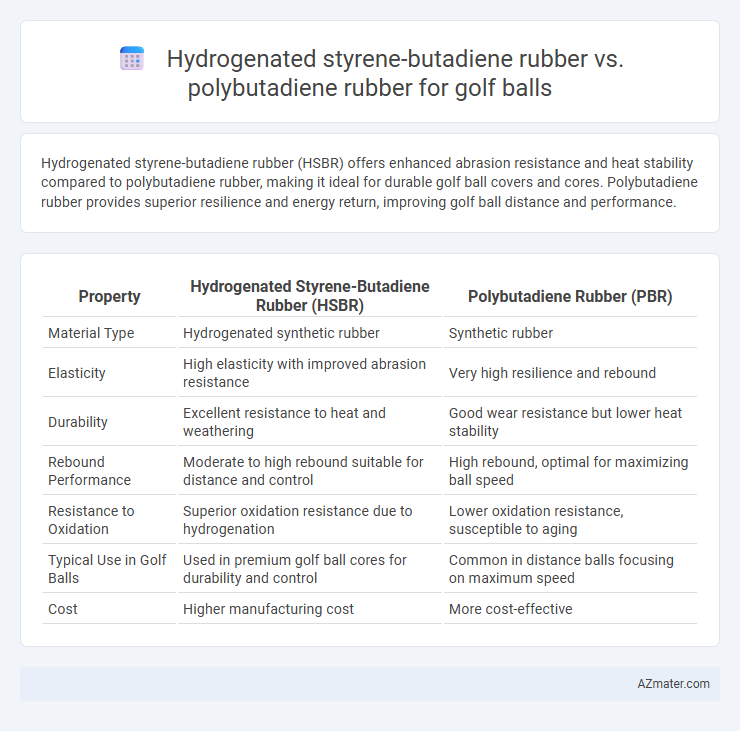
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and heat stability compared to polybutadiene rubber, making it ideal for durable golf ball covers and cores. Polybutadiene rubber provides superior resilience and energy return, improving golf ball distance and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Hydrogenated synthetic rubber | Synthetic rubber |
| Elasticity | High elasticity with improved abrasion resistance | Very high resilience and rebound |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to heat and weathering | Good wear resistance but lower heat stability |
| Rebound Performance | Moderate to high rebound suitable for distance and control | High rebound, optimal for maximizing ball speed |
| Resistance to Oxidation | Superior oxidation resistance due to hydrogenation | Lower oxidation resistance, susceptible to aging |
| Typical Use in Golf Balls | Used in premium golf ball cores for durability and control | Common in distance balls focusing on maximum speed |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | More cost-effective |
Introduction: Key Rubber Materials in Golf Ball Manufacturing
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) and polybutadiene rubber (PBR) are essential elastomers in golf ball manufacturing, offering distinct performance attributes. HSBR provides enhanced oxidation resistance and durability due to its saturated polymer backbone, improving the longevity of golf balls under repeated impact. Polybutadiene rubber is prized for its high resilience and energy return, contributing to the golf ball's distance and overall playability.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic elastomer characterized by enhanced heat resistance, chemical stability, and improved durability compared to traditional Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR). Its hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation in polymer chains, leading to superior resistance to oxidation and ozone, which is critical for maintaining consistent performance in golf ball covers and cores. HSBR contributes to enhanced resilience and energy return in golf balls, resulting in optimized distance and control for players.
Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR): Properties and Uses
Polybutadiene rubber (PBR) is preferred in golf ball manufacturing due to its exceptional resilience, high tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance, which enhance ball durability and energy transfer for longer distance. Unlike hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber, PBR exhibits superior elasticity and low heat build-up, critical for maintaining performance consistency during repeated impacts. Its molecular structure allows for enhanced compression molding capabilities, making it ideal for creating the core of golf balls that require optimal balance of hardness and flexibility.
Molecular Structure Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) features saturation of double bonds in the butadiene segments, enhancing oxidative stability and abrasion resistance, while polybutadiene rubber (PBR) retains a higher concentration of reactive double bonds, providing superior resilience and low-temperature flexibility. The incorporation of styrene units in HSBR influences its microphase-separated morphology, resulting in a tougher, more durable matrix compared to the predominantly elastomeric PBR chains. Molecular crosslink density in PBR governs high rebound properties vital for golf ball performance, whereas HSBR's hydrogenation reduces unsaturation sites, optimizing longevity under repetitive impact conditions.
Impact on Golf Ball Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) enhances golf ball durability and resilience by providing improved abrasion resistance and lower heat build-up compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), resulting in longer-lasting ball performance. HSBR's hydrogenation process increases oxidative stability, which helps maintain consistent compression and energy transfer for optimizing ball distance and control. In contrast, PBR offers superior initial rebound and softness, benefiting feel and spin but often sacrificing long-term durability under repeated impacts.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior oxidative stability and enhanced resistance to thermal degradation compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), resulting in increased durability under repeated impact and environmental stress for golf ball cores. The increased saturation in HSBR's polymer backbone reduces chain scission and cross-linking, extending the material's lifecycle and maintaining performance consistency over prolonged use. In contrast, PBR's higher unsaturation level leads to faster aging and compromised elasticity, limiting the overall longevity of golf balls manufactured with this material.
Elasticity and Resilience Differences
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits higher resilience and improved elasticity compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), making it more effective in energy return during golf ball impacts. The hydrogenation process in HSBR reduces unsaturation, enhancing thermal stability and maintaining elasticity under repetitive stress. Polybutadiene rubber, while offering excellent initial elasticity, tends to have lower resilience and degrades faster under heat, resulting in diminished performance over time.
Weather and Aging Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior weather and aging resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR) due to its enhanced saturation level, which reduces susceptibility to ozone and UV degradation. HSBR maintains mechanical properties and elasticity in harsh environmental conditions, extending golf ball durability and performance over time. Polybutadiene rubber, while offering excellent resilience and impact resistance, is more prone to oxidative aging and cracking when exposed to prolonged outdoor elements.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical and heat resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), impacting manufacturing processes with longer curing times and increased energy consumption. Polybutadiene rubber remains cost-effective due to its widespread availability and simpler processing, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious golf ball production. Manufacturers balance HSBR's superior durability and performance benefits against its higher material and processing costs when selecting rubber compounds for golf ball cores and covers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Rubber for Golf Balls
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and enhanced resilience compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), making it ideal for golf balls requiring durability and consistent performance. PBR remains favored for its excellent rebound and lower cost, contributing to increased ball speed and distance in competitive play. Selecting the optimal rubber depends on prioritizing HSBR for longevity and control, whereas PBR is preferred for maximizing distance and affordability.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Golf ball
 azmater.com
azmater.com