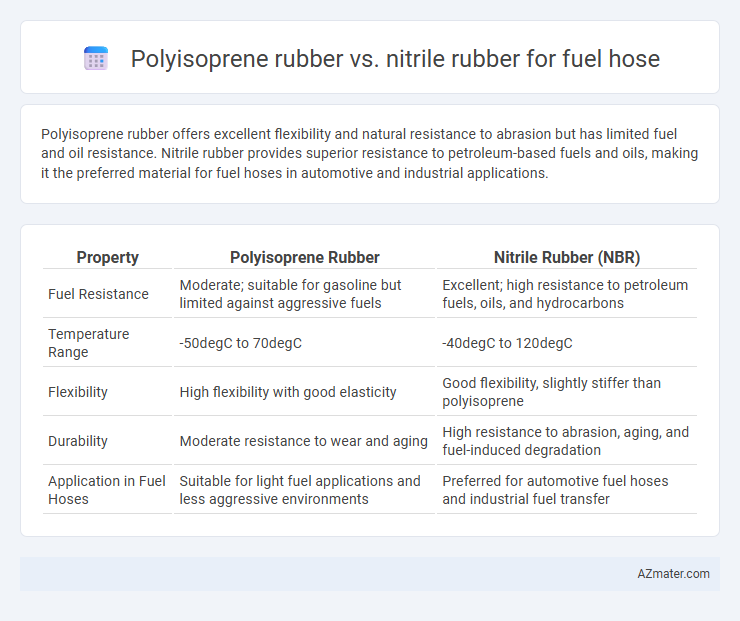
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and natural resistance to abrasion but has limited fuel and oil resistance. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and oils, making it the preferred material for fuel hoses in automotive and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Moderate; suitable for gasoline but limited against aggressive fuels | Excellent; high resistance to petroleum fuels, oils, and hydrocarbons |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with good elasticity | Good flexibility, slightly stiffer than polyisoprene |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to wear and aging | High resistance to abrasion, aging, and fuel-induced degradation |
| Application in Fuel Hoses | Suitable for light fuel applications and less aggressive environments | Preferred for automotive fuel hoses and industrial fuel transfer |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Fuel hoses require materials with excellent resistance to fuels and oils, making polyisoprene rubber and nitrile rubber common choices. Polyisoprene rubber offers good flexibility and abrasion resistance but has limited fuel resistance compared to nitrile rubber, which provides superior chemical stability and resistance to petroleum-based fuels. Nitrile rubber's enhanced durability under exposure to hydrocarbons makes it the preferred material for fuel hose applications in automotive and industrial sectors.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, a synthetic alternative to natural rubber, offers excellent flexibility and high tensile strength, making it suitable for fuel hose applications requiring durability and resistance to wear. Its outstanding elasticity and low compression set provide superior sealing capabilities, essential for handling fuel under varying pressure conditions. While polyisoprene is less resistant to oils and fuels than nitrile rubber, its enhanced heat resistance and environmental friendliness make it a preferred choice in specific fuel hose designs.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber, also known as NBR or Buna-N, is a synthetic polymer highly resistant to petroleum-based fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hose applications that require durability and chemical stability. It exhibits excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and temperature tolerance ranging from -40degC to 120degC, ensuring reliable performance in demanding automotive and industrial environments. Compared to polyisoprene rubber, nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to swelling and degradation when exposed to hydrocarbons, providing enhanced longevity and safety in fuel transfer systems.
Chemical Compatibility with Fuels
Polyisoprene rubber offers moderate chemical resistance to hydrocarbons but degrades faster when exposed to gasoline and diesel, limiting its use in fuel hoses. Nitrile rubber exhibits superior chemical compatibility with a wide range of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and ethanol blends, due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons. This makes nitrile rubber the preferred choice for fuel hose applications requiring durability and long-term performance in aggressive fuel environments.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber offers temperature resistance typically ranging from -50degC to 70degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature fuel hose applications. Nitrile rubber, known for its superior heat resistance, can withstand temperatures from -40degC up to 120degC, ensuring better durability in fuel hoses exposed to hot environments. The higher thermal stability of nitrile rubber makes it the preferred choice for fuel hoses where heat resistance is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and tensile strength, making it suitable for fuel hoses requiring high elasticity and resistance to mechanical stress. Nitrile rubber, known for superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability, provides enhanced mechanical strength under exposure to fuels and oils, ensuring durability in rigorous environments. While polyisoprene excels in flexibility, nitrile rubber outperforms in resistance to fuel degradation and mechanical wear, crucial for long-term fuel hose applications.
Durability and Aging Performance
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and low-temperature performance but has inferior resistance to fuels and oils compared to nitrile rubber, limiting its durability in fuel hose applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides outstanding resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and aging due to its strong carbon-carbon backbone and acrylonitrile content, making it highly durable and reliable for long-term fuel hose use. In terms of aging performance, nitrile rubber outperforms polyisoprene with superior resistance to ozone, oxidation, and thermal degradation, ensuring extended service life in harsh fuel environments.
Cost Differences and Availability
Polyisoprene rubber offers moderate cost advantages but is less commonly used in fuel hoses compared to nitrile rubber, which is widely available due to its superior fuel resistance and durability. Nitrile rubber's consistent supply and mass production contribute to lower overall costs and better availability in automotive and industrial markets. The cost difference can vary depending on regional demand, with nitrile rubber typically favored for fuel hoses due to its optimized performance and accessible sourcing.
Typical Applications in Automotive and Industry
Polyisoprene rubber is commonly used in automotive fuel hoses due to its excellent flexibility, low gas permeability, and resistance to heat and aging, making it ideal for delivering gasoline and diesel fuels. Nitrile rubber (NBR), known for its superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, is widely employed in industrial fuel hose applications where exposure to aggressive fluids and high-pressure environments is common. Both materials serve critical roles in their respective sectors, with polyisoprene preferred for flexibility and environmental resistance, while nitrile rubber excels in chemical durability and mechanical strength.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Fuel Hoses
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for less aggressive fuel applications but lacks strong chemical resistance. Nitrile rubber provides superior fuel resistance, durability, and compatibility with petroleum-based fuels, ensuring longer hose life under harsh conditions. Selecting nitrile rubber for fuel hoses is optimal when exposure to fuels and oils is frequent, while polyisoprene may be considered for environments where flexibility and low cost are prioritized.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com