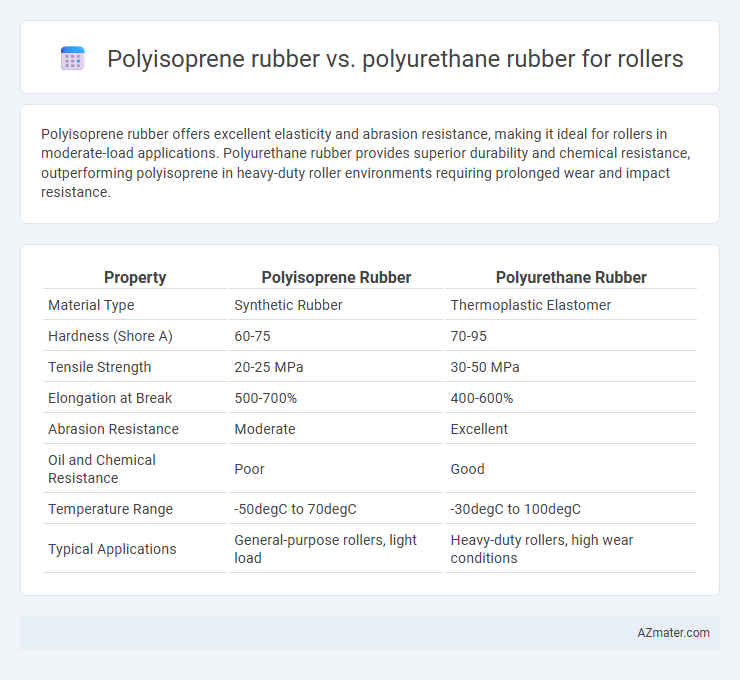
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for rollers in moderate-load applications. Polyurethane rubber provides superior durability and chemical resistance, outperforming polyisoprene in heavy-duty roller environments requiring prolonged wear and impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Rubber | Thermoplastic Elastomer |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60-75 | 70-95 |
| Tensile Strength | 20-25 MPa | 30-50 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 500-700% | 400-600% |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Poor | Good |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Typical Applications | General-purpose rollers, light load | Heavy-duty rollers, high wear conditions |
Introduction to Polyisoprene and Polyurethane Rubbers
Polyisoprene rubber, a synthetic analogue of natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, tear resistance, and resilience, making it ideal for roller applications requiring flexibility and durability. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and load-bearing capacity, which enhances roller performance in harsh industrial environments. Both materials serve critical roles in roller manufacturing, with polyisoprene favored for softness and polyurethane for toughness and longevity.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyisoprene rubber consists of long chains of repeating isoprene units with cis-1,4-polyisoprene configuration, providing high elasticity and resilience due to its natural rubber-like chemical structure. Polyurethane rubber contains segmented block copolymers composed of soft polyol segments and hard isocyanate-derived segments, which impart superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability. The chemical composition of polyisoprene favors flexibility and tensile strength, whereas polyurethane's urethane linkages enhance durability and resistance to oils and solvents in roller applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits high elasticity and excellent tensile strength, making it ideal for roller applications requiring flexibility and resistance to abrasion. Polyurethane rubber offers superior load-bearing capacity, enhanced wear resistance, and greater resistance to oil and chemicals, which extends roller lifespan in heavy-duty environments. The choice between them depends on the need for softness and resilience (polyisoprene) versus durability and toughness (polyurethane) in roller performance.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior wear resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber due to its enhanced abrasion properties and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for roller applications subjected to heavy loads and continuous friction. Polyisoprene rubber offers moderate durability with good elasticity but tends to degrade faster under abrasive conditions, limiting its lifespan in industrial roller use. Choosing polyurethane rubber results in longer service intervals and reduced maintenance costs in demanding environments, providing a more durable solution for rollers requiring extended wear resistance.
Performance Under Load and Stress
Polyisoprene rubber demonstrates excellent elasticity and resilience under load, providing superior cushioning and shock absorption for rollers operating in moderate stress conditions. Polyurethane rubber outperforms in abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, maintaining dimensional stability and durability under high stress and heavy-duty applications. Choosing polyurethane enhances roller lifespan and performance in environments with prolonged mechanical stress and high impact forces.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility at low temperatures but has limited resistance to ozone and harsh chemicals, making it less suitable for extreme environmental conditions. Polyurethane rubber demonstrates superior temperature tolerance, typically from -40degC to 90degC, and exceptional resistance to abrasion, oils, and solvents, ideal for rollers exposed to varying industrial environments. Selecting polyurethane rubber enhances roller durability in high-wear applications with fluctuating temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polyisoprene rubber offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it more budget-friendly for applications requiring moderate durability in rollers. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior wear resistance and longevity, leading to reduced replacement frequency and long-term maintenance costs. Economic considerations favor polyisoprene for short-term projects, whereas polyurethane is cost-effective for high-demand environments due to its enhanced performance and lifecycle benefits.
Applications of Polyisoprene vs Polyurethane in Rollers
Polyisoprene rubber is commonly used for rollers in applications requiring high elasticity, excellent resilience, and good abrasion resistance, making it ideal for printing presses and conveyor systems with moderate mechanical stress. Polyurethane rubber excels in heavy-duty roller applications due to its superior wear resistance, high load-bearing capacity, and chemical resistance, often found in industrial settings like metal processing and automotive manufacturing. The choice between polyisoprene and polyurethane rollers depends on specific operational demands, with polyisoprene favored for flexibility and cushioning, and polyurethane preferred for durability and longevity under harsh conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity of Rubber Rollers
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience, making it easier to maintain due to its natural resistance to wear and tear, which enhances the longevity of rubber rollers in moderate environments. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and chemical stability, providing superior durability and extended service life for rollers used in harsher industrial conditions with exposure to oils, solvents, and mechanical stress. Selecting polyurethane rollers results in reduced maintenance frequency and cost over time, while polyisoprene rollers benefit applications requiring softer touch and impact absorption with moderate durability demands.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Roller Application
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity, tear resistance, and resilience, making it ideal for rollers requiring high flexibility and smooth surface interaction. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and chemical resistance, suited for rollers operating in harsh environments or heavy-duty applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on factors such as operating conditions, required durability, and specific mechanical properties needed for roller performance.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com