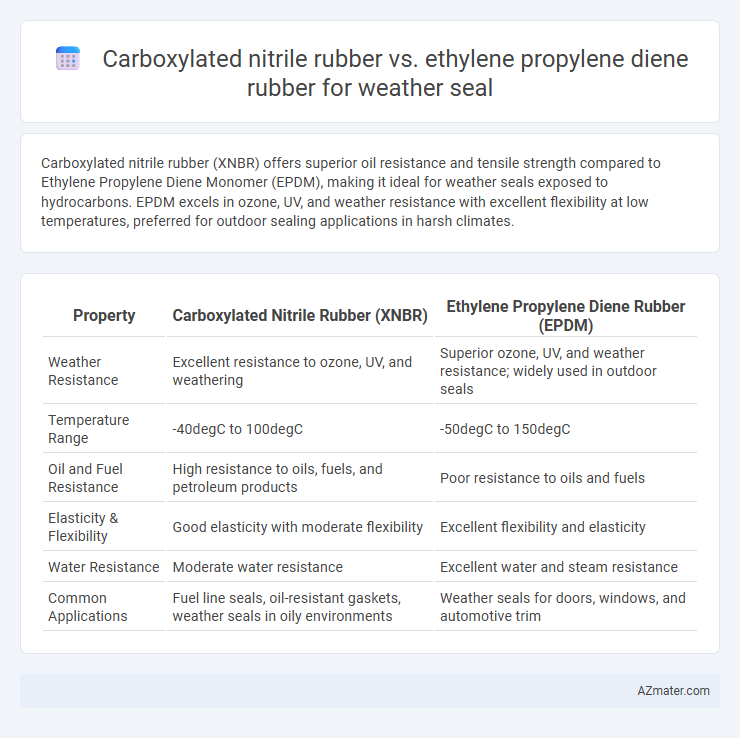
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making it ideal for weather seals exposed to hydrocarbons. EPDM excels in ozone, UV, and weather resistance with excellent flexibility at low temperatures, preferred for outdoor sealing applications in harsh climates.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance; widely used in outdoor seals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | High resistance to oils, fuels, and petroleum products | Poor resistance to oils and fuels |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Good elasticity with moderate flexibility | Excellent flexibility and elasticity |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water resistance | Excellent water and steam resistance |
| Common Applications | Fuel line seals, oil-resistant gaskets, weather seals in oily environments | Weather seals for doors, windows, and automotive trim |
Overview of Weather Sealing Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent oil resistance and good mechanical properties, making it suitable for weather seals exposed to hydrocarbons and harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber stands out for superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance, providing long-lasting performance in outdoor sealing applications. Both materials are widely used in automotive and industrial weather seals, with EPDM preferred for extreme weather durability and XNBR favored where oil resistance is critical.
Introduction to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and chemical durability compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it highly effective for weather seal applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its polar carboxyl groups improve adhesion properties and resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, outperforming ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) in oil resistance and mechanical stability. XNBR's superior compression set and low gas permeability ensure long-lasting sealing performance in automotive and industrial weather sealing solutions.
Introduction to Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to weather, ozone, and UV rays, making it ideal for weather sealing applications. Compared to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR), EPDM offers superior flexibility at low temperatures and excellent aging stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in outdoor environments. Its chemical structure, featuring a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with unsaturation in the diene monomer, contributes to its remarkable durability against environmental factors.
Comparative Chemical Structures
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains polar carboxyl groups attached to the nitrile polymer backbone, enhancing its chemical resistance and adhesion properties. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with diene monomers providing sites for vulcanization, resulting in excellent ozone, UV, and weather resistance. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR leads to stronger intermolecular forces, while EPDM's non-polar nature offers superior flexibility and durability in harsh weather seal applications.
Weather Resistance and UV Stability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior weather resistance and UV stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it highly effective for weather seal applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. XNBR's enhanced resistance to ozone, sunlight, and oxidation ensures prolonged durability and minimal degradation under UV exposure. EPDM provides good general weather resistance but typically shows faster aging and brittleness under intense UV radiation compared to carboxylated nitrile formulations.
Performance in Temperature Extremes
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and maintains elasticity at low temperatures down to -40degC, making it effective for weather seals exposed to harsh conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in withstanding high temperatures up to 150degC and resists ozone, UV radiation, and weathering without losing flexibility. EPDM is often preferred in applications requiring long-term durability in extreme heat, while XNBR is advantageous for seals exposed to cold environments and hydrocarbon exposure.
Resistance to Ozone and Oxidation
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior resistance to ozone and oxidation compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making it ideal for weather seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. XNBR's polar groups enhance its durability against ozone-induced cracking and oxidative degradation, extending the service life of seals in automotive and industrial applications. EPDM exhibits good ozone resistance but falls short against oxidative stress in oil-contaminated or high-temperature environments where XNBR excels.
Mechanical Properties and Longevity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making it highly effective for weather seal applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. EPDM excels in flexibility and aging resistance, providing excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, which enhances seal longevity in outdoor environments. Choosing between XNBR and EPDM depends on the specific mechanical load conditions and environmental exposure, with XNBR preferred for heavy-duty mechanical demands and EPDM favored for extended weather and UV resistance.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and durability, making it a cost-effective choice for weather seals in industrial applications where chemical exposure is prevalent, despite its higher initial price compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM). EPDM is widely available and provides excellent resistance to ozone, UV rays, and weathering, often resulting in lower overall costs due to its accessibility and ease of processing. For cost-effectiveness and availability, EPDM generally outperforms XNBR in standard weather seal applications, especially where chemical resistance is less critical.
Summary: Choosing the Right Rubber for Weather Seals
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, tensile strength, and durability, making it ideal for weather seals exposed to harsh chemicals and mechanical stress. Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM) excels in UV, ozone, and extreme weather resistance, providing excellent flexibility and longevity in outdoor weather seal applications. Selecting between XNBR and EPDM depends on the specific environmental exposure and performance needs, with EPDM favored for outdoor UV stability and XNBR preferred for chemical and abrasion resistance.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com