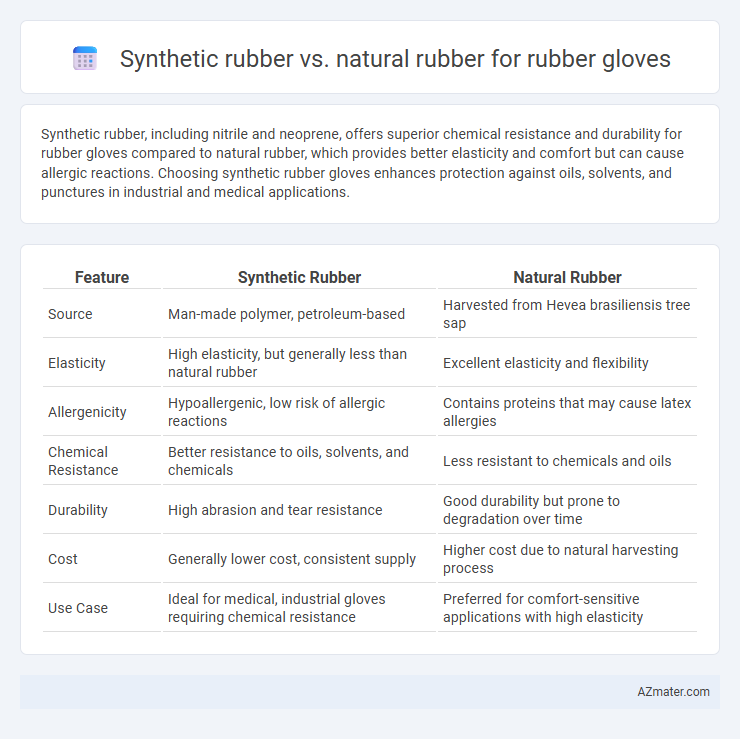
Synthetic rubber, including nitrile and neoprene, offers superior chemical resistance and durability for rubber gloves compared to natural rubber, which provides better elasticity and comfort but can cause allergic reactions. Choosing synthetic rubber gloves enhances protection against oils, solvents, and punctures in industrial and medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymer, petroleum-based | Harvested from Hevea brasiliensis tree sap |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, but generally less than natural rubber | Excellent elasticity and flexibility |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic, low risk of allergic reactions | Contains proteins that may cause latex allergies |
| Chemical Resistance | Better resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Less resistant to chemicals and oils |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good durability but prone to degradation over time |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, consistent supply | Higher cost due to natural harvesting process |
| Use Case | Ideal for medical, industrial gloves requiring chemical resistance | Preferred for comfort-sensitive applications with high elasticity |
Introduction to Rubber Glove Materials
Rubber gloves are primarily manufactured using two types of materials: natural rubber and synthetic rubber, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific applications. Natural rubber gloves provide superior elasticity, tactile sensitivity, and biodegradability, making them ideal for medical and dental uses where dexterity is critical. Synthetic rubber gloves, such as nitrile and neoprene, deliver enhanced chemical resistance, hypoallergenic qualities, and durability, which are essential for industrial and laboratory environments.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber, primarily composed of polymers like styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber when used in rubber gloves. It provides superior protection against oils, solvents, and punctures, making it ideal for medical, industrial, and laboratory applications where exposure to harsh substances is common. While natural rubber delivers excellent elasticity and comfort, synthetic rubber's resistance to allergens and environmental degradation makes it a preferred material in manufacturing gloves for sensitive users and specialized tasks.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and barrier protection, making it a preferred material for medical and industrial rubber gloves. Its superior biodegradability and natural resistance to certain chemicals enhance its sustainability profile compared to synthetic alternatives. However, natural rubber gloves may trigger allergies in some users due to proteins present in the latex.
Source and Production Processes
Synthetic rubber for rubber gloves is primarily derived from petrochemical sources through polymerization of monomers such as styrene and butadiene, allowing controlled customization of properties. Natural rubber originates from the latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis rubber trees, harvested via tapping and processed through coagulation and vulcanization. Production of synthetic rubber involves complex chemical synthesis in industrial plants, whereas natural rubber relies on agricultural cultivation and traditional extraction methods.
Physical Properties Comparison
Synthetic rubber gloves exhibit superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion compared to natural rubber gloves, making them more durable in industrial and medical environments. Natural rubber gloves provide excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and barrier protection against biological hazards but are prone to degradation from oils and UV exposure. The choice between synthetic and natural rubber gloves depends on specific physical property requirements such as flexibility, durability, and allergenic risk.
Allergenicity and Skin Reactions
Synthetic rubber gloves, often made from nitrile or neoprene, exhibit significantly lower allergenicity compared to natural rubber latex gloves, reducing the risk of Type I allergic reactions such as contact urticaria or anaphylaxis. Natural rubber latex contains proteins that can trigger immune responses in sensitive individuals, leading to dermatitis and respiratory symptoms. Choosing synthetic rubber gloves effectively minimizes adverse skin reactions while maintaining durability and tactile sensitivity essential for medical and industrial use.
Durability and Resistance to Chemicals
Synthetic rubber gloves, such as those made from nitrile, offer superior durability and enhanced resistance to a wider range of chemicals compared to natural rubber gloves. Natural rubber gloves, while flexible and comfortable, are more prone to degradation when exposed to oils, solvents, and certain acids. The chemical resistance properties of synthetic rubber make it a preferred choice in medical and industrial environments where exposure to harsh substances is common.
Environmental Impact
Synthetic rubber for rubber gloves is primarily derived from petrochemicals, resulting in higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradability compared to natural rubber, which is biodegradable and sourced from renewable rubber tree latex. The cultivation of natural rubber supports carbon sequestration through rubber tree plantations and minimizes landfill waste due to its compostable properties. However, synthetic rubber production can lead to soil and water pollution from chemical processing, whereas natural rubber's environmental footprint is influenced by sustainable farming practices and land use.
Cost and Market Availability
Synthetic rubber used in rubber gloves offers lower production costs due to its dependence on petrochemical resources, making it more cost-effective and widely accessible in global markets. Natural rubber, derived from rubber trees, tends to have higher costs influenced by agricultural variables and limited plantation regions, impacting consistent market availability. The synthetic variety dominates in large-scale manufacturing, while natural rubber gloves cater to premium segments prioritizing biodegradability and elasticity.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Gloves
Synthetic rubber, including nitrile and neoprene, offers superior chemical resistance, puncture durability, and allergen-free properties, making it ideal for medical and industrial gloves. Natural rubber latex provides exceptional elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity but may cause allergic reactions in some users due to its protein content. Selecting the right rubber involves balancing factors like protection level, flexibility, allergy risk, and specific application requirements to ensure optimal glove performance and user safety.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Rubber glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com