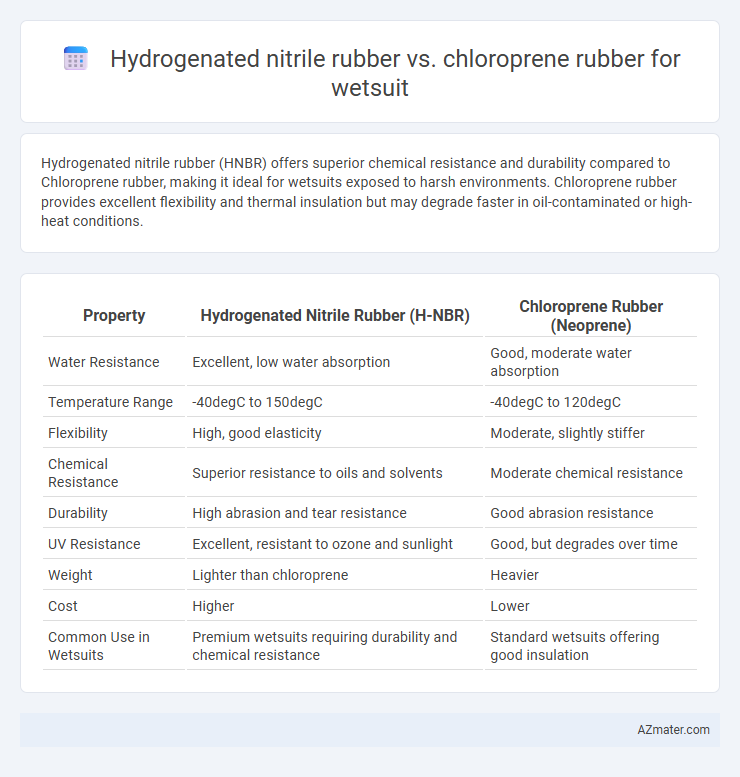
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to Chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for wetsuits exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent flexibility and thermal insulation but may degrade faster in oil-contaminated or high-heat conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (H-NBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Excellent, low water absorption | Good, moderate water absorption |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Flexibility | High, good elasticity | Moderate, slightly stiffer |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| UV Resistance | Excellent, resistant to ozone and sunlight | Good, but degrades over time |
| Weight | Lighter than chloroprene | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Use in Wetsuits | Premium wetsuits requiring durability and chemical resistance | Standard wetsuits offering good insulation |
Introduction to Wetsuit Material Technologies
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, durability, and thermal stability compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it an innovative choice for wetsuit material technologies focused on enhanced performance in harsh marine environments. Chloroprene rubber, traditionally used in wetsuits, provides excellent flexibility, water resistance, and insulation but can degrade faster under UV exposure and ozone. Advances in wetsuit material technologies increasingly favor HNBR for extended lifespan and improved protection, balancing elasticity and strength for divers and watersport enthusiasts.
What is Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)?
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its superior chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance compared to traditional nitrile rubber, making it an excellent choice for wetsuit applications requiring durability and flexibility. Its hydrogenation process enhances resistance to oxidation and ozone, ensuring longer lifespan in harsh marine environments. In contrast to Chloroprene rubber, HNBR offers improved oil resistance and mechanical properties, which can enhance wetsuit performance and longevity.
Understanding Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene)
Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as Neoprene, is widely preferred in wetsuit manufacturing due to its excellent flexibility, thermal insulation, and resistance to water, oils, and chemicals. Unlike hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), Neoprene maintains elasticity and durability across a broad temperature range, providing superior comfort and protection in aquatic environments. Its closed-cell foam structure traps air, enhancing buoyancy and insulation, which are critical properties for wetsuit performance.
Key Physical Properties: HNBR vs Chloroprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, higher tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it more durable for wetsuit applications. Chloroprene rubber provides better flexibility and elasticity at lower temperatures, ensuring enhanced comfort and fit during prolonged water exposure. While HNBR maintains structural integrity in extreme conditions, chloroprene is preferred for its balanced thermal insulation and buoyancy.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior thermal insulation for wetsuits due to its enhanced resistance to heat and cold, maintaining flexibility and durability in low temperatures better than chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, provides good thermal insulation but tends to degrade faster in extreme temperature conditions and loses elasticity more quickly compared to HNBR. The molecular structure of HNBR allows for improved resistance to thermal aging and chemical exposure, resulting in longer-lasting thermal protection in wetsuit applications.
Resistance to Chemicals and Ozone
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to chemicals such as oils, fuels, and solvents, making it highly durable for wetsuits exposed to harsh marine environments. Chloroprene rubber (neoprene) provides excellent ozone and weather resistance, maintaining flexibility and protection over prolonged sun and saltwater exposure. While HNBR excels in chemical and abrasion resistance, chloroprene is preferred for wetsuits requiring outstanding ozone durability and thermal insulation.
Flexibility and Comfort in Water Sports
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it highly durable yet slightly stiffer compared to chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, provides exceptional elasticity and softness, ensuring maximum comfort and ease of movement in wetsuits for water sports such as surfing, diving, and snorkeling. The enhanced flexibility of chloroprene greatly improves fit and thermal insulation, making it the preferred choice for wetsuit applications where comfort and freedom of motion are critical.
Durability and Longevity of Wetsuit Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and resistance to heat, oils, and abrasion compared to chloroprene rubber, making it highly suitable for wetsuit applications requiring prolonged use. Chloroprene rubber, widely known as neoprene, provides excellent flexibility and water resistance but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and chemical contact. For wetsuit longevity, HNBR's enhanced molecular stability ensures extended wear life and structural integrity in harsh marine environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to oils and chemicals with a longer lifespan, potentially reducing waste compared to chloroprene rubber (CR) commonly used in wetsuits. Chloroprene rubber production involves significant energy consumption and releases hazardous byproducts, whereas HNBR manufacturing has a lower environmental impact due to fewer toxic emissions. Sustainable wetsuit options increasingly favor HNBR for its durability and reduced ecological footprint, aligning with growing industry demands for eco-friendly materials.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Wetsuits
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it highly durable and ideal for long-term wetsuit use in harsh conditions. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) provides excellent flexibility, insulation, and buoyancy, which are critical for comfort and thermal protection in most wetsuit applications. Selecting between HNBR and chloroprene depends on the specific requirements of durability versus flexibility and thermal performance, with chloroprene remaining the industry standard for general wetsuit manufacturing.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Wetsuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com