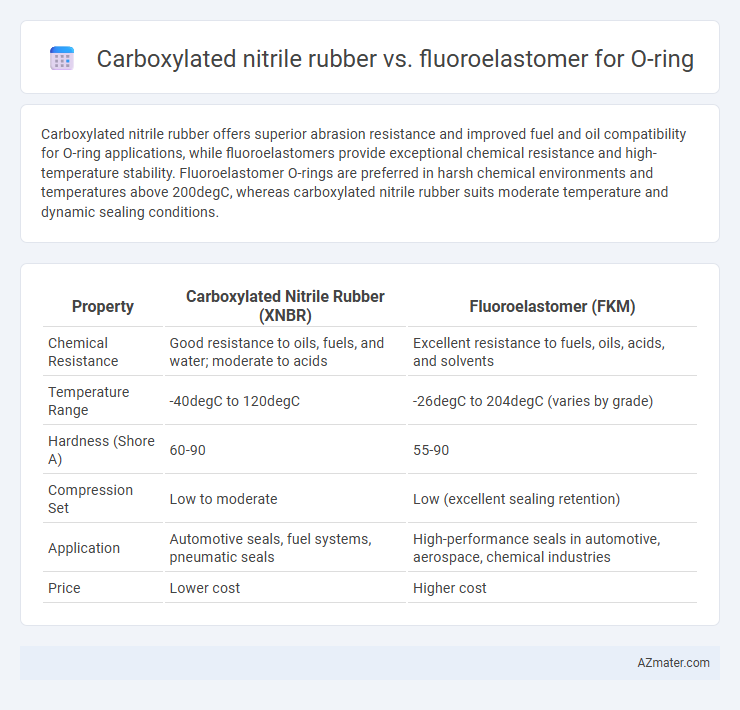
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and improved fuel and oil compatibility for O-ring applications, while fluoroelastomers provide exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability. Fluoroelastomer O-rings are preferred in harsh chemical environments and temperatures above 200degC, whereas carboxylated nitrile rubber suits moderate temperature and dynamic sealing conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and water; moderate to acids | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, acids, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -26degC to 204degC (varies by grade) |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60-90 | 55-90 |
| Compression Set | Low to moderate | Low (excellent sealing retention) |
| Application | Automotive seals, fuel systems, pneumatic seals | High-performance seals in automotive, aerospace, chemical industries |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to O-Ring Material Selection
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) provides excellent mechanical strength and superior resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for applications involving oils, fuels, and chemicals at moderate temperatures up to 120degC. Fluoroelastomers (FKM) excel in high-temperature environments exceeding 200degC and offer exceptional chemical resistance, especially to aggressive fuels, acids, and solvents. Selecting O-ring materials requires balancing factors such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and mechanical demands to optimize sealing performance and longevity.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and enhanced oil and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications. The carboxyl groups in XNBR improve cross-link density, which enhances mechanical properties and heat resistance up to approximately 120degC. XNBR O-rings provide excellent sealing performance in automotive, industrial, and hydraulic systems where durability and resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals are critical.
Overview of Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings offer exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for demanding applications in automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Their molecular structure provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, solvents, and aggressive chemicals compared to Carboxylated nitrile rubber, ensuring longer service life in harsh environments. FKM materials typically perform reliably in temperatures ranging from -26degC to 204degC, outperforming many other elastomer types in thermal and chemical durability.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent resistance to aliphatic oils, fuels, and some hydraulic fluids, while fluoroelastomers (FKM) provide superior chemical resistance against a broader range of aggressive chemicals including aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and strong acids. Fluoroelastomers maintain integrity and performance in high-temperature and harsh chemical environments, making them ideal for applications involving aggressive solvents and glycol-based fluids where XNBR may deteriorate. The selection between XNBR and FKM for O-rings depends on the specific chemical exposure, with FKM generally preferred for demanding environments requiring enhanced chemical durability.
Temperature Tolerance Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) O-rings typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making them suitable for moderate thermal environments. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings offer superior temperature resistance, operating reliably between -26degC and 204degC, which is essential for high-temperature applications like automotive and aerospace seals. The enhanced thermal stability of fluoroelastomers results from their fluorine content, providing excellent heat, oil, and chemical resistance compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) O-rings offer superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to standard nitrile, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings excel in chemical resistance and maintain excellent mechanical properties under high temperatures, with superior wear resistance in harsh environments. In terms of wear resistance, FKM outperforms XNBR in exposure to oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals, while XNBR provides better performance in dynamic sealing under mechanical stress.
Compatibility with Fluids and Chemicals
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and water-based fluids, making it suitable for hydraulic and automotive applications exposed to mineral oils and water glycol solutions. Fluoroelastomers (FKM) demonstrate superior chemical compatibility with aggressive fluids such as fuels, oils, acids, and solvents, including resistance to high-temperature aromatic hydrocarbons and ketones. For applications requiring exposure to harsh chemicals and elevated temperatures, fluoroelastomer O-rings provide longer service life compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Cost Considerations for XNBR vs FKM
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers a cost-effective solution for O-rings due to its lower raw material and production expenses compared to fluoroelastomer (FKM), making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. FKM delivers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature performance but at a significantly higher price point, often limiting its use to demanding environments. Selecting XNBR over FKM can reduce overall costs by up to 40%, depending on the volume and specific application requirements.
Typical Applications for Each Material
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) O-rings are typically used in hydraulic systems, automotive fuel handling, and oil seals due to their excellent resistance to abrasion, fuels, and oils. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings are preferred in high-temperature environments, chemical processing, and aerospace applications because of their superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and solvents. Both materials serve critical roles in sealing technologies, with XNBR excelling in mechanical durability and FKM providing exceptional chemical and thermal stability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your O-Ring Needs
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good chemical compatibility with fuels and oils, making it ideal for dynamic sealing in automotive and industrial applications. Fluoroelastomers (FKM), known for superior heat resistance up to 200degC and outstanding chemical inertness against aggressive fluids, provide long-term durability in harsh environments such as aerospace and chemical processing. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, with XNBR preferred for high wear resistance and FKM for superior thermal and chemical resilience.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Fluoroelastomer for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com