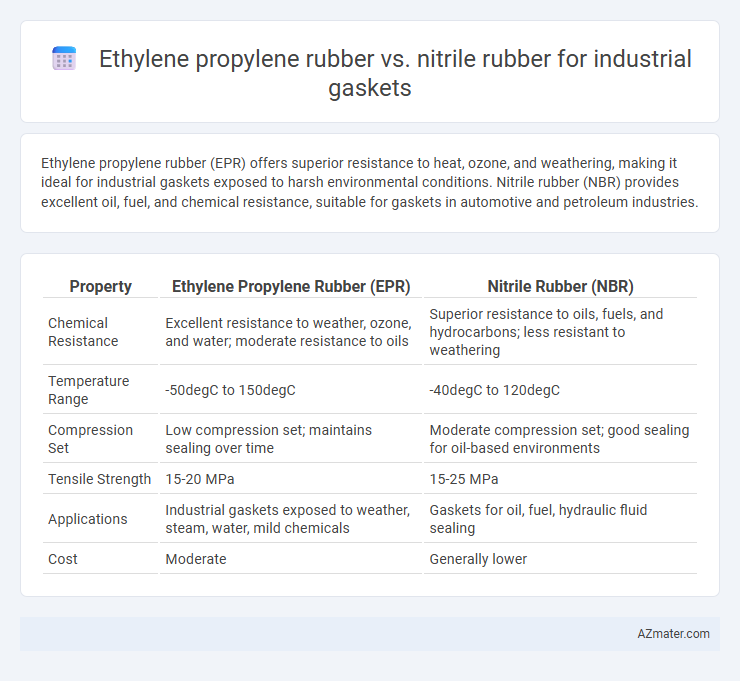
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for industrial gaskets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, suitable for gaskets in automotive and petroleum industries.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to weather, ozone, and water; moderate resistance to oils | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons; less resistant to weathering |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Compression Set | Low compression set; maintains sealing over time | Moderate compression set; good sealing for oil-based environments |
| Tensile Strength | 15-20 MPa | 15-25 MPa |
| Applications | Industrial gaskets exposed to weather, steam, water, mild chemicals | Gaskets for oil, fuel, hydraulic fluid sealing |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally lower |
Introduction to Industrial Gasket Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and nitrile rubber (NBR) are widely used materials in industrial gaskets due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. EPR offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for applications requiring high flexibility and durability under harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber excels in resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, providing superior sealing performance in petroleum-based industrial environments.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to heat, oxidation, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for industrial gasket applications exposed to harsh environments. Its excellent flexibility and resilience at low temperatures, combined with strong resistance to water, steam, and polar substances, distinguish it from Nitrile Rubber, which excels in oil and fuel resistance but lacks EPDM's weathering durability. This balance of chemical and environmental resistance enables EPDM gaskets to maintain sealing integrity in varied industrial settings, especially where exposure to outdoor conditions and aggressive chemicals is prevalent.
Key Properties of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for industrial gaskets exposed to petrochemical environments. Its excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength ensure durability under mechanical stress, while NBR's temperature tolerance ranges from -40degC to 120degC, suitable for varied industrial applications. Compared to ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), NBR's enhanced compatibility with hydrocarbons and better sealing performance drive its preference in gasket manufacturing for engines and hydraulic systems.
Chemical Resistance: EPDM vs NBR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and water-based fluids, making it ideal for industrial gasket applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases, providing excellent sealing performance in applications involving hydrocarbons and lubricants. For industrial gaskets requiring chemical resistance, EPDM is preferred for aqueous and chemical exposure, while NBR is optimal for oil and fuel environments.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) typically withstands temperatures from -50degC to 150degC, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial gasket applications requiring excellent heat resistance. Nitrile rubber (NBR), with a temperature tolerance range of -40degC to 120degC, offers superior resistance to oils and fuels but has lower heat endurance compared to EPR. Selecting EPR over NBR enhances gasket performance in environments with elevated thermal exposure, ensuring durability and elasticity under extreme heat conditions.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) demonstrates excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat but shows limited compatibility with oils and fuels, making it less suitable for gaskets exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to a wide range of oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making it the preferred material for industrial gaskets in oil and fuel environments. For applications requiring high oil and fuel compatibility, nitrile rubber gaskets provide enhanced durability and sealing performance compared to ethylene propylene rubber.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent tensile strength and superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, making it highly durable for industrial gaskets used in harsh environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits higher mechanical strength against oils, fuels, and chemicals, ensuring robust performance in oil-resistant gasket applications. For industrial gaskets requiring long-term durability with chemical resistance, nitrile rubber excels, while ethylene propylene rubber provides enhanced mechanical resilience in outdoor and high-temperature conditions.
Common Industrial Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is widely used in industrial gaskets for applications involving exposure to heat, steam, and weather due to its excellent resistance to ozone, aging, and chemicals. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and hydraulic fluid resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive, aerospace, and petroleum industries. Selection between EPR and NBR depends on operational conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Cost and Availability Factors
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) generally offers a lower cost and greater availability compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) for industrial gasket applications, especially in high-volume production scenarios. EPR provides excellent resistance to heat, oxidation, and weathering, making it economically favorable for environments with moderate oil exposure, whereas NBR is typically more expensive due to its superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. The widespread production and demand for EPR contribute to its cost-effectiveness and readily available supply, while NBR may require longer lead times and higher procurement costs depending on the specific compound and quality requirements.
Selecting the Right Rubber for Gasket Performance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat, making it ideal for industrial gaskets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, providing superior sealing performance in applications involving hydrocarbons and solvents. Choosing between EPR and NBR depends on the specific operating environment, chemical exposure, and temperature range required for optimal gasket durability and effectiveness.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Industrial gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com