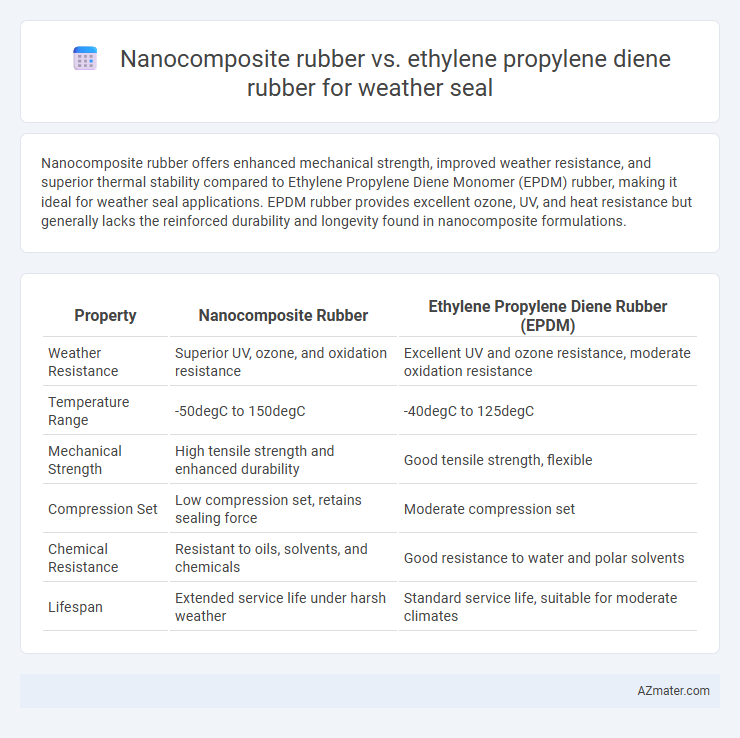
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced mechanical strength, improved weather resistance, and superior thermal stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for weather seal applications. EPDM rubber provides excellent ozone, UV, and heat resistance but generally lacks the reinforced durability and longevity found in nanocomposite formulations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Superior UV, ozone, and oxidation resistance | Excellent UV and ozone resistance, moderate oxidation resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 125degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and enhanced durability | Good tensile strength, flexible |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, retains sealing force | Moderate compression set |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Good resistance to water and polar solvents |
| Lifespan | Extended service life under harsh weather | Standard service life, suitable for moderate climates |
Introduction to Automotive Weather Seals
Nanocomposite rubber enhances automotive weather seals by incorporating nano-sized fillers, improving mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental factors compared to conventional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM remains a standard material for weather seals due to its excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering but can benefit from nanocomposite technology to address limitations such as abrasion and aging. The integration of nanocomposite materials in weather seals offers superior durability and lifespan, crucial for automotive applications exposed to diverse climatic conditions.
Overview of Nanocomposite Rubber
Nanocomposite rubber incorporates nanoscale fillers such as silica or carbon nanotubes, significantly enhancing mechanical strength, thermal stability, and weather resistance compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. The nanofillers improve barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, extending the service life of weather seals in harsh environmental conditions. This advanced material exhibits superior durability, making it an optimal choice for long-lasting weather seals in automotive and construction applications.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) Explained
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a widely used synthetic elastomer known for exceptional weather, ozone, and UV resistance, making it ideal for weather seals in automotive and construction applications. Unlike traditional nanocomposite rubber, EPDM offers superior durability in extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions without requiring reinforcement materials. Its excellent elasticity, water resistance, and aging stability ensure long-lasting sealing performance, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing overall seal reliability.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced abrasion resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it more durable for weather seal applications. Its improved modulus and elongation at break contribute to better flexibility and resilience under cyclic stresses. EPDM rubber, while offering excellent ozone and UV resistance, generally shows lower mechanical strength and stiffness than nanocomposite formulations reinforced with nanoscale fillers.
Weather Resistance and Aging Performance
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior weather resistance and aging performance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, owing to its enhanced barrier properties and improved UV and ozone resistance. The inclusion of nanofillers, such as layered silicates or carbon nanotubes, in nanocomposite rubber significantly reduces gas permeability and slows oxidative degradation, resulting in prolonged durability under harsh environmental conditions. In contrast, while EPDM rubber offers good baseline resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, its aging stability is limited by polymer chain scission and crosslink density changes, making nanocomposite rubber a more robust choice for extended-life weather seals.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Tolerance
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior thermal stability and temperature tolerance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for weather seal applications exposed to extreme conditions. The incorporation of nanoscale fillers, such as clay or carbon nanotubes, enhances its resistance to thermal degradation and maintains elasticity at higher temperatures above 150degC, whereas EPDM typically withstands temperatures up to 120degC. This increased thermal resilience ensures extended service life and improved sealing performance in automotive and industrial weatherproofing uses.
Resistance to Ozone and UV Degradation
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior resistance to ozone and UV degradation compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, due to the enhanced barrier properties provided by the uniformly dispersed nanoparticles within the polymer matrix. The incorporation of nanofillers in nanocomposite rubber significantly reduces oxidative chain scission and surface cracking, which are common failure modes in EPDM under prolonged environmental exposure. This improved durability makes nanocomposite rubber an ideal material for weather seals in harsh outdoor conditions requiring extended ozone and UV resistance.
Processability and Manufacturing Considerations
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced processability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, due to improved filler dispersion which facilitates smoother extrusion and molding, optimizing manufacturing efficiency. EPDM rubber provides reliable weather resistance but tends to exhibit higher viscosity and less uniform filler distribution, potentially complicating compound mixing and processing steps. Manufacturers prioritizing precise dimensional control and improved mechanical properties in weather seals may prefer nanocomposite rubbers for streamlined production workflows and superior end-use performance.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced durability and weather resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time. While the initial material cost for nanocomposite rubber is higher due to advanced filler integration, its longer service life and improved performance can lead to lower total ownership costs, especially in harsh environmental conditions. EPDM rubber provides a cost-effective solution with moderate weather resistance, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects where lifecycle cost considerations are less critical.
Future Trends in Weather Seal Material Innovation
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior barrier properties, enhanced mechanical strength, and improved thermal stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it a promising candidate for advanced weather seal applications. Emerging trends focus on integrating nanofillers like graphene and carbon nanotubes into EPDM matrices to create hybrid composites that offer increased durability, resistance to UV radiation, and reduced permeability. Future innovations in weather seal materials emphasize sustainability and multifunctionality, leveraging nanotechnology to develop eco-friendly elastomers with self-healing and adaptive response capabilities.
Infographic: Nanocomposite rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com