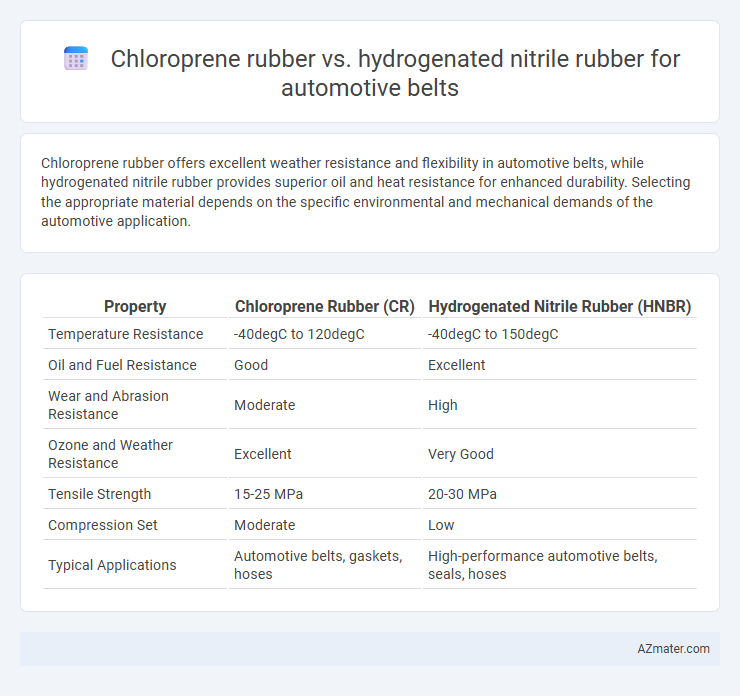
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent weather resistance and flexibility in automotive belts, while hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides superior oil and heat resistance for enhanced durability. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the specific environmental and mechanical demands of the automotive application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Wear and Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Tensile Strength | 15-25 MPa | 20-30 MPa |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low |
| Typical Applications | Automotive belts, gaskets, hoses | High-performance automotive belts, seals, hoses |
Introduction to Automotive Belt Materials
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) are prominent materials used in automotive belts due to their superior mechanical strength and heat resistance. CR offers excellent ozone and weather resistance, making it suitable for exposure to harsh environmental conditions in engine compartments. HNBR provides enhanced thermal stability and oil resistance, improving belt durability and performance in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers exceptional oil and weather resistance, making it a reliable choice for automotive belts exposed to harsh environments. Its inherent flame resistance and excellent tensile strength contribute to enhanced durability and safety in engine applications. CR's balanced flexibility and resistance to ozone and aging ensure prolonged performance under continuous mechanical stress.
Properties of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to Chloroprene Rubber, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh environments. HNBR demonstrates excellent tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, and enhanced durability under continuous mechanical stress. Its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and high temperatures ensures longer service life and consistent performance in automotive applications.
Thermal Resistance: CR vs HNBR
Chloroprene rubber (CR) typically offers thermal resistance up to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate heat exposure in automotive belts. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) significantly outperforms CR with thermal resistance ranging from 150degC to 160degC, enabling superior durability under high-temperature engine conditions. This enhanced thermal stability of HNBR contributes to longer service life and improved performance in demanding automotive belt applications.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oil exposure, making it suitable for automotive belts exposed to outdoor environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical and oil resistance, particularly against hydrocarbons, fuels, and lubricants, ensuring enhanced durability in harsh engine conditions. HNBR's improved thermal stability and resistance to swelling make it the preferred choice for automotive belts requiring long-term exposure to aggressive oils and chemicals.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent mechanical strength with high tensile and tear resistance, making it suitable for automotive belts exposed to dynamic stresses. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior durability due to its enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure, ensuring longer service life in harsh engine environments. When selecting materials for automotive belts, CR excels in mechanical robustness while HNBR outperforms in maintaining performance under thermal and chemical degradation.
Flexibility and Fatigue Performance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent flexibility and moderate fatigue resistance, making it suitable for automotive belts exposed to dynamic stress and bending. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior fatigue performance and higher resistance to heat, oil, and ozone, which enhances belt durability under aggressive engine conditions. For automotive belts requiring a balance of elasticity and long-term fatigue resistance, HNBR is often preferred due to its enhanced mechanical properties and chemical stability.
Cost Efficiency for Automotive Belts
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior ozone resistance and mechanical durability, making it a cost-efficient choice for automotive belts requiring long service life and exposure to harsh environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides excellent heat and chemical resistance but generally comes at a higher price point, which can increase overall manufacturing costs for automotive belts. For applications where budget constraints dominate and moderate performance is acceptable, chloroprene rubber presents a more cost-effective solution without significantly compromising durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits moderate resistance to ozone and weathering but relies on chlorine-based chemistry, which raises concerns about environmental toxicity and challenges in recycling. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and chemical resistance with lower environmental impact due to its chlorine-free formulation and better recyclability. The sustainability profile of HNBR is enhanced by reduced emissions during production and longer service life, making it a more eco-friendly choice for automotive belt applications.
Application Suitability: Choosing Between CR and HNBR
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oil exposure, making it suitable for automotive belts operating in diverse external environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, chemical, and oil resistance, ideal for belts subjected to higher temperatures and aggressive fluids in engine compartments. Selecting between CR and HNBR depends on the specific operating conditions, with HNBR preferred for demanding thermal and chemical applications while CR suits environments requiring robust ozone and weather resistance.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com