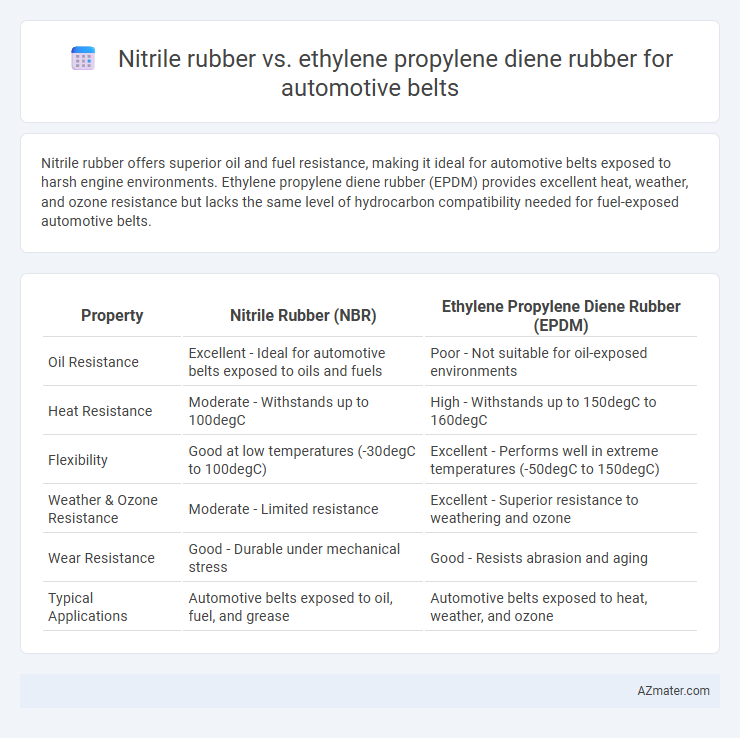
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh engine environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides excellent heat, weather, and ozone resistance but lacks the same level of hydrocarbon compatibility needed for fuel-exposed automotive belts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent - Ideal for automotive belts exposed to oils and fuels | Poor - Not suitable for oil-exposed environments |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate - Withstands up to 100degC | High - Withstands up to 150degC to 160degC |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures (-30degC to 100degC) | Excellent - Performs well in extreme temperatures (-50degC to 150degC) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Moderate - Limited resistance | Excellent - Superior resistance to weathering and ozone |
| Wear Resistance | Good - Durable under mechanical stress | Good - Resists abrasion and aging |
| Typical Applications | Automotive belts exposed to oil, fuel, and grease | Automotive belts exposed to heat, weather, and ozone |
Overview of Nitrile Rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and heat, making it ideal for automotive belt applications exposed to harsh environments. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber offers outstanding weather, ozone, and heat resistance, along with excellent flexibility and durability, which makes it suitable for belts requiring exposure to outdoor conditions and high temperatures. Both NBR and EPDM provide distinct advantages in automotive belt manufacturing, with NBR excelling in chemical resistance and EPDM in environmental durability.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by polar nitrile groups that provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to lubricants. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber consists of ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer, offering superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but limited oil resistance due to its saturated hydrocarbon backbone. The chemical structure of NBR's polar nitrile groups enhances hydrocarbon compatibility, whereas EPDM's saturated and non-polar structure yields excellent environmental durability but reduces its suitability for oil and fuel contact applications in automotive belts.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to oils, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides greater flexibility and outstanding resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, ensuring durability under varying temperatures. While NBR excels in mechanical strength against fuels and lubricants, EPDM delivers enhanced elasticity and resilience critical for extended belt lifespan in automotive applications.
Heat and Temperature Resistance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent heat resistance up to approximately 120degC, making it suitable for automotive belts exposed to moderate engine temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits superior high-temperature resistance, maintaining performance at temperatures up to 150degC or higher, ideal for belts in high-heat environments near engine components. EPDM also provides enhanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and steam, which are critical factors for long-term durability in automotive belt applications.
Oil, Chemical, and Ozone Resistance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making it highly suitable for automotive belts exposed to engine oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. EPDM offers outstanding ozone and weathering resistance, ensuring durability in external environments with prolonged exposure to ozone and UV radiation. Selecting NBR enhances performance in oily and chemical-rich conditions, while EPDM is preferred for belts subjected to harsh atmospheric elements.
Durability and Lifespan in Automotive Applications
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and high temperatures, making it highly durable for automotive belt applications exposed to harsh engine environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weather, ozone, and heat resistance, providing longer lifespan in external belt systems exposed to environmental factors. For automotive belts experiencing continuous oil contact and heat, NBR typically ensures enhanced durability, whereas EPDM belts perform better in climate-exposed conditions, impacting overall service life and maintenance intervals.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers a cost-effective solution for automotive belts due to its widespread availability and strong resistance to oil and fuel, making it economically favorable for large-scale production. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), while generally more expensive, provides superior heat and weather resistance, increasing initial material costs but potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Availability of NBR is higher given its extensive use in the automotive industry, whereas EPDM's supply can be more limited and variable, influencing procurement costs and lead times.
Performance in Real-World Automotive Belt Systems
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and heat, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to engine fluids and high temperatures, enhancing durability and longevity in real-world belt systems. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides exceptional weather, ozone, and heat resistance but performs less effectively against petroleum-based fluids, limiting its use in belts exposed to oily environments. Real-world automotive belt performance often favors NBR for oil-contaminated applications, while EPDM suits exterior or non-oil-contact belts requiring excellent aging and weather resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) used in automotive belts offers superior oil and fuel resistance, but its production relies heavily on non-renewable petrochemical resources, contributing to a higher carbon footprint. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber demonstrates enhanced resistance to weathering and ozone while being more amenable to recycling processes, making it a more sustainable choice in terms of environmental impact. Selection of EPDM for automotive belts supports long-term sustainability goals due to its durability and lower ecological footprint compared to NBR.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Belt Applications
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to engine fluids and harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides excellent weather, ozone, and heat resistance, which is crucial for belts operating in extreme temperature fluctuations and outdoor conditions. Choosing between nitrile and EPDM depends on the specific exposure requirements, where nitrile is preferred for chemical resistance, and EPDM excels in durability under environmental stress.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com