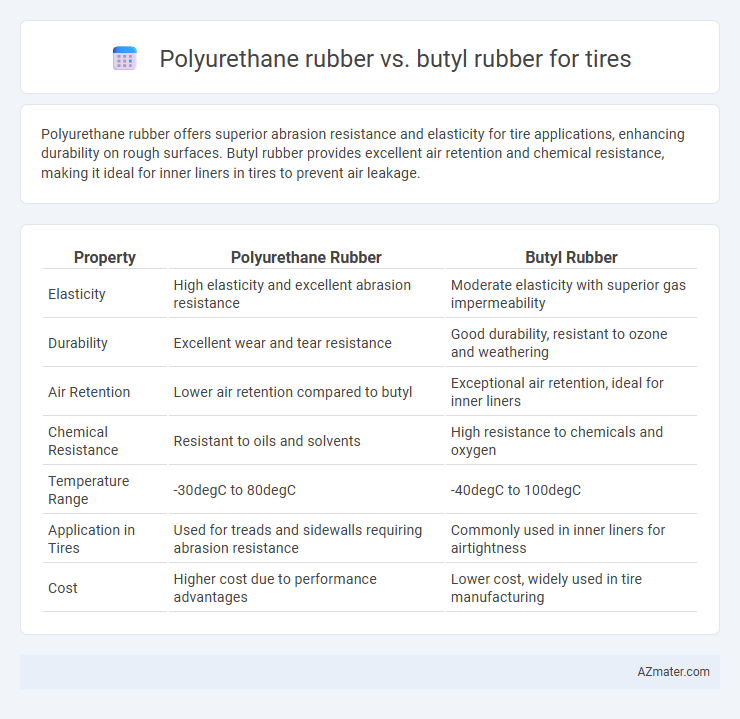
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity for tire applications, enhancing durability on rough surfaces. Butyl rubber provides excellent air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner liners in tires to prevent air leakage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | High elasticity and excellent abrasion resistance | Moderate elasticity with superior gas impermeability |
| Durability | Excellent wear and tear resistance | Good durability, resistant to ozone and weathering |
| Air Retention | Lower air retention compared to butyl | Exceptional air retention, ideal for inner liners |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | High resistance to chemicals and oxygen |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Application in Tires | Used for treads and sidewalls requiring abrasion resistance | Commonly used in inner liners for airtightness |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance advantages | Lower cost, widely used in tire manufacturing |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Butyl Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its high abrasion resistance, elasticity, and durability, making it ideal for tire applications requiring strength and longevity. Butyl rubber, a synthetic rubber derived from isobutylene with minor isoprene, excels in air impermeability, excellent weather resistance, and chemical stability, ensuring tire airtightness and durability under harsh conditions. Both materials serve distinct purposes in tires, with polyurethane offering mechanical toughness and butyl rubber providing superior sealing and weather resilience.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyurethane rubber consists of segmented block copolymers formed by the reaction of diisocyanates with polyols, resulting in hard and soft segments that provide high abrasion resistance and flexibility. Butyl rubber is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, characterized by saturated hydrocarbon chains that impart excellent impermeability to gases and superior resistance to heat and chemicals. The chemical structure of polyurethane enables enhanced mechanical properties and durability, while butyl's saturated backbone ensures exceptional air retention, crucial for tire applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for tire treads requiring durability and wear resistance. Butyl rubber offers exceptional air impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures, enhancing tire inflation retention and ride comfort. The higher tear resistance and elasticity of polyurethane rubber contribute to improved performance under mechanical stress, whereas butyl rubber's damping properties reduce vibration for smoother handling.
Durability and Lifespan in Tires
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, significantly enhancing tire durability under harsh road conditions. Butyl rubber provides exceptional air retention and resistance to aging and oxidation, contributing to longer tire lifespan by maintaining consistent pressure and flexibility. Tires combining polyurethane's toughness with butyl's impermeability yield optimal performance and extended service life.
Resistance to Chemicals and Weather
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it highly durable against aggressive chemicals in tire applications. Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, ensuring long-lasting performance in outdoor conditions. Tires combining polyurethane's chemical resistance and butyl's weatherproof properties deliver enhanced durability in diverse environmental challenges.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and maintains flexibility at higher temperatures, making it ideal for tires subjected to extreme heat. Butyl rubber excels in low-temperature performance, providing excellent air retention and resistance to ozone and weathering, which is essential for tire durability in cold conditions. The choice depends on operating temperature ranges: polyurethane suits high-heat environments, while butyl rubber is preferred for cold-weather stability.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Polyurethane rubber exhibits lower rolling resistance compared to butyl rubber, leading to enhanced fuel efficiency in tire applications due to its superior elasticity and energy return properties. Butyl rubber, while highly impermeable and resistant to air loss, generally demonstrates higher rolling resistance, which can reduce overall fuel economy. Selecting polyurethane rubber can contribute to reduced fuel consumption and emissions by improving tire performance in terms of rolling resistance.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyurethane rubber generally incurs higher production costs due to its complex polymer structure and specialized curing processes, which can increase manufacturing time and equipment expenses. Butyl rubber offers cost advantages with more straightforward processing techniques and abundant raw materials, making it economically favorable for tire inner liners and applications requiring excellent air retention. Manufacturers must weigh polyurethane's enhanced abrasion resistance and durability against butyl rubber's cost-effectiveness and ease of production to optimize tire performance and profitability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyurethane rubber offers higher durability and resistance to abrasion, extending tire lifespan and reducing waste generation compared to Butyl rubber, which has lower mechanical strength but superior air retention properties in tires. In terms of environmental impact, Butyl rubber is less energy-intensive to produce, while polyurethane's polymer chemistry presents more challenges for eco-friendly disposal and recycling processes. Recyclability of Butyl rubber is better established through devulcanization techniques, enabling more efficient material recovery compared to polyurethane, whose complex cross-linking limits effective recycling options.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type in Tires
Polyurethane rubber excels in high-performance tire applications requiring exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for off-road and industrial tires. Butyl rubber's superior air impermeability and chemical stability make it the preferred choice for inner liners in pneumatic tires, enhancing air retention and durability. Selecting polyurethane rubber optimizes tire longevity under heavy stress, while butyl rubber ensures consistent tire pressure and reliability in passenger and commercial vehicles.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com