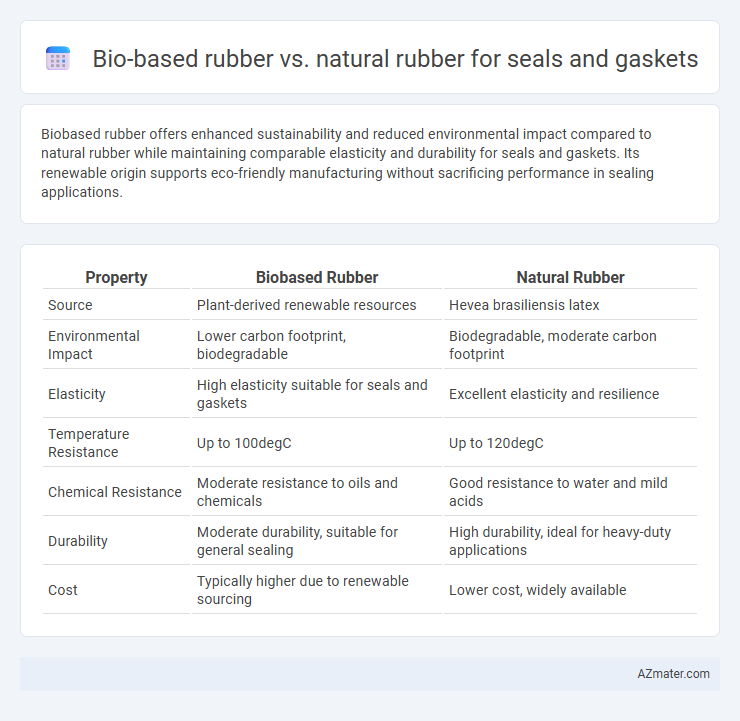
Biobased rubber offers enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to natural rubber while maintaining comparable elasticity and durability for seals and gaskets. Its renewable origin supports eco-friendly manufacturing without sacrificing performance in sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-derived renewable resources | Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, biodegradable | Biodegradable, moderate carbon footprint |
| Elasticity | High elasticity suitable for seals and gaskets | Excellent elasticity and resilience |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | Good resistance to water and mild acids |
| Durability | Moderate durability, suitable for general sealing | High durability, ideal for heavy-duty applications |
| Cost | Typically higher due to renewable sourcing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Rubber Materials: Biobased vs Natural
Biobased rubber and natural rubber serve critical roles in seal and gasket applications, each offering unique material properties derived from renewable sources. Biobased rubber is synthesized from plant-derived monomers, providing enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional natural rubber harvested from Hevea brasiliensis latex. Both materials exhibit excellent elasticity, resilience, and chemical resistance, but biobased rubber often incorporates modified polymers to improve performance metrics such as thermal stability and aging resistance in industrial sealing solutions.
Key Differences Between Biobased and Natural Rubber
Biobased rubber is synthesized from renewable biomass sources such as plant oils and carbohydrates, offering consistent quality and enhanced environmental sustainability compared to natural rubber, which is harvested from rubber tree latex and subject to seasonal and geographic variability. Natural rubber provides superior elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for dynamic seals and gaskets requiring high tensile strength and cut resistance, whereas biobased rubber formulations often enhance chemical resistance and aging performance through tailored polymer structures. The key differences lie in the source material's renewability, performance consistency, and specific mechanical properties critical for sealing and gasket applications under varying operational stresses.
Material Composition and Source Overview
Biobased rubber for seals and gaskets primarily consists of polymers derived from renewable biomass sources such as plant oils, starches, and lignocellulosic materials, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional natural rubber. Natural rubber is obtained from the latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis trees, composed mainly of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, known for its high elasticity and resilience. The material composition differences influence properties like biodegradability and chemical resistance, with biobased rubbers potentially enhanced through chemical modifications to match or exceed natural rubber performance in sealing applications.
Environmental Impact: Biobased vs Natural Rubber
Biobased rubber offers a reduced environmental footprint compared to natural rubber by utilizing renewable resources and minimizing reliance on traditional latex extraction, which often disrupts ecosystems. The production of biobased rubber typically generates lower greenhouse gas emissions and requires less water, contributing to enhanced sustainability in seal and gasket manufacturing. While natural rubber is biodegradable, biobased rubber incorporates eco-friendly polymers that improve durability without compromising environmental benefits.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Biobased rubber for seals and gaskets offers enhanced sustainability while maintaining comparable tensile strength and elongation to traditional natural rubber. It exhibits superior resistance to heat aging and chemical degradation, which improves long-term performance in harsh environments. Mechanical properties such as compression set and tear resistance in biobased rubber often meet or exceed those of natural rubber, ensuring reliable sealing under dynamic conditions.
Chemical Resistance for Seals and Gaskets
Biobased rubber exhibits enhanced chemical resistance compared to conventional natural rubber, making it ideal for seals and gaskets exposed to aggressive oils, fuels, and solvents. The molecular structure of biobased rubber allows improved resistance to swelling and degradation, ensuring longer service life in harsh chemical environments. This superior chemical stability reduces maintenance needs and leakage risks in industrial applications.
Longevity and Durability Analysis
Biobased rubber demonstrates enhanced longevity and durability compared to traditional natural rubber when used in seals and gaskets due to its improved resistance to oxidation, UV degradation, and chemical exposure. Studies indicate biobased rubber maintains mechanical integrity and flexibility over extended operating temperatures, reducing wear and tear under dynamic conditions. The superior aging properties of biobased formulations result in longer service life and decreased maintenance frequency in sealing applications.
Manufacturing and Processing Considerations
Biobased rubber offers a sustainable alternative to natural rubber for seals and gaskets, with processing parameters closely aligned to those of natural rubber, including similar vulcanization temperatures and curing times. Manufacturing considerations highlight biobased rubber's potential for reduced carbon footprint without significant modifications to existing compounding and molding equipment. However, natural rubber maintains advantages in resilience and flexibility, which may influence processing choices and final product performance in demanding sealing applications.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Biobased rubber often presents a higher upfront cost compared to natural rubber due to advanced production methods and limited economies of scale, impacting seal and gasket manufacturing budgets. Natural rubber remains more widely available globally, benefiting from established supply chains and mature markets, supporting cost-effective sourcing for industrial applications. Growing demand for sustainable materials drives gradual increases in biobased rubber availability, but natural rubber currently dominates market presence and cost efficiency.
Future Trends in Rubber Selection for Seals and Gaskets
Future trends in rubber selection for seals and gaskets emphasize sustainability, driving increased adoption of biobased rubber due to its reduced environmental footprint and enhanced biodegradability compared to traditional natural rubber. Advances in biobased polymer technology are improving the mechanical properties and chemical resistance of biobased rubber, making it a viable alternative for high-performance sealing applications. The integration of biobased rubbers aligns with circular economy goals and regulatory pressures, positioning them as key materials in the evolving landscape of sustainable industrial sealing solutions.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Natural rubber for Seal and gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com