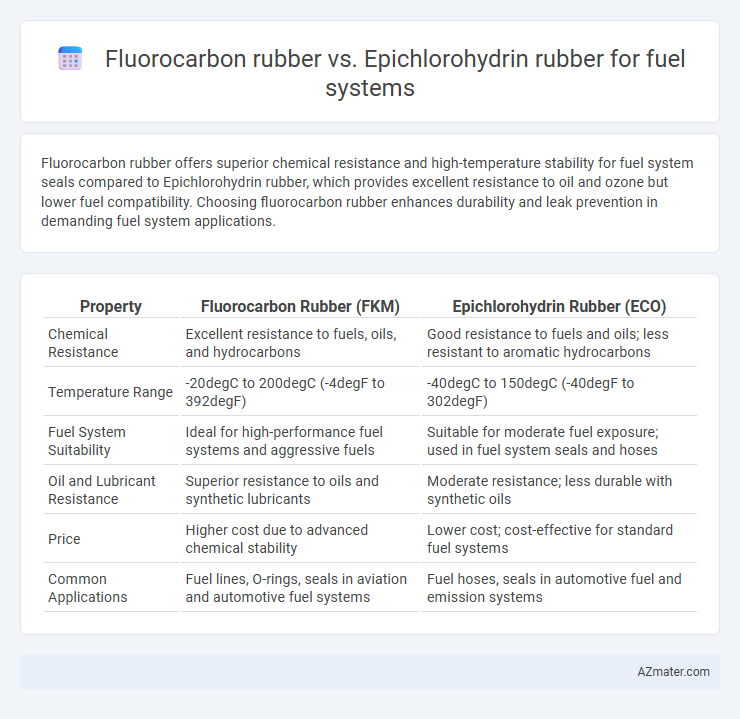
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability for fuel system seals compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, which provides excellent resistance to oil and ozone but lower fuel compatibility. Choosing fluorocarbon rubber enhances durability and leak prevention in demanding fuel system applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and hydrocarbons | Good resistance to fuels and oils; less resistant to aromatic hydrocarbons |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) |
| Fuel System Suitability | Ideal for high-performance fuel systems and aggressive fuels | Suitable for moderate fuel exposure; used in fuel system seals and hoses |
| Oil and Lubricant Resistance | Superior resistance to oils and synthetic lubricants | Moderate resistance; less durable with synthetic oils |
| Price | Higher cost due to advanced chemical stability | Lower cost; cost-effective for standard fuel systems |
| Common Applications | Fuel lines, O-rings, seals in aviation and automotive fuel systems | Fuel hoses, seals in automotive fuel and emission systems |
Introduction to Fluorocarbon and Epichlorohydrin Rubbers
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for fuel system seals exposed to aggressive hydrocarbons and solvents. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) combines excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and ozone with moderate temperature tolerance, providing a cost-effective solution for fuel system components requiring flexibility and durability. Both rubbers serve critical roles in automotive and aerospace fuel systems by enhancing performance and longevity under harsh operating conditions.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) consists of a carbon backbone with fluorine atoms, providing exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, ideal for aggressive fuel environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a copolymer of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide, offering excellent resistance to fuel permeability and ozone but with lower heat resistance than FKM. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds in fluorocarbon rubber enhance durability against hydrocarbons, while epichlorohydrin's polar ether groups contribute to flexibility and fuel resistance in moderate temperature applications.
Fuel System Application Requirements
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for fuel system seals and gaskets exposed to harsh automotive fuels. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits good resistance to fuel and ozone but has lower temperature stability, typically up to 125degC, which limits its use in high-heat fuel system components. For critical fuel system applications requiring durability against fuel permeation, oxidative degradation, and thermal aging, fluorocarbon rubber is the preferred material due to its enhanced performance and longevity.
Fuel Resistance and Chemical Compatibility
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior fuel resistance and chemical compatibility across a wide range of hydrocarbons, including gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuels, making it ideal for demanding fuel system applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to polar solvents, including alcohol-blended fuels and certain oils, but displays moderate compatibility with aromatic hydrocarbons, limiting its use in high-aromatic content fuels. Selecting FKM ensures enhanced durability and stability in aggressive fuel environments, while ECO provides cost-effective performance where polar fuel components predominate.
Temperature Performance Range
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers an exceptional temperature performance range, typically from -26degC to 204degC, making it highly suitable for fuel system seals exposed to extreme heat and chemical exposure. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) operates effectively within a narrower temperature range of approximately -45degC to 125degC, providing good oil and fuel resistance but limited high-temperature endurance. Selecting between FKM and ECO hinges on the required thermal stability and exposure conditions in the fuel system application.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for fuel system seals exposed to harsh fuels and elevated temperatures. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides excellent oil resistance and flexibility with good mechanical strength but has lower heat resistance compared to fluorocarbon rubber. In terms of durability, fluorocarbon rubber excels in maintaining elasticity and preventing swelling in aggressive fuel environments, whereas epichlorohydrin rubber is more prone to degradation under prolonged exposure to fuel system chemicals.
Environmental and Weathering Resistance
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior environmental resistance to fuels, oils, and high temperatures, ensuring long-term durability in fuel system applications, particularly in harsh weather conditions. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate fuel exposure but degrades faster under aggressive hydrocarbon environments. FKM's enhanced performance against UV radiation, oxidation, and chemical attack makes it the preferred choice for demanding fuel system seals and gaskets exposed to variable weather conditions.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Fluorocarbon rubber typically incurs higher costs due to its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability in fuel system applications, making it ideal for harsh environments despite its premium price. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers a more cost-effective solution with good fuel resistance and moderate availability, often favored for less demanding fuel system components seeking budget efficiency. Market availability for epichlorohydrin rubber tends to be broader due to simpler manufacturing processes, whereas fluorocarbon rubber may face supply constraints related to its specialized production.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) excels in fuel system applications due to its superior resistance to hydrocarbons and high temperatures, meeting stringent ASTM D471 and SAE J200 fuel resistance standards. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to fuel and ozone, often complying with OEM certifications such as GM 62M1 and Ford ESF-M99B158-A for fuel system seals. Both materials are recognized under ISO 23936-2 for compatibility with fuels but FKM's broader chemical resistance makes it a preferred choice for high-performance engine seals.
Summary: Choosing the Right Rubber for Fuel Systems
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits exceptional resistance to gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuels, maintaining integrity under high temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure, making it ideal for demanding fuel system applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to fuels containing alcohol and water, with good flexibility and ozone resistance, suitable for fuel system components exposed to ethanol-blended fuels. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific fuel type, temperature range, and environmental conditions, where fluorocarbon rubber excels in high-performance, chemically aggressive environments, while epichlorohydrin provides cost-effective durability with good compatibility in mixed fuel systems.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Fuel system
 azmater.com
azmater.com