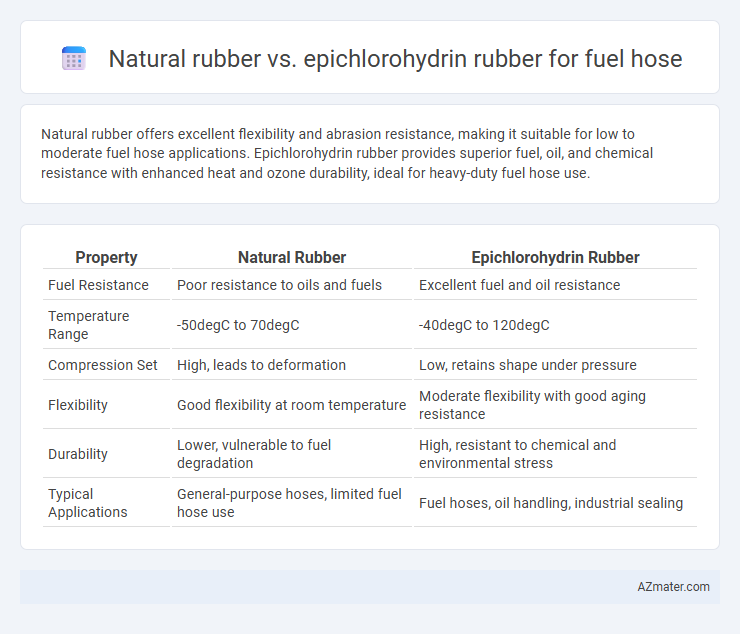
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for low to moderate fuel hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides superior fuel, oil, and chemical resistance with enhanced heat and ozone durability, ideal for heavy-duty fuel hose use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber | Epichlorohydrin Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Poor resistance to oils and fuels | Excellent fuel and oil resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Compression Set | High, leads to deformation | Low, retains shape under pressure |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at room temperature | Moderate flexibility with good aging resistance |
| Durability | Lower, vulnerable to fuel degradation | High, resistant to chemical and environmental stress |
| Typical Applications | General-purpose hoses, limited fuel hose use | Fuel hoses, oil handling, industrial sealing |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance for fuel hoses but has limited chemical resistance to fuels and oils. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior fuel and oil resistance, temperature stability, and ozone resistance, making it a preferred choice for fuel hose applications in automotive and industrial settings. Selection between these materials depends on specific fuel type compatibility, operating temperature ranges, and durability requirements.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, making it widely used in fuel hose applications. Its superior flexibility under a broad temperature range ensures reliable sealing and durability in dynamic conditions. However, natural rubber may have limited resistance to petroleum-based fuels compared to specialized synthetic rubbers like epichlorohydrin rubber.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring enhanced durability and longevity. ECO exhibits excellent ozone and weathering resistance, alongside strong low-temperature flexibility, maintaining optimal performance in harsh environments where natural rubber tends to degrade faster. Its chemical structure, featuring epichlorohydrin units, provides enhanced compatibility with petroleum-based fluids and improved elasticity under mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance in Fuel Hose Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance in fuel hose applications, maintaining integrity against gasoline, diesel, and various hydrocarbons due to its unique molecular structure. Natural rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to degrade faster when exposed to fuels and oils, resulting in swelling and loss of mechanical properties. Therefore, epichlorohydrin rubber is preferred for fuel hoses requiring enhanced resistance to chemical exposure and longer service life in aggressive fuel environments.
Temperature Performance Comparisons
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to natural rubber, maintaining elasticity and structural integrity in a broader temperature range of approximately -40degC to 125degC, ideal for fuel hose applications exposed to varying conditions. Natural rubber typically operates effectively within a narrower range of -50degC to 70degC but shows degradation at higher temperatures, leading to swelling and reduced tensile strength. The enhanced thermal stability of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures long-lasting performance and resistance to fuel-related chemical interactions under fluctuating temperatures.
Flexibility and Mechanical Properties
Natural rubber exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for fuel hoses requiring high resilience and resistance to dynamic bending. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers enhanced chemical resistance, oil resistance, and excellent mechanical properties such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance, suitable for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environments. The choice between the two depends on the specific application demands, balancing flexibility with mechanical durability and chemical exposure.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but is less resistant to petroleum-based fuels, leading to faster degradation in fuel hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against fuels and oils, resulting in enhanced durability and extended service life for fuel hoses. The longevity of fuel hoses made from epichlorohydrin rubber significantly surpasses that of natural rubber under exposure to aggressive fuel environments.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Natural rubber offers lower cost and wider availability for fuel hose applications due to its abundant natural sources and established supply chains. Epichlorohydrin rubber, though more expensive because of synthetic production processes and limited raw material availability, provides superior fuel resistance and durability. Cost analysis reveals natural rubber is economically favorable for general use, while epichlorohydrin rubber justifies higher investment in specialized fuel hose applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Natural rubber, derived from renewable latex sources, offers biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to synthetic epichlorohydrin rubber, which is petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals but releases hazardous substances during production and disposal, raising safety concerns. Fuel hoses made from natural rubber prioritize environmental sustainability, whereas epichlorohydrin rubber emphasizes chemical stability and safety against fuel permeation.
Final Recommendations: Choosing the Right Rubber for Fuel Hoses
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to fuel, oil, and ozone, making it the preferred choice for fuel hoses operating in harsh chemical environments. Natural rubber, while providing excellent flexibility and tensile strength, is less resistant to hydrocarbons and may degrade faster when exposed to fuel. For fuel hose applications demanding long-term durability and chemical resistance, epichlorohydrin rubber is the recommended material to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com