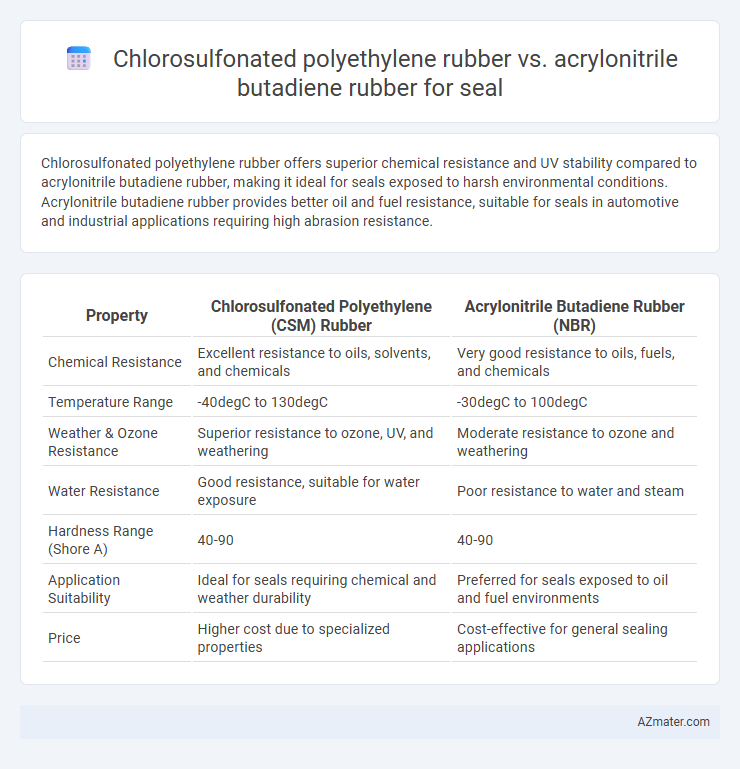
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber provides better oil and fuel resistance, suitable for seals in automotive and industrial applications requiring high abrasion resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Very good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 130degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Superior resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Moderate resistance to ozone and weathering |
| Water Resistance | Good resistance, suitable for water exposure | Poor resistance to water and steam |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40-90 | 40-90 |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for seals requiring chemical and weather durability | Preferred for seals exposed to oil and fuel environments |
| Price | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Cost-effective for general sealing applications |
Introduction to Seal Materials: CSM vs NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance, ozone stability, and weatherability compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh outdoor environments and aggressive chemicals. NBR excels in oil and fuel resistance, maintaining durability and flexibility in applications involving petroleum-based fluids, which positions it as a preferred choice in automotive and industrial seals. Both materials provide excellent sealing performance, but CSM is favored for high-resistance environmental sealing, while NBR is optimized for oil-resistant sealing solutions.
Chemical Structure Comparison of CSM and NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber features a saturated polyethylene backbone with chlorosulfonyl functional groups, imparting superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) consists of butadiene and acrylonitrile units, offering excellent oil and fuel resistance due to the polar nitrile groups within its unsaturated backbone. The chemical structure of CSM enables enhanced durability in harsh environmental conditions, while NBR's polarity provides better performance in hydrocarbon exposure applications.
Key Physical Properties for Seal Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals with a tensile strength typically ranging from 10 to 20 MPa and elongation at break around 250-500%, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance with tensile strength between 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break about 300-600%, providing superior sealing performance in automotive and industrial applications involving hydrocarbons. The choice between CSM and NBR seals depends on the specific operational environment, where CSM's enhanced weather and chemical resistance contrasts with NBR's better oil resistance and mechanical properties.
Chemical Resistance: CSM Rubber vs NBR Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including ozone, ultraviolet light, acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents, making it ideal for harsh chemical sealing applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels but has limited performance against ozone, weathering, and certain solvents. For seals exposed to aggressive chemicals and outdoor conditions, CSM rubber offers enhanced durability and longer service life compared to NBR rubber.
Temperature Range Suitability for Sealing Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits excellent temperature resistance typically ranging from -40degC to 150degC, making it suitable for sealing applications exposed to moderate heat and harsh chemical environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) performs well in a temperature range of -40degC to 120degC, excelling in oil and fuel resistance but with a slightly lower thermal stability compared to CSM. For sealing applications requiring higher temperature endurance and chemical resistance, CSM rubber is generally preferred over NBR rubber.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance in CSM and NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for seals exposed to outdoor environments. CSM's unique molecular structure resists degradation caused by ozone, UV radiation, and harsh weather conditions, maintaining elasticity and durability over extended periods. In contrast, NBR shows moderate ozone resistance and tends to crack or harden under prolonged exposure to environmental stressors, limiting its application in demanding outdoor sealing solutions.
Oil and Fuel Resistance: Critical Differences
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior oil and fuel resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), largely due to its enhanced chemical stability and resistance to swelling in hydrocarbon environments. CSM maintains flexibility and mechanical integrity in prolonged exposure to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for demanding sealing applications in automotive and industrial sectors. NBR, while effective against aliphatic hydrocarbons, typically shows reduced performance against aromatic fuels and aggressive oils, limiting its use in high-temperature or chemically aggressive sealing conditions.
Compression Set and Aging Characteristics
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior compression set resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), maintaining elasticity under prolonged pressure which ensures long-lasting seals. CSM shows excellent aging characteristics, resisting ozone, UV, heat, and chemical exposure better than NBR, making it suitable for harsh environments. NBR offers good oil and fuel resistance but typically suffers from higher compression set and faster degradation under oxidative aging.
Cost and Availability for Industrial Seals
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability, but it typically incurs higher costs and limited availability compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). NBR is more widely available in industrial markets and is generally more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for sealing applications requiring moderate resistance to oils and fuels. For industrial seals where budget constraints and ease of procurement are critical, NBR provides a more economical and readily accessible solution.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Seal Application
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior chemical resistance, weatherability, and ozone resistance compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for outdoor and harsh chemical environments. NBR excels in oil, fuel, and hydrocarbon resistance, making it better suited for applications involving petroleum-based fluids and high abrasion. Selecting the right rubber for your seal depends on the operating temperature range, chemical exposure, and physical demands of the application to ensure durability and optimal performance.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com