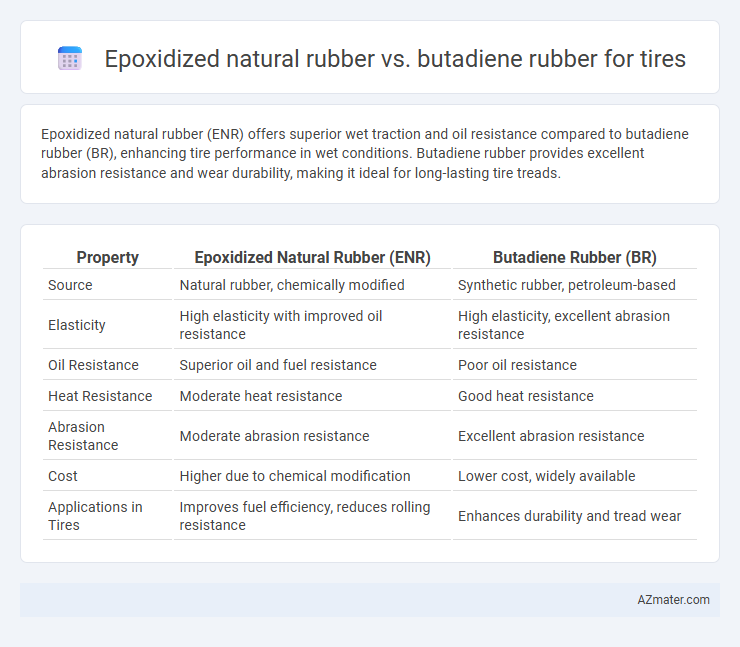
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior wet traction and oil resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), enhancing tire performance in wet conditions. Butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and wear durability, making it ideal for long-lasting tire treads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Butadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural rubber, chemically modified | Synthetic rubber, petroleum-based |
| Elasticity | High elasticity with improved oil resistance | High elasticity, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Oil Resistance | Superior oil and fuel resistance | Poor oil resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Good heat resistance |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to chemical modification | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications in Tires | Improves fuel efficiency, reduces rolling resistance | Enhances durability and tread wear |
Introduction to Rubber Types in Tire Manufacturing
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and fuel efficiency compared to butadiene rubber (BR), commonly used in tire manufacturing for its high resilience and wet grip. ENR's incorporation of epoxy groups improves compatibility with other rubber compounds, boosting tire performance and durability. Butadiene rubber remains essential for impact resistance and low-temperature flexibility, making its blend with ENR crucial for optimized tire tread and sidewall properties.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil resistance, improved gas barrier properties, and higher tensile strength compared to conventional natural rubber. ENR is produced by introducing epoxy groups into the polymer chain, which increases polarity and compatibility with other tire compounding materials, resulting in better durability and abrasion resistance. Compared to butadiene rubber (BR), ENR offers superior wet grip and reduced rolling resistance, making it valuable for high-performance and eco-friendly tire applications.
Characteristics of Butadiene Rubber (BR)
Butadiene Rubber (BR) exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, making it ideal for tire treads to enhance durability and grip. Its high resilience and good aging stability contribute to improved tire performance over varied road conditions. Compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber, BR offers superior wear resistance and mechanical strength, essential for heavy-duty tire applications.
Key Chemical Differences Between ENR and BR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) contains oxirane groups introduced by epoxidation of the double bonds in natural rubber, enhancing polarity and compatibility with polar fillers, while butadiene rubber (BR) is a synthetic polymer composed mainly of 1,3-butadiene units with minimal polarity. ENR exhibits higher gas barrier properties and improved oil resistance due to the presence of epoxy groups, contrasting with BR's superior abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility stemming from its non-polar hydrocarbon structure. The chemical modification in ENR facilitates better interaction with silica fillers in tire compounds, whereas BR relies more on carbon black for reinforcement due to its non-polar nature.
Comparative Mechanical Properties: ENR vs BR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it suitable for enhanced tire durability. ENR's improved elasticity and better wet grip performance contrast with BR's superior low-temperature flexibility and lower hysteresis, which contributes to fuel efficiency. The choice between ENR and BR in tire manufacturing depends on balancing mechanical properties for specific performance requirements such as wear resistance, traction, and rolling resistance.
Performance in Wet and Dry Conditions
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior wet traction compared to butadiene rubber (BR) due to its enhanced polarity and better interaction with water molecules, providing improved grip on wet road surfaces. In dry conditions, butadiene rubber offers better abrasion resistance and durability, resulting in longer tread life and stability under high temperatures. Tire compounds blending ENR and BR optimize performance by balancing wet traction and dry durability, meeting diverse driving condition demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to butadiene rubber (BR), which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. ENR reduces greenhouse gas emissions during production and improves tire sustainability by incorporating renewable resources, while BR relies heavily on fossil fuels contributing to environmental pollution. The use of ENR in tires supports circular economy principles and aligns with increasing industry demand for eco-friendly materials.
Cost Efficiency and Production Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and better adhesion properties compared to butadiene rubber (BR), leading to longer tire life and reduced maintenance costs. While ENR is generally more expensive than BR due to the modification process, its superior durability can offset initial costs in high-performance tire applications. Production considerations include the need for specialized compounding and processing techniques for ENR, whereas BR benefits from well-established, cost-effective manufacturing protocols.
Application Suitability in Tire Components
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced wet grip, abrasion resistance, and ozone resistance, making it suitable for tire treads and sidewalls requiring improved durability and traction. Butadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent low-temperature flexibility, high resilience, and wear resistance, making it ideal for tire treads aimed at high-performance and fuel-efficient tires. Combining ENR and BR in tire compounds optimizes overall tire performance by balancing wet grip, rolling resistance, and wear characteristics.
Future Trends and Innovations in Rubber Compounds for Tires
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance and enhanced wet grip compared to butadiene rubber, positioning it as a promising material for next-generation tire compounds aimed at improving safety and durability. Innovations in rubber formulations increasingly incorporate ENR to reduce rolling resistance and enhance fuel efficiency, aligning with the automotive industry's sustainability goals. Research focuses on hybrid blends that combine ENR's eco-friendly attributes with the resilience of butadiene rubber to optimize performance and meet stringent regulatory standards for low emissions and extended tire life.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com