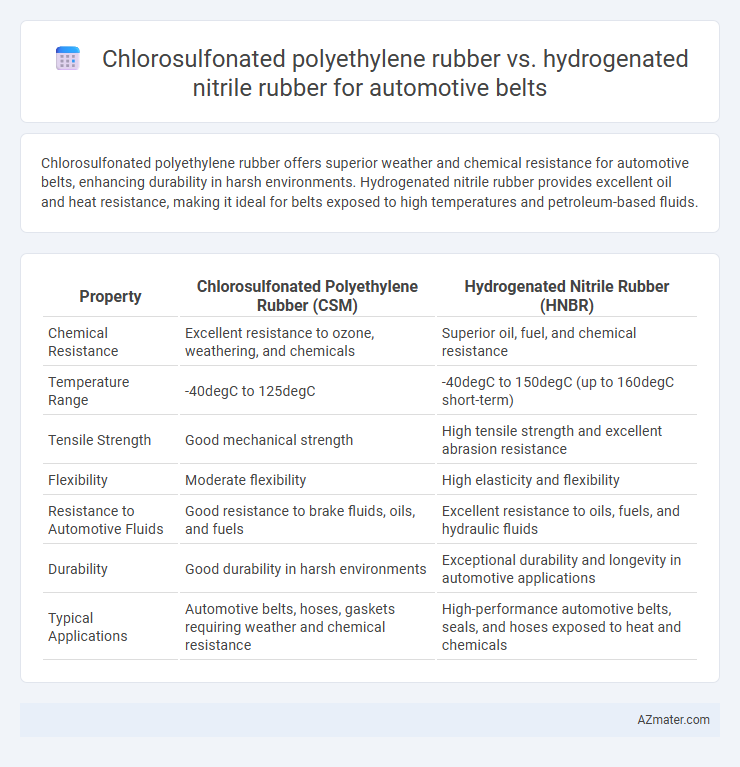
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior weather and chemical resistance for automotive belts, enhancing durability in harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides excellent oil and heat resistance, making it ideal for belts exposed to high temperatures and petroleum-based fluids.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals | Superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -40degC to 150degC (up to 160degC short-term) |
| Tensile Strength | Good mechanical strength | High tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Resistance to Automotive Fluids | Good resistance to brake fluids, oils, and fuels | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids |
| Durability | Good durability in harsh environments | Exceptional durability and longevity in automotive applications |
| Typical Applications | Automotive belts, hoses, gaskets requiring weather and chemical resistance | High-performance automotive belts, seals, and hoses exposed to heat and chemicals |
Introduction to Automotive Belt Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals, making it a robust choice for automotive belts exposed to harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in oil resistance and mechanical strength, providing durability under high temperatures and dynamic stress found in engine bays. Both materials enhance belt longevity and performance, but CSM is preferred for external applications while HNBR suits internal engine components.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is renowned for its exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, chemicals, and heat, making it highly suitable for automotive belt applications where durability is critical. Its molecular structure, containing chlorosulfonyl groups, imparts enhanced oil resistance and mechanical strength compared to many other elastomers. CSM offers a balanced combination of flexibility and toughness, enabling automotive belts to perform reliably under harsh operating conditions, including exposure to oil, fuels, and elevated temperatures.
Characteristics of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) exhibits exceptional heat resistance, retaining mechanical properties up to 150degC, making it ideal for automotive belt applications exposed to high temperatures. Its superior oil and chemical resistance enhances durability against engine fluids and fuels, outperforming Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber in harsh environments. HNBR also provides excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, ensuring long service life and reliability under continuous mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance: CSM vs HNBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent chemical resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering, making it highly suitable for automotive belts exposed to harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals, particularly petroleum-based fluids, with enhanced durability under high-temperature conditions. While both materials perform well chemically, HNBR typically outperforms CSM in resistance to fuels and abrasion, making it the preferred choice for demanding automotive applications requiring longevity.
Heat and Ozone Resistance in Automotive Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior heat and ozone resistance, maintaining mechanical integrity in automotive belts under high-temperature conditions up to 130degC and prolonged ozone exposure, thereby preventing cracking and degradation. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers excellent heat resistance, typically up to 150degC, and enhanced ozone resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, making it suitable for belts exposed to aggressive automotive environments and oil contaminants. The selection between CSM and HNBR for automotive belts depends on specific operational temperatures and exposure to ozone and chemicals, with HNBR favored for higher temperature tolerance and CSM preferred for cost-effective ozone resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and excellent tensile strength, making it highly durable for automotive belt applications under mechanical stress. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced thermal stability and higher resistance to oil and chemical exposure, combined with good tensile strength and elongation properties. Both elastomers provide robust mechanical performance, but CSM is preferred for its durability in abrasive environments, while HNBR excels in oil-rich and high-temperature conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Belt Usage
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, ensuring superior durability in automotive belt applications exposed to harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) delivers outstanding heat resistance and mechanical strength, offering excellent longevity under continuous high-temperature and oil-exposed conditions typical in engine compartments. For automotive belts, CSM's chemical resilience extends belt life in external exposures, while HNBR's thermal stability enhances performance longevity in high-stress, heat-intensive areas.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior weather and ozone resistance at a moderate cost, making it a cost-effective choice for automotive belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides excellent oil and chemical resistance with higher temperature tolerance but typically comes at a higher price and less widespread availability compared to CSM. Automotive manufacturers often select CSM for applications prioritizing durability and budget, while HNBR is preferred when enhanced performance justifies the increased material cost and sourcing complexity.
Typical Automotive Belt Applications for CSM and HNBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is commonly used in automotive belts requiring excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for serpentine belt covers and timing belts exposed to harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in high-temperature and oil-resistant applications, commonly employed in power steering belts and V-belts where exposure to automotive fluids and elevated thermal conditions demands superior mechanical strength and durability. Both CSM and HNBR are preferred for their enhanced abrasion resistance and long service life in dynamic, abrasive conditions typical of automotive belt operation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Rubber for Automotive Belts
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior chemical resistance, excellent UV and ozone stability, and robust weathering properties, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides outstanding oil and fuel resistance combined with high tensile strength, ensuring durability in belts subjected to high mechanical stress and exposure to automotive fluids. Selecting the optimal rubber depends on the specific application requirements, where chlorosulfonated polyethylene excels in environmental durability and hydrogenated nitrile rubber delivers enhanced performance against hydrocarbons and mechanical wear.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com