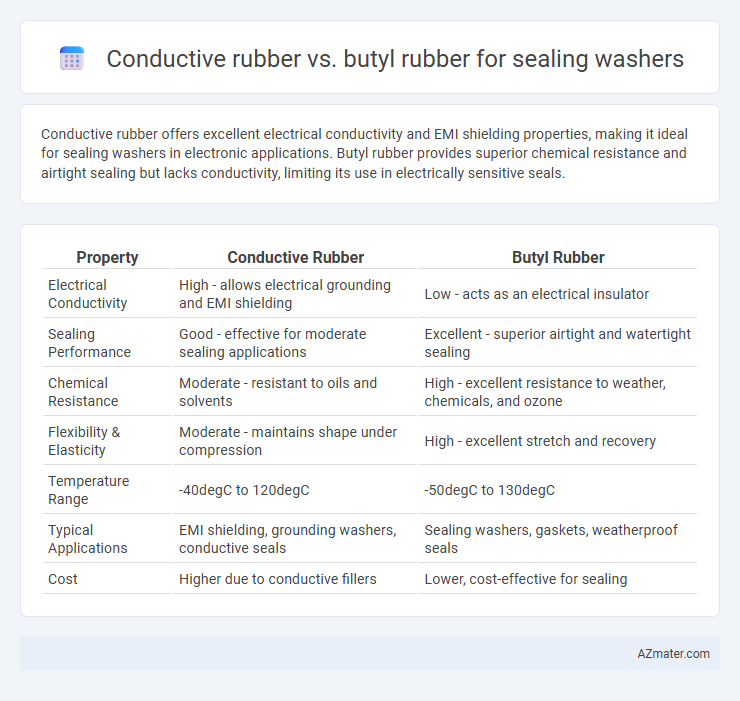
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and EMI shielding properties, making it ideal for sealing washers in electronic applications. Butyl rubber provides superior chemical resistance and airtight sealing but lacks conductivity, limiting its use in electrically sensitive seals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High - allows electrical grounding and EMI shielding | Low - acts as an electrical insulator |
| Sealing Performance | Good - effective for moderate sealing applications | Excellent - superior airtight and watertight sealing |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate - resistant to oils and solvents | High - excellent resistance to weather, chemicals, and ozone |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | Moderate - maintains shape under compression | High - excellent stretch and recovery |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 130degC |
| Typical Applications | EMI shielding, grounding washers, conductive seals | Sealing washers, gaskets, weatherproof seals |
| Cost | Higher due to conductive fillers | Lower, cost-effective for sealing |
Overview of Conductive Rubber and Butyl Rubber
Conductive rubber combines elastomeric properties with electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and grounding in sealing washers. Butyl rubber exhibits excellent chemical resistance, low permeability, and superior flexibility, which enhances sealing performance under diverse environmental conditions. Comparing these materials, conductive rubber is preferred for electronic sealing needs, while butyl rubber excels in general-purpose sealing where durability and impermeability are critical.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Conductive rubber typically consists of silicone or EPDM infused with conductive fillers such as carbon or metal particles, offering excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. Butyl rubber, a copolymer of isobutylene and isoprene, provides superior impermeability to gases, chemical resistance, and excellent flexibility under low temperatures, making it ideal for sealing applications in harsh chemical environments. The choice between conductive and butyl rubber for sealing washers depends on the need for electrical conductivity versus enhanced chemical and gas barrier properties.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Conductive rubber sealing washers contain conductive fillers such as carbon black or metal particles, providing electrical conductivity essential for grounding and EMI shielding applications. Butyl rubber, commonly used for sealing washers, lacks inherent electrical conductivity due to its polymer structure and is primarily valued for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. When electrical conductivity is critical for sealing applications, conductive rubber significantly outperforms butyl rubber by enabling current flow and reducing electromagnetic interference.
Performance in Sealing Applications
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity and excellent EMI shielding, making it ideal for sealing washers in electronic enclosures where signal integrity is critical. Butyl rubber excels in chemical resistance, low permeability to gases, and durability under extreme temperatures, providing reliable seals in automotive and industrial applications. While conductive rubber enhances electrical performance, butyl rubber ensures long-term sealing effectiveness against moisture and environmental factors.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Conductive rubber sealing washers exhibit excellent resistance to temperature fluctuations and electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for electronic and automotive applications. Butyl rubber offers superior resistance to moisture, ozone, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-term sealing performance in harsh outdoor and industrial environments. When selecting a sealing washer, the choice between conductive rubber and butyl rubber depends on the specific environmental stressors, such as electromagnetic exposure versus chemical and moisture durability.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Conductive rubber sealing washers generally cost more than butyl rubber due to their specialized conductive fillers and limited manufacturing sources. Butyl rubber is widely available and budget-friendly, benefiting from large-scale production and common use in sealing applications. Availability of conductive rubber can be restricted to niche suppliers, while butyl rubber products are easily sourced globally, impacting lead times and overall project costs.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Conductive rubber sealing washers offer enhanced electrical conductivity while maintaining moderate wear resistance but generally exhibit lower longevity under continuous mechanical stress compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber excels in wear resistance and provides superior longevity due to its excellent elasticity, chemical inertness, and resistance to ozone and weathering, making it ideal for long-term sealing applications. When prioritizing sealing washer durability, butyl rubber is often preferred for environments demanding extended service life and consistent sealing performance.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Conductive rubber sealing washers offer superior ease of installation due to their flexibility and ability to conform tightly to uneven surfaces, reducing the need for precise alignment. Butyl rubber washers provide excellent maintenance benefits, as their chemical resistance and durability resist degradation from environmental exposure, minimizing the frequency of replacements. The conductive properties of conductive rubber also ensure reliable electrical grounding, which is crucial in applications requiring electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding while maintaining ease of removal for inspection.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Conductive rubber sealing washers excel in electronic and telecommunications industries where electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and static dissipation are critical for device performance and protection. Butyl rubber sealing washers are preferred in automotive, HVAC, and plumbing sectors due to their superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ensuring durable, airtight seals in harsh environments. Industry-specific applications rely on conductive rubber for electrical conductivity and signal integrity, while butyl rubber prioritizes chemical inertness and flexibility under thermal stress.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Sealing Washers
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and is ideal for sealing washers in electronic applications requiring grounding or electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Butyl rubber excels in chemical resistance, air impermeability, and durability, making it suitable for sealing washers in automotive, plumbing, and industrial environments exposed to moisture and harsh chemicals. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific sealing requirements: use conductive rubber when electrical performance is critical, and choose butyl rubber for superior sealing against air, water, and chemical infiltration.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Butyl rubber for Sealing washer
 azmater.com
azmater.com