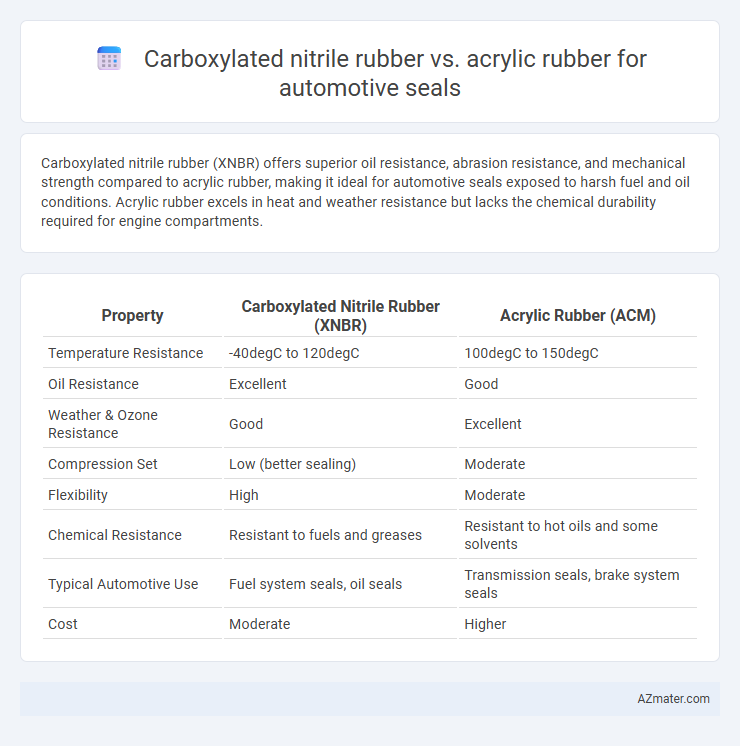
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and mechanical strength compared to acrylic rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh fuel and oil conditions. Acrylic rubber excels in heat and weather resistance but lacks the chemical durability required for engine compartments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Acrylic Rubber (ACM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | 100degC to 150degC |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low (better sealing) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to fuels and greases | Resistant to hot oils and some solvents |
| Typical Automotive Use | Fuel system seals, oil seals | Transmission seals, brake system seals |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced oil resistance, tensile strength, and durability, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh fluids and abrasion. Acrylic rubber (ACM) excels in heat resistance and weathering stability, ensuring reliable sealing performance in high-temperature engine compartments. Both materials provide critical sealing solutions, with XNBR favored in fuel system applications and ACM preferred for soot and transmission seals.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and improved mechanical strength compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh fluids and extreme temperatures. Its molecular structure includes carboxyl groups that promote stronger intermolecular bonding, resulting in superior abrasion resistance and durability. These properties enable XNBR seals to maintain elasticity and sealing performance in engines, transmissions, and fuel systems where exposure to oils, fuels, and solvents is critical.
Properties of Acrylic Rubber
Acrylic rubber (ACM) offers exceptional resistance to heat aging, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environments. Its superior resistance to oils, fuel, and hydraulic fluids ensures long-lasting performance in engine and transmission systems. Compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber, acrylic rubber provides better dimensional stability and elasticity at elevated temperatures, enhancing seal durability and reliability in automotive applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to automotive fluids such as oils, fuels, and greases compared to acrylic rubber, making it ideal for sealing applications exposed to aggressive hydrocarbon environments. Acrylic rubber provides excellent resistance to dilute acids, alkalis, and oxygenated solvents but performs poorly against oils and fuels, limiting its use in engine compartments. XNBR's enhanced polarity and cross-link density contribute to its robust performance against a broader spectrum of automotive chemicals, ensuring longer seal life and reliability.
Temperature Performance Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior temperature resistance, maintaining elasticity and sealing integrity between -40degC and 120degC, making it suitable for under-hood automotive seals exposed to higher thermal stress. Acrylic rubber (ACM) performs well in high-temperature environments, typically up to 150degC, but exhibits reduced low-temperature flexibility, limiting its application in seals exposed to cold climates. The distinct thermal properties of XNBR and ACM influence their selection based on the specific temperature range requirements in automotive sealing applications.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to acrylic rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to dynamic mechanical stresses. XNBR exhibits excellent oil and fuel resistance alongside good low-temperature flexibility, enhancing durability in harsh automotive environments. Acrylic rubber, while providing good weather and ozone resistance, typically has lower mechanical strength and reduced elasticity, limiting its effectiveness in high-stress sealing applications.
Compatibility with Automotive Fluids
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior resistance to automotive fluids such as engine oils, transmission fluids, and fuels due to its enhanced polarity and crosslinking density, making it highly compatible for seals in harsh environments. Acrylic rubber (ACM) offers excellent resistance to heat and oxidation but shows limited compatibility with petroleum-based fluids, resulting in potential swelling and degradation when exposed to oils and grease. Selecting XNBR over ACM ensures better fluid resistance and longer seal life in demanding automotive applications involving exposure to diverse fluids.
Cost and Availability Factors
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers better oil resistance and durability in automotive seals but comes at a higher cost compared to acrylic rubber, which is more affordable and widely available. Acrylic rubber seals provide good weathering and ozone resistance but may underperform in oil exposure, affecting long-term reliability. Availability of acrylic rubber is generally higher due to simpler production processes, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale automotive sealing applications.
Typical Applications in Automotive Seals
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is widely used in automotive seals due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and high temperatures, making it ideal for engine gaskets, fuel system seals, and transmission seals. Acrylic rubber (ACM) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and aging, which suits it for applications such as weatherstripping, door seals, and HVAC system components. Both materials provide durability and chemical resistance, but carboxylated nitrile rubber is preferred for dynamic sealing under exposure to automotive fluids, while acrylic rubber excels in static sealing where prolonged heat exposure is common.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and aging, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh chemical environments. Acrylic rubber excels in high-temperature resistance and weatherability but has lower oil resistance compared to carboxylated nitrile. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific performance requirements: prioritize carboxylated nitrile for oil-rich conditions and acrylic rubber for prolonged exposure to heat and weather.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Acrylic rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com