Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil, chemical, and ozone resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for industrial roller applications in harsh environments. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the enhanced durability and chemical stability of Epichlorohydrin rubber.
Table of Comparison
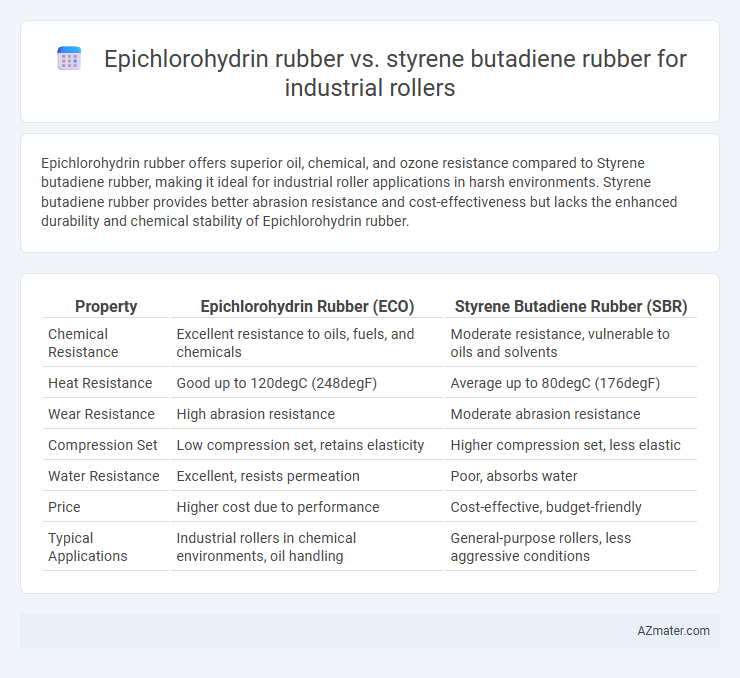
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Moderate resistance, vulnerable to oils and solvents |
| Heat Resistance | Good up to 120degC (248degF) | Average up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Wear Resistance | High abrasion resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, retains elasticity | Higher compression set, less elastic |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, resists permeation | Poor, absorbs water |
| Price | Higher cost due to performance | Cost-effective, budget-friendly |
| Typical Applications | Industrial rollers in chemical environments, oil handling | General-purpose rollers, less aggressive conditions |
Introduction to Industrial Rubber Rollers
Industrial rubber rollers require materials with excellent wear resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making Epichlorohydrin (ECO) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) common choices. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil, ozone, and solvent resistance, ideal for industries with aggressive chemical exposure. SBR provides good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but has lower chemical resistance compared to Epichlorohydrin, influencing material selection based on specific industrial roller operating environments.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent oil resistance, low gas permeability, and superior mechanical properties compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). It offers high chemical resistance, particularly against hydraulic fluids and oils, making it ideal for industrial rollers exposed to harsh environments. ECO also exhibits good resistance to aging and weathering, enhancing the durability and lifespan of industrial rollers in demanding applications.
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer widely used in industrial roller applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and good aging stability compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber. SBR offers superior performance in dry and moderately wet environments, making it ideal for rollers in printing, conveyor systems, and material handling. Its cost-effectiveness and balanced mechanical properties ensure durability and extended service life in diverse industrial conditions.
Key Performance Properties: ECO vs SBR
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior oil resistance, low gas permeability, and excellent ozone and weather resistance, making it ideal for industrial rollers exposed to harsh environments and aggressive fluids. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the chemical and weather resistance found in ECO, limiting its durability in industrial roller applications involving oils and solvents. ECO's enhanced mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength and resilience, provide longer service life and better performance under continuous operational stress compared to SBR.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fats, and chemicals such as ketones and alcohols, making it highly suitable for industrial rollers exposed to aggressive chemical environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate chemical resistance but is vulnerable to aromatic hydrocarbons and certain solvents, limiting its use in highly corrosive applications. The enhanced chemical stability of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures prolonged durability and performance in industrial settings with harsh chemical exposure.
Temperature Stability and Heat Aging
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior temperature stability and heat aging resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for industrial rollers exposed to elevated temperatures. Its molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to thermal degradation, maintaining elasticity and mechanical properties over extended heat exposure. In contrast, Styrene butadiene rubber tends to degrade faster under heat, leading to decreased lifespan and performance in high-temperature industrial roller applications.
Mechanical Strength and Wear Properties
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for industrial rollers subjected to harsh conditions. Its exceptional wear resistance and resilience against oils and solvents extend the service life of rollers in heavy-duty applications. Styrene butadiene rubber offers good abrasion resistance but falls short in chemical resistance and mechanical durability under continuous exposure to aggressive industrial environments.
Cost Analysis for Industrial Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance and oil resistance ideal for industrial rollers but comes at a higher material cost compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which provides more economical pricing with moderate wear resistance and good abrasion resistance. The lifecycle cost of Epichlorohydrin rubber can be lower in applications requiring extended durability due to its enhanced longevity and reduced downtime, whereas SBR benefits budget-sensitive projects with shorter operational cycles through its lower initial investment. Selecting between these elastomers involves balancing upfront expenditure against maintenance and replacement frequency to optimize total cost of ownership in industrial roller applications.
Typical Uses in Industrial Rollers
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is commonly utilized in industrial rollers requiring excellent oil, chemical, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for applications in printing, paper handling, and food processing industries. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) excels in providing abrasion resistance and durability, often chosen for conveyor belts, printing rollers, and general-purpose industrial roller covers. ECO is preferred in environments with exposure to lubricants and hydraulic fluids, while SBR suits applications demanding mechanical toughness and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for Industrial Rollers
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and heat, making it ideal for industrial rollers exposed to harsh environments and aggressive substances. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general-purpose rollers with moderate exposure to wear and chemicals. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific application demands: choose epichlorohydrin for high-performance, chemically aggressive conditions, and styrene butadiene for durable, economical solutions in less severe settings.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Industrial roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com