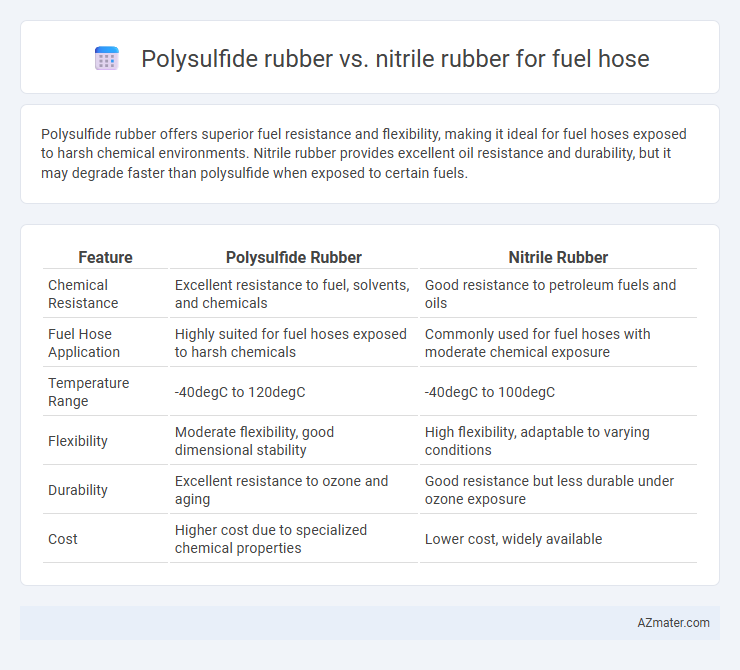
Polysulfide rubber offers superior fuel resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh chemical environments. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil resistance and durability, but it may degrade faster than polysulfide when exposed to certain fuels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polysulfide Rubber | Nitrile Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuel, solvents, and chemicals | Good resistance to petroleum fuels and oils |
| Fuel Hose Application | Highly suited for fuel hoses exposed to harsh chemicals | Commonly used for fuel hoses with moderate chemical exposure |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, good dimensional stability | High flexibility, adaptable to varying conditions |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to ozone and aging | Good resistance but less durable under ozone exposure |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized chemical properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Fuel hoses require materials with excellent chemical resistance and flexibility to safely handle hydrocarbons and withstand pressure fluctuations. Polysulfide rubber offers superior resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents with excellent impermeability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for fuel hose applications. Nitrile rubber also provides robust fuel resistance and durability but is more commonly selected for light fuel and oil transfer due to slightly lower chemical resistance compared to polysulfide rubber.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a high-performance elastomer known for its excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for fuel hose applications. Its superior chemical stability and flexibility under extreme temperatures ensure durability and long service life in harsh environments. Compared to nitrile rubber, polysulfide rubber offers enhanced resistance to oxidative and ozone degradation, providing better performance in demanding fuel handling systems.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in fuel hose applications due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons. NBR offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and low gas permeability compared to polysulfide rubber, making it ideal for maintaining fuel hose integrity under high pressure and temperature conditions. Its chemical stability and durability in harsh environments ensure reliable performance in automotive and industrial fuel delivery systems.
Chemical Resistance: Polysulfide vs Nitrile
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, such as gasoline and diesel, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to aggressive fuels. Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons, and fuels but shows reduced performance against aromatic compounds compared to polysulfide rubber. The high durability of polysulfide rubber against solvents and fuel additives ensures longer service life in harsh chemical environments than nitrile rubber.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Polysulfide rubber exhibits exceptional temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and sealing properties in a range from -40degC to 120degC, making it highly suitable for fuel hoses exposed to extreme heat and cold. Nitrile rubber performs well within a narrower temperature range, typically from -30degC to 100degC, offering good resistance to fuel but less stability under prolonged high-temperature conditions. For fuel hose applications requiring superior thermal durability, polysulfide rubber provides enhanced performance over nitrile rubber in maintaining integrity and preventing degradation at elevated temperatures.
Flexibility and Durability Analysis
Polysulfide rubber offers superior flexibility and remarkable chemical resistance, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to aggressive fuels and varying temperatures. Nitrile rubber provides excellent durability against oil and fuel degradation with enhanced tear and abrasion resistance, but it exhibits slightly less flexibility compared to polysulfide rubber. In fuel hose systems requiring optimal balance between flexibility and long-term durability, polysulfide rubber is preferred for dynamic movement environments, while nitrile rubber excels in high-wear, static sealing scenarios.
Compatibility with Fuels and Additives
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, oxygenated fuels, and a wide range of additives, making it highly compatible with modern fuel formulations. Nitrile rubber offers superior compatibility with petroleum-based fuels and excels in resistance to oils and fuel additives such as antioxidants and detergents. Fuel hoses made from polysulfide rubber or nitrile rubber should be selected based on specific fuel types and additive compositions to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility for fuel hoses but tends to have higher production costs and limited availability compared to nitrile rubber. Nitrile rubber is widely available and more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for general fuel hose applications despite slightly lower fuel resistance. Industries balance Polysulfide's durability against Nitrile's affordability and accessibility when selecting materials for fuel hose manufacturing.
Typical Applications in the Fuel Industry
Polysulfide rubber is widely used in the fuel industry for fuel hoses due to its excellent resistance to hydrocarbons, fuels, and oils, making it ideal for aviation fuel systems and automotive fuel lines. Nitrile rubber is favored for fuel hose applications requiring high resistance to gasoline, diesel, and synthetic oils, commonly found in industrial and marine fuel transfer hoses. Both materials offer durability and flexibility, but polysulfide excels in fuel vapor impermeability, while nitrile provides superior abrasion and wear resistance in dynamic fuel handling environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Fuel Hose
Polysulfide rubber offers exceptional resistance to fuels, oil, and ozone, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions, while nitrile rubber provides excellent fuel and oil resistance with superior flexibility and abrasion resistance. When choosing the right material for your fuel hose, consider polysulfide rubber for applications requiring longer service life under extreme temperatures and chemical exposure, whereas nitrile rubber suits situations demanding high mechanical performance and dynamic flexibility. Evaluating factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range (-40degC to 135degC for polysulfide, -40degC to 120degC for nitrile), and durability ensures optimal fuel hose performance and safety.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com