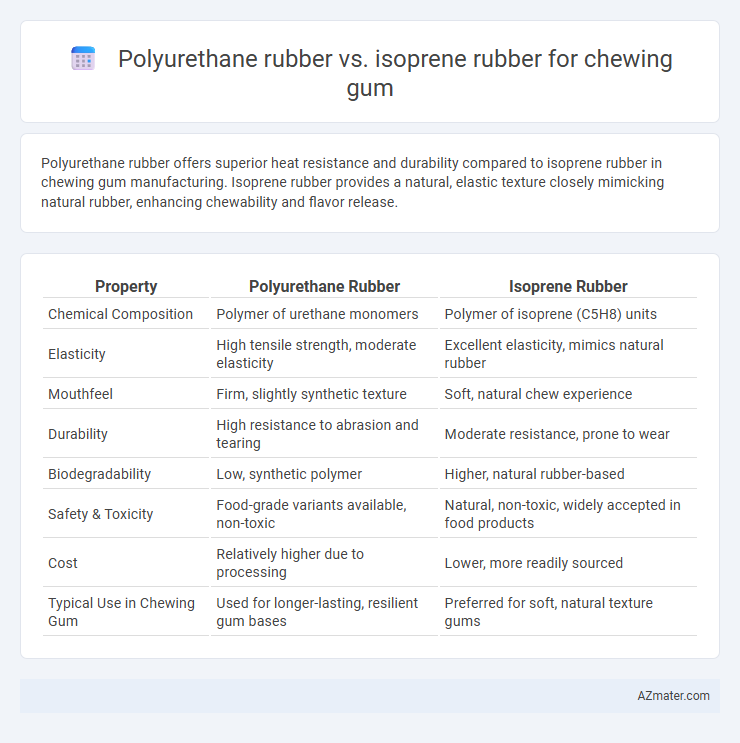
Polyurethane rubber offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to isoprene rubber in chewing gum manufacturing. Isoprene rubber provides a natural, elastic texture closely mimicking natural rubber, enhancing chewability and flavor release.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber | Isoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Polymer of urethane monomers | Polymer of isoprene (C5H8) units |
| Elasticity | High tensile strength, moderate elasticity | Excellent elasticity, mimics natural rubber |
| Mouthfeel | Firm, slightly synthetic texture | Soft, natural chew experience |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and tearing | Moderate resistance, prone to wear |
| Biodegradability | Low, synthetic polymer | Higher, natural rubber-based |
| Safety & Toxicity | Food-grade variants available, non-toxic | Natural, non-toxic, widely accepted in food products |
| Cost | Relatively higher due to processing | Lower, more readily sourced |
| Typical Use in Chewing Gum | Used for longer-lasting, resilient gum bases | Preferred for soft, natural texture gums |
Introduction to Chewing Gum Base Materials
Polyurethane rubber and isoprene rubber serve distinct roles in chewing gum base formulation, with isoprene rubber traditionally favored for its natural elasticity and resilience, closely mimicking the properties of natural rubber. Polyurethane rubber offers enhanced durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it a modern alternative for synthetic gum bases that require longer-lasting chew and structural integrity. The choice between these materials impacts the gum's texture, chewiness, and shelf life, influencing consumer experience and manufacturing processes.
What is Polyurethane Rubber?
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile synthetic elastomer composed of polymer chains linked by urethane groups, renowned for its high abrasion resistance and elasticity, making it suitable for chewing gum bases that require durability and chewiness. Unlike isoprene rubber, which is a natural elastomer derived from latex offering softness and biodegradability, polyurethane provides superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, enhancing the gum's texture and longevity. Its tailored molecular structure allows manufacturers to customize physical properties, ensuring consistent performance in diverse chewing gum products.
What is Isoprene Rubber?
Isoprene rubber, a natural polymer derived from the latex of rubber trees, is widely used in chewing gum for its excellent elasticity and non-toxicity, which enhances the gum's chewiness and mouthfeel. Compared to polyurethane rubber, which is synthetic and offers greater durability and resistance to abrasion, isoprene rubber provides a more natural and biodegradable option, aligning with consumer preferences for eco-friendly products. The molecular structure of isoprene rubber allows it to mimic the texture and flexibility of traditional gum base, making it a preferred choice in formulations focused on natural ingredients and biocompatibility.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber exhibits high chemical resistance and excellent tensile strength due to its segmented polymer structure containing urethane linkages, making it less prone to degradation in chewing gum applications. Isoprene rubber, a natural polymer primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, offers superior elasticity and biodegradability but has lower resistance to oxidation and hydrolysis compared to polyurethane. The chemical stability of polyurethane enhances the gum's durability, whereas isoprene provides a softer texture with faster biodegradation, influencing the overall gum quality and shelf life.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyurethane rubber in chewing gum raises safety concerns due to potential toxicity and difficulty in digestibility, unlike isoprene rubber, which is a natural, non-toxic polymer commonly recognized as safe for food applications. Isoprene rubber exhibits superior biocompatibility and lower likelihood of allergic reactions, making it preferable for oral contact products. Regulatory agencies favor isoprene rubber over polyurethane for chewing gum bases because of its established safety profile and minimal health risks.
Sensory Experience: Taste and Texture
Polyurethane rubber in chewing gum offers a smoother and more elastic texture, enhancing the chew duration without compromising flavor release, whereas isoprene rubber provides a more natural, latex-like chew with a slightly firmer texture that some consumers find preferable. The taste profile of polyurethane rubber is often neutral, allowing for more consistent and prolonged flavor retention, while isoprene rubber may impart subtle natural notes that can influence the overall taste experience. Sensory perception of texture and taste is critical in gum formulation, with polyurethane delivering a synthetic but highly controlled chew and isoprene offering a traditional, natural mouthfeel.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Polyurethane rubber is less biodegradable compared to isoprene rubber, leading to a longer environmental persistence when used in chewing gum bases. Isoprene rubber, being a natural polymer derived from latex, offers superior biodegradability and poses a lower ecological risk, contributing to reduced microplastic pollution. The environmental impact of polyurethane-rubber-based chewing gum is more significant due to its synthetic nature and slower breakdown rate in natural ecosystems.
Cost and Manufacturing Factors
Polyurethane rubber typically incurs higher production costs than isoprene rubber due to its complex polymerization process and use of specialized catalysts. Isoprene rubber benefits from established large-scale manufacturing methods, resulting in more cost-effective and consistent material supply for chewing gum production. Manufacturing factors favor isoprene rubber as it enables easier processing, better elasticity, and flavor retention, ultimately reducing overall production expenses.
Regulatory Approvals for Food Use
Polyurethane rubber is rarely used in chewing gum due to limited regulatory approvals for food contact, as it often fails to meet FDA and EFSA standards for direct food use. Isoprene rubber, being a synthetic equivalent of natural rubber, has broader acceptance and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, making it suitable for chewing gum bases. Compliance with food safety regulations such as FDA 21 CFR and EU Regulation 10/2011 is crucial for any gum base ingredient, favoring isoprene rubber over polyurethane in regulatory contexts.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Chewing Gum
Choosing the right rubber for chewing gum involves comparing polyurethane rubber and isoprene rubber based on elasticity, safety, and flavor retention. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent durability and resistance to breakdown, enhancing long-lasting chew quality, while isoprene rubber, being a natural polymer, provides superior biodegradability and a softer texture preferred for traditional gum textures. Manufacturers often prefer isoprene rubber for natural formulation and consumer safety, whereas polyurethane rubber is favored for specialized gum products requiring enhanced mechanical properties.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Chewing gum
 azmater.com
azmater.com