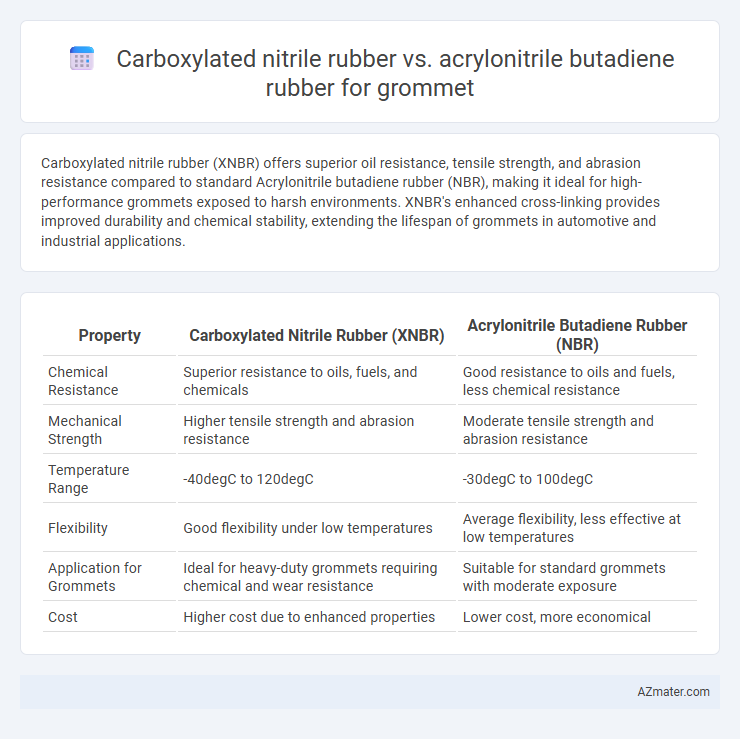
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance compared to standard Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-performance grommets exposed to harsh environments. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking provides improved durability and chemical stability, extending the lifespan of grommets in automotive and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and fuels, less chemical resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility under low temperatures | Average flexibility, less effective at low temperatures |
| Application for Grommets | Ideal for heavy-duty grommets requiring chemical and wear resistance | Suitable for standard grommets with moderate exposure |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties | Lower cost, more economical |
Introduction to Grommet Material Selection
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) are common materials used for grommets due to their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. XNBR offers enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability compared to standard NBR, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications where durability is critical. Selecting the right material depends on operating temperature range, exposure to solvents, and mechanical stress, with XNBR often preferred for high-performance sealing and protective grommets in automotive and aerospace industries.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) features enhanced oil and chemical resistance along with improved tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to standard Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), making it ideal for grommet applications requiring durability in harsh environments. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR allows for better cross-linking, resulting in superior mechanical properties and heat resistance. These characteristics make XNBR preferable over conventional NBR in automotive and industrial grommets subjected to oils, fuels, and mechanical stress.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for grommet applications requiring durability in harsh environments. Its high tensile strength and abrasion resistance ensure long-lasting performance, while the material maintains flexibility across a wide temperature range from -40degC to 100degC. Compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber, NBR provides superior oil resistance but may have lower resistance to compression set, affecting its suitability depending on specific grommet design requirements.
Chemical Resistance: XNBR vs NBR
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to standard acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), particularly against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for grommets exposed to harsh chemical environments. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR enhances abrasion resistance and reduces swelling in aggressive media, whereas NBR can degrade faster when in prolonged contact with aromatic hydrocarbons and ketones. XNBR's improved cross-linking density also contributes to its better performance and durability in sealing applications where chemical exposure is critical.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it more durable for grommet applications under mechanical stress. XNBR exhibits enhanced hardness and improved elasticity, providing better compression set resistance and dimensional stability in dynamic environments. In contrast, NBR has good oil and chemical resistance but lower mechanical strength, which may reduce grommet lifespan under heavy load conditions.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior temperature performance and stability compared to standard acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), maintaining elasticity and resistance at elevated temperatures up to 120degC. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking provides improved chemical resistance and dimensional stability, which is critical for grommets exposed to fluctuating thermal environments. Standard NBR typically performs best within a temperature range of -40degC to 100degC, making XNBR the preferred choice when higher thermal endurance and prolonged durability are required.
Aging and Ozone Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior aging and ozone resistance compared to conventional acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for grommet applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking and polar groups improve its durability against ozone cracks and oxidative degradation over time. NBR, while cost-effective and oil-resistant, tends to degrade faster under extended ozone and aging exposure, reducing the lifespan of grommets in outdoor or industrial settings.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced oil resistance and durability for grommet applications but typically incurs higher material costs compared to standard acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber remains more cost-efficient and widely available globally, making it the preferred choice for large-scale production where budget constraints are critical. Supply chain stability and lower raw material prices further position NBR as the economically viable option for manufacturing grommets in diverse industrial sectors.
Typical Grommet Applications for XNBR and NBR
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and enhanced mechanical strength, making it ideal for grommets used in heavy-duty automotive and industrial sealing applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance, commonly applied in grommets for fluid handling systems, fuel lines, and pneumatic devices. XNBR grommets typically withstand harsher environments and dynamic stresses, while NBR grommets provide reliable performance in oil-contaminated and moderate temperature conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Grommet
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability compared to standard acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for grommets exposed to harsh chemical environments and high temperatures. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber provides good flexibility and cost-effectiveness for general-purpose grommets in less demanding applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on application-specific requirements such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and durability of the grommet.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Grommet
 azmater.com
azmater.com