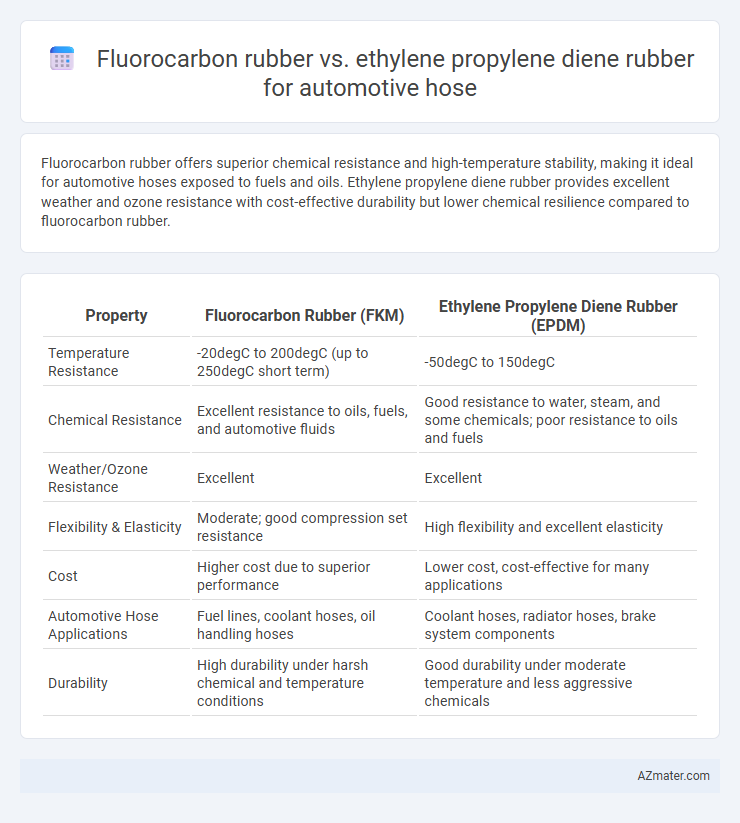
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for automotive hoses exposed to fuels and oils. Ethylene propylene diene rubber provides excellent weather and ozone resistance with cost-effective durability but lower chemical resilience compared to fluorocarbon rubber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -20degC to 200degC (up to 250degC short term) | -50degC to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and automotive fluids | Good resistance to water, steam, and some chemicals; poor resistance to oils and fuels |
| Weather/Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | Moderate; good compression set resistance | High flexibility and excellent elasticity |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance | Lower cost, cost-effective for many applications |
| Automotive Hose Applications | Fuel lines, coolant hoses, oil handling hoses | Coolant hoses, radiator hoses, brake system components |
| Durability | High durability under harsh chemical and temperature conditions | Good durability under moderate temperature and less aggressive chemicals |
Introduction to Automotive Hose Materials
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) are essential materials in automotive hose manufacturing due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. FKM offers superior resistance to heat, fuel, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for high-temperature engine compartments and fuel systems. EPDM provides excellent weathering, ozone, and heat resistance, commonly used in coolant and heater hoses where flexibility and durability in diverse environmental conditions are critical.
Overview of Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM)
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and oils, making it ideal for automotive hoses exposed to harsh fluids and extreme conditions. Its superior impermeability to gases and excellent mechanical performance enable longer service life and reliability compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM). FKM's durability in aggressive environments supports automotive applications requiring enhanced performance and endurance in fuel, coolant, and hydraulic systems.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in automotive hoses due to its excellent resistance to heat, oxidation, ozone, and weathering. EPDM maintains flexibility over a broad temperature range (-40degC to 150degC), making it ideal for coolant, heater, and radiator hoses. Its chemical resistance to water, steam, and many chemicals contrasts with the superior fuel and oil resistance offered by Fluorocarbon rubber, guiding material selection based on specific automotive hose requirements.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to automotive fluids such as oils, fuels, and aggressive solvents, maintaining performance in high-temperature and harsh chemical environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to water, steam, and polar substances but degrades when exposed to hydrocarbons and oils. For automotive hose applications requiring exposure to fuels and oils, fluorocarbon rubber provides enhanced durability and longer service life compared to EPDM.
Temperature Performance Analysis
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and chemical stability in extreme conditions ranging from -26degC to 204degC, making it ideal for automotive hoses exposed to high engine temperatures and aggressive fluids. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber performs well in lower temperature ranges, typically from -40degC to 125degC, offering excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and steam but degrades faster under prolonged high heat and exposure to automotive oils. Temperature performance analysis highlights FKM's advantage in high-heat environments common in fuel and oil delivery systems, whereas EPDM suits coolant and low-temperature seal applications.
Durability and Longevity
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for automotive hoses exposed to harsh fluids and extreme engine temperatures, which significantly enhances durability and longevity. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam, providing strong performance in coolant and water hoses but with lower tolerance to oil and fuel compared to FKM. For applications requiring extended service life in aggressive environments, FKM hoses typically outperform EPDM in maintaining elasticity and structural integrity over time.
Compatibility with Automotive Fluids
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance, maintaining integrity when exposed to a wide range of automotive fluids such as gasoline, diesel, brake fluids, and oils, making it highly compatible for automotive hose applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to water, steam, and some brake fluids but degrades rapidly when exposed to oils and fuels, limiting its suitability for fuel line hoses. The enhanced compatibility of FKM with aggressive automotive fluids ensures longer service life and reliability in demanding engine and fuel system environments.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and oils in automotive hose applications but comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM is more affordable and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for hoses exposed to less aggressive environments. Automotive manufacturers balance these factors by selecting EPDM for general use and FKM for specialized, high-performance hoses requiring enhanced durability.
Typical Applications in Automotive Hoses
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) excels in automotive hoses exposed to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals, such as fuel lines, coolant hoses, and turbocharger hoses, due to its exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is commonly used in radiator hoses, heater hoses, and vapor recovery hoses, offering superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam but limited fuel and oil resistance. Choosing between FKM and EPDM for automotive hoses depends on the specific application requirements involving temperature range, chemical exposure, and durability under harsh operating conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber Material for Automotive Hoses
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent fuel and oil compatibility, making it ideal for automotive hoses in demanding engine environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in ozone, weather, and heat resistance with temperature tolerance up to 150degC, best suited for coolant and brake fluid hoses with less exposure to hydrocarbons. Selecting the right rubber depends on the hose application, fluid compatibility, and operating temperature requirements to ensure durability and performance in automotive systems.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com