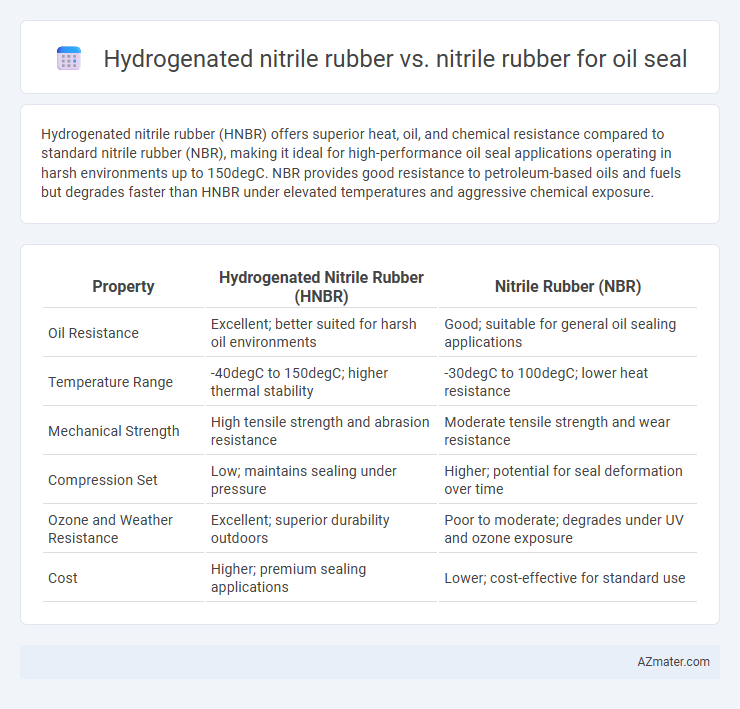
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-performance oil seal applications operating in harsh environments up to 150degC. NBR provides good resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels but degrades faster than HNBR under elevated temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent; better suited for harsh oil environments | Good; suitable for general oil sealing applications |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC; higher thermal stability | -30degC to 100degC; lower heat resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength and wear resistance |
| Compression Set | Low; maintains sealing under pressure | Higher; potential for seal deformation over time |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Excellent; superior durability outdoors | Poor to moderate; degrades under UV and ozone exposure |
| Cost | Higher; premium sealing applications | Lower; cost-effective for standard use |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) and Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a saturated version of Nitrile Rubber (NBR), offering superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for demanding oil seal applications. NBR, a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, provides good resistance to oil, fuel, and other hydrocarbons but has lower thermal and chemical stability compared to HNBR. The enhanced molecular structure of HNBR results in improved elasticity, durability, and long-term performance in harsher operating environments, distinguishing it as a premium choice for oil seals in automotive and industrial sectors.
Chemical Structure Differences: HNBR vs NBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated polymer backbone obtained by hydrogenating the double bonds present in nitrile rubber (NBR), resulting in enhanced chemical and thermal resistance. NBR contains unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds in its polymer chain, making it more susceptible to oxidative degradation and heat aging compared to HNBR. The hydrogenation process in HNBR reduces the vulnerability of the polymer chains to attack by oils, chemicals, and high temperatures, providing superior durability in oil seal applications.
Oil Resistance Comparison: HNBR vs NBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior oil resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced saturation of polymer chains, which improves stability against heat, oxidation, and chemical degradation in oil environments. HNBR maintains physical properties and sealing performance at higher temperatures and prolonged exposure to aggressive oils, making it ideal for demanding oil seal applications. NBR offers good oil resistance but may deteriorate faster under harsh conditions, leading to reduced seal life and potential leaks.
Temperature Range Suitability for Oil Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature range suitability for oil seals, effectively operating between -40degC to 150degC, compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), which typically functions within -30degC to 100degC. The enhanced thermal stability of HNBR ensures better performance in higher temperature environments commonly encountered in automotive and industrial oil sealing applications. This makes HNBR a preferred choice for seals exposed to elevated temperatures and more aggressive conditions, providing extended service life and reliability.
Mechanical Properties and Durability Analysis
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), including enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and compression set performance, making it more suitable for demanding oil seal applications. HNBR's hydrogenation process significantly improves its resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical degradation, resulting in extended durability and longer operational life under harsh environmental conditions. The enhanced molecular stability of HNBR provides improved oil and fuel resistance, reducing the risk of seal failure and ensuring reliable performance in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Compatibility with Automotive Fluids and Oils
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to a wide range of automotive fluids and oils compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), maintaining its mechanical properties under high temperatures and prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals. HNBR's enhanced saturation of its polymer backbone significantly improves compatibility with synthetic engine oils, transmission fluids, and fuels containing ethanol or methanol blends. Nitrile rubber tends to swell and degrade faster in contact with oxidized or aromatic hydrocarbons, making HNBR the preferred choice for oil seals in automotive applications requiring extended durability and fluid compatibility.
Aging and Ozone Resistance: Performance in Harsh Environments
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior aging and ozone resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), making it more durable in harsh environments with prolonged exposure to heat and oxidative conditions. The enhanced saturation in HNBR's polymer backbone reduces susceptibility to chain scission and ozone cracking, ensuring longer service life for oil seals under extreme temperatures and oxidative stress. NBR seals, while cost-effective, tend to degrade faster when exposed to ozone and aging factors, leading to reduced reliability in demanding oil sealing applications.
Cost Analysis: HNBR vs NBR for Oil Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) oil seals typically incur higher material costs compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR) due to enhanced chemical and heat resistance properties extending seal lifespan under extreme conditions. NBR oil seals offer cost-effective solutions for applications with moderate temperature and chemical exposure, providing sufficient performance at a lower price point. Factoring in total cost of ownership, HNBR seals can reduce maintenance and replacement frequency in demanding environments, potentially offsetting the initial higher investment.
Typical Applications in Oil Seal Manufacturing
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for oil seals used in high-temperature automotive engines and industrial machinery. NBR is commonly utilized in oil seals for general-purpose applications involving moderate temperatures and exposure to petroleum oils and fuels. The enhanced durability of HNBR allows oil seals to maintain integrity in harsher environments, extending service life in demanding sealing applications.
Choosing the Right Material: HNBR or NBR for Oil Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and wear resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive oil seal applications. NBR remains cost-effective and provides excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids at moderate temperatures, suitable for general-purpose oil seals. Selecting HNBR over NBR depends on the operating temperature range, exposure to oxidative environments, and mechanical stress requirements in oil seal performance.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com