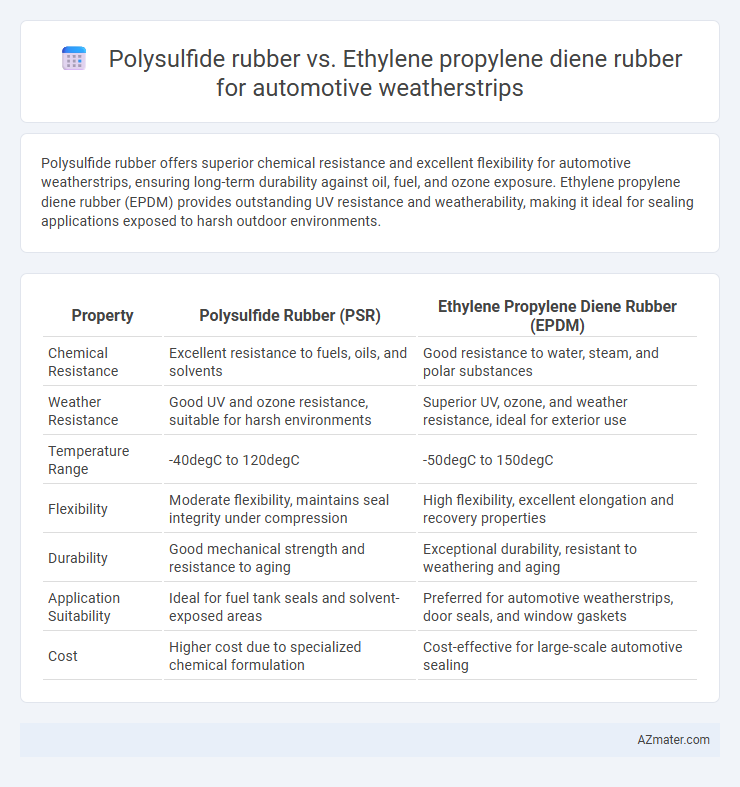
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent flexibility for automotive weatherstrips, ensuring long-term durability against oil, fuel, and ozone exposure. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides outstanding UV resistance and weatherability, making it ideal for sealing applications exposed to harsh outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber (PSR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents | Good resistance to water, steam, and polar substances |
| Weather Resistance | Good UV and ozone resistance, suitable for harsh environments | Superior UV, ozone, and weather resistance, ideal for exterior use |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, maintains seal integrity under compression | High flexibility, excellent elongation and recovery properties |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength and resistance to aging | Exceptional durability, resistant to weathering and aging |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for fuel tank seals and solvent-exposed areas | Preferred for automotive weatherstrips, door seals, and window gaskets |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized chemical formulation | Cost-effective for large-scale automotive sealing |
Introduction to Automotive Weatherstrip Materials
Polysulfide rubber offers exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and ozone, making it ideal for long-lasting automotive weatherstrip seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior flexibility, UV resistance, and excellent sealing performance against water and dust, commonly used in exterior automotive weatherstrips. Both materials are essential in automotive weatherstrip applications, with polysulfide rubber favored for chemical durability and EPDM prized for weather and aging resistance.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber exhibits exceptional resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for automotive weatherstrips exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its unique molecular structure provides excellent flexibility and impermeability to gases and moisture, ensuring long-lasting sealing performance. Compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), polysulfide rubber offers superior solvent resistance and durability in aggressive atmospheres, though EPDM excels in UV and heat resistance.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is widely used in automotive weatherstrips due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, UV rays, and weathering, making it ideal for exterior sealing applications. EPDM offers superior flexibility and durability over a broad temperature range, maintaining its performance under harsh environmental conditions. Compared to Polysulfide rubber, EPDM provides better resistance to oxidation and aging, which extends the lifespan of automotive weatherstripping components.
Comparative Weather Resistance
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior weather resistance in automotive weatherstripping applications due to its excellent ozone, UV, and chemical resistance, maintaining elasticity under prolonged environmental exposure. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) also offers good weather resistance but tends to degrade faster under intense UV and ozone exposure compared to polysulfide. Polysulfide's enhanced durability improves sealing performance, reducing maintenance and replacement frequency in harsh weather conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it highly durable for automotive weatherstrips exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and high temperatures, ensuring prolonged flexibility and weatherability in outdoor applications. For chemical resistance and long-term durability in automotive weatherstrips, polysulfide offers enhanced protection, while EPDM provides excellent resilience against atmospheric aging factors.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Polysulfide rubber offers superior flexibility with excellent resistance to weathering, making it ideal for automotive weatherstrip applications requiring long-term sealing performance under varying environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in elasticity, providing exceptional stretch and recovery that enhances the durability and fit of weatherstrips exposed to dynamic movements and temperature fluctuations. The key difference lies in polysulfide's chemical resistance and low permeability compared to EPDM's high elasticity and UV resistance, influencing material selection based on specific automotive sealing needs.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Polysulfide rubber demonstrates exceptional temperature tolerance ranging from -40degC to 120degC, maintaining superior chemical resistance and flexibility in automotive weatherstrip applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber withstands extreme temperatures between -50degC and 150degC, offering enhanced UV resistance and durability against ozone degradation. EPDM's wider temperature range and better weatherability often result in longer-lasting performance for automotive seals compared to polysulfide rubber.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and durability for automotive weatherstrips but tends to have higher production costs due to more complex curing processes and limited raw material availability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) is more cost-effective, benefiting from widespread availability and simpler manufacturing, which reduces overall expenses. Automakers often prefer EPDM for large-scale applications where budget constraints and consistent supply are critical.
Applications in Automotive Weatherstripping
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and weatherability, making it ideal for automotive weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions and automotive fluids. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in UV resistance, ozone resistance, and flexibility at low temperatures, ensuring durable sealing against rain, dust, and noise in automotive door and window seals. EPDM's superior elasticity and resistance to aging often make it the preferred choice for weatherstrips requiring long-term performance and environmental resilience.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Automotive Weatherstrip
Polysulfide rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and fuel exposure, making it ideal for automotive weatherstrip applications that demand long-term durability in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in flexibility, excellent heat and cold resistance, and cost-effectiveness, providing a reliable seal against water and air infiltration. For automotive weatherstrip, EPDM is typically the best choice due to its balanced performance, durability, and economic advantages in mass production.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com