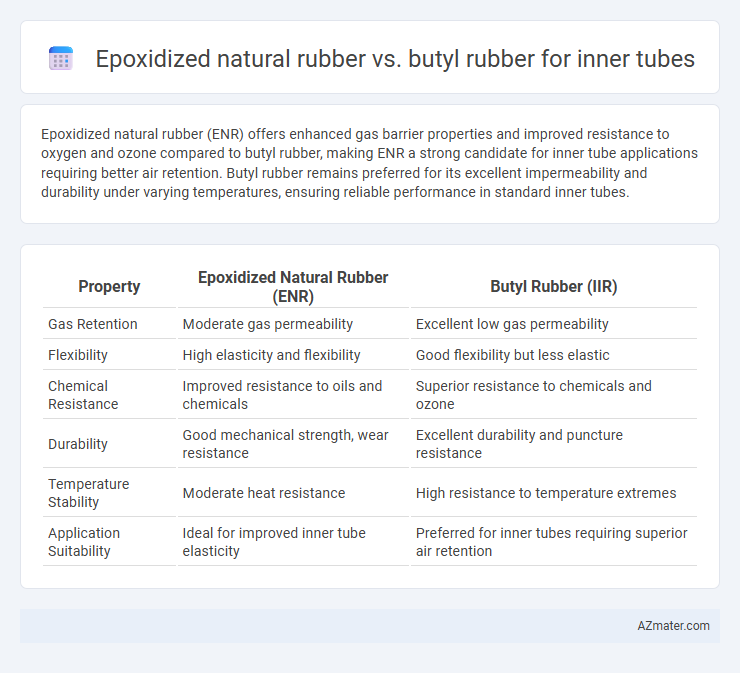
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced gas barrier properties and improved resistance to oxygen and ozone compared to butyl rubber, making ENR a strong candidate for inner tube applications requiring better air retention. Butyl rubber remains preferred for its excellent impermeability and durability under varying temperatures, ensuring reliable performance in standard inner tubes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Retention | Moderate gas permeability | Excellent low gas permeability |
| Flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility | Good flexibility but less elastic |
| Chemical Resistance | Improved resistance to oils and chemicals | Superior resistance to chemicals and ozone |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, wear resistance | Excellent durability and puncture resistance |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate heat resistance | High resistance to temperature extremes |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for improved inner tube elasticity | Preferred for inner tubes requiring superior air retention |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Inner tubes require materials with excellent air retention, flexibility, and resistance to wear and environmental factors. Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced gas impermeability and improved oil resistance due to its chemical structure, making it suitable for durable inner tubes. Butyl rubber is highly favored for inner tubes because of its superior airtightness, excellent resilience, and resistance to heat and aging, ensuring long-lasting inflation.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil, heat, and gas barrier properties, making it an ideal material for inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions. Compared to Butyl rubber, ENR offers higher elasticity and better abrasion resistance, resulting in improved durability and flexibility under varying temperatures. These characteristics contribute to increased performance and longer life span in inner tubes used in automotive and bicycle tires.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent air impermeability, chemical resistance, and durability, making it highly suitable for inner tube applications. Its unique polymer structure, primarily composed of isobutylene with small amounts of isoprene, provides superior puncture resistance and low gas permeability compared to epoxidized natural rubber. This results in enhanced tire pressure retention and extended service life, crucial for maintaining performance and safety in inner tubes.
Key Performance Criteria for Inner Tubes
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance, enhanced air impermeability, and better fuel resistance compared to conventional natural rubber, making it suitable for high-performance inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions. Butyl rubber excels in low gas permeability and excellent air retention, ensuring prolonged inflation and durability in inner tubes used for long-distance or high-speed applications. The choice between ENR and Butyl rubber depends on the desired balance of elasticity, air retention, and resistance to chemicals and abrasion for specific inner tube requirements.
Air Retention and Impermeability Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers improved air retention due to its enhanced polarity, providing superior impermeability compared to traditional natural rubber but still falls short of the exceptional air retention capabilities of butyl rubber. Butyl rubber exhibits superior impermeability attributed to its dense molecular structure and low permeability to gases, making it the preferred material for inner tubes that require long-lasting air retention. In applications demanding maximum air retention and resistance to gas diffusion, butyl rubber outperforms ENR, despite ENR's greater elasticity and environmental benefits.
Durability and Aging Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior durability and enhanced aging resistance in inner tubes due to its improved resistance to oxygen, ozone, and heat degradation compared to conventional natural rubber. Butyl rubber, known for its exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to ozone and weathering, provides robust aging resistance but may exhibit lower mechanical durability under dynamic stress conditions. Choosing between ENR and butyl rubber for inner tubes depends on the balance between high elasticity and aging endurance, with ENR excelling in mechanical resilience and butyl rubber in long-term environmental stability.
Flexibility and Elastic Properties
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior flexibility and elasticity compared to butyl rubber, making it highly suitable for inner tubes that require enhanced resilience and stretchability. ENR's improved polymer chain mobility and higher natural rubber content contribute to better elongation at break and rebound resilience, which are critical for absorbing shocks and maintaining airtightness. Butyl rubber, while excellent in air impermeability and chemical resistance, generally exhibits lower elasticity and stiffness, resulting in reduced flexibility under dynamic loads.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior biodegradability and is derived from renewable resources, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to synthetic butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, made from petrochemical sources, poses challenges in disposal and recycling due to its non-biodegradable nature and long degradation time. ENR's enhanced sustainability aligns with eco-friendly tire manufacturing initiatives, promoting reduced carbon footprint and improved end-of-life rubber management for inner tube applications.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced elasticity and gas impermeability compared to butyl rubber, but typically comes at a higher production cost due to more complex manufacturing processes. Butyl rubber remains the preferred choice for inner tubes due to its superior air retention, widespread market availability, and lower price point, making it more cost-efficient for mass production. Market data indicates that butyl rubber's established supply chain and economies of scale contribute to consistently lower material costs compared to ENR.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Material for Inner Tubes
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior resilience, enhanced abrasion resistance, and better oxygen barrier properties compared to butyl rubber, making it highly suitable for inner tubes subjected to dynamic stresses. Butyl rubber excels in air retention and chemical inertness, ensuring longer inflation intervals and resistance to fuel and ozone degradation. Selecting between ENR and butyl rubber depends on prioritizing either performance under mechanical strain or extended air impermeability for optimal inner tube functionality.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com