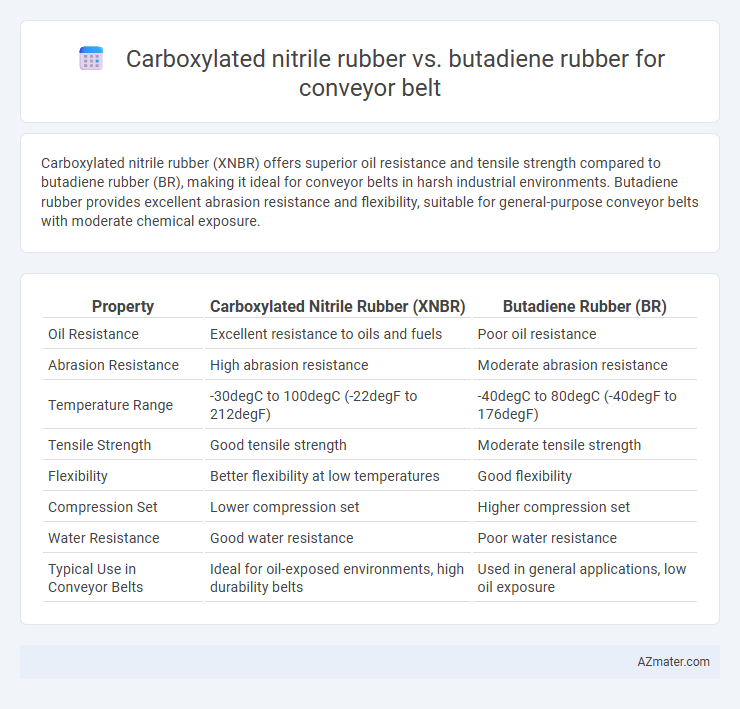
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose conveyor belts with moderate chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Butadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and fuels | Poor oil resistance |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 100degC (-22degF to 212degF) | -40degC to 80degC (-40degF to 176degF) |
| Tensile Strength | Good tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Better flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility |
| Compression Set | Lower compression set | Higher compression set |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Poor water resistance |
| Typical Use in Conveyor Belts | Ideal for oil-exposed environments, high durability belts | Used in general applications, low oil exposure |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. Butadiene rubber provides excellent flexibility and impact resistance, often favored in applications requiring high tensile strength and wear resistance under moderate conditions. Selecting between XNBR and BR for conveyor belts depends on the specific operational demands, such as exposure to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) is a specialized synthetic rubber known for its enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and superior oil and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belt applications in harsh environments. XNBR's carboxyl groups improve cross-linking density, resulting in better mechanical properties and durability under high stress and temperature variations. This rubber type outperforms Butadiene Rubber (BR) in oil resistance and longevity, crucial for conveyor belts used in industrial settings with exposure to oils, chemicals, and abrasive materials.
Key Properties of Butadiene Rubber (BR)
Butadiene rubber (BR) offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent low-temperature flexibility, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh environments. Its high tensile strength and good resilience ensure durability and resistance to mechanical wear, outperforming carboxylated nitrile rubber in impact and tear resistance. BR's ability to maintain performance under dynamic stress and varying temperatures enhances conveyor belt longevity and operational efficiency in demanding industrial applications.
Abrasion Resistance: XNBR vs BR
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it highly suitable for conveyor belts subjected to heavy wear and tear. The enhanced cross-linking in XNBR improves its durability against mechanical stress and surface degradation. BR, while flexible and cost-effective, tends to wear faster under abrasive conditions, reducing conveyor belt lifespan.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior chemical and oil resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it more suitable for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial fluids and hydrocarbons. XNBR's enhanced oil resistance stems from its polar carboxyl groups, which provide a tighter polymer matrix, reducing swelling and degradation in oils and solvents. In contrast, butadiene rubber is more vulnerable to chemical attack and oil absorption, leading to faster wear and reduced belt lifespan in demanding chemical environments.
Temperature Performance Under Conveyor Conditions
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior temperature resistance and durability under conveyor belt operating conditions, maintaining flexibility and mechanical strength between -40degC to 120degC. Butadiene rubber (BR) performs well at lower temperatures but shows reduced heat resistance and accelerated aging when exposed to sustained high conveyor belt temperatures above 80degC. In high-temperature industrial conveyor applications, XNBR enhances belt lifespan and operational reliability by preventing thermal degradation and preserving abrasion resistance.
Flexibility and Dynamic Fatigue Behavior
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) demonstrates superior flexibility and enhanced resistance to dynamic fatigue compared to butadiene rubber (BR) when used in conveyor belts, making it ideal for high-flex applications. The polar carboxyl groups in XNBR improve intermolecular bonding, resulting in better tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and prolonged fatigue life under cyclic stress. In contrast, butadiene rubber offers moderate flexibility but lower resistance to cracking and mechanical fatigue, limiting its effectiveness in high-wear, repetitive flexing conveyor systems.
Cost Implications and Material Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), resulting in longer conveyor belt lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in harsh industrial environments. Although XNBR typically has higher raw material costs due to specialized production processes, its enhanced durability often offsets initial expenses through lower replacement frequency. Butadiene rubber, widely available and cheaper, provides cost-effective solutions for general conveyor belt applications but may incur higher lifecycle costs when exposed to oils or abrasion.
Typical Applications in Conveyor Belt Manufacturing
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is preferred in conveyor belt manufacturing for applications requiring excellent oil, chemical resistance, and enhanced abrasion toughness, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments such as mining and oil processing. Butadiene rubber (BR) is commonly used for conveyor belts needing superior impact resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and high wear resistance, typically found in bulk material handling and general manufacturing sectors. The choice between XNBR and BR depends on specific operational demands, with XNBR offering superior chemical resistance and BR providing better mechanical durability in harsh conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Conveyor Belt Longevity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, oil resistance, and tensile strength compared to butadiene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. Butadiene rubber provides excellent flexibility and low-temperature performance but falls short in chemical and oil resistance, which can reduce belt longevity in demanding applications. Selecting XNBR for conveyor belts ensures enhanced durability, reduced maintenance costs, and prolonged service life in oil-contaminated or abrasive conditions.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com