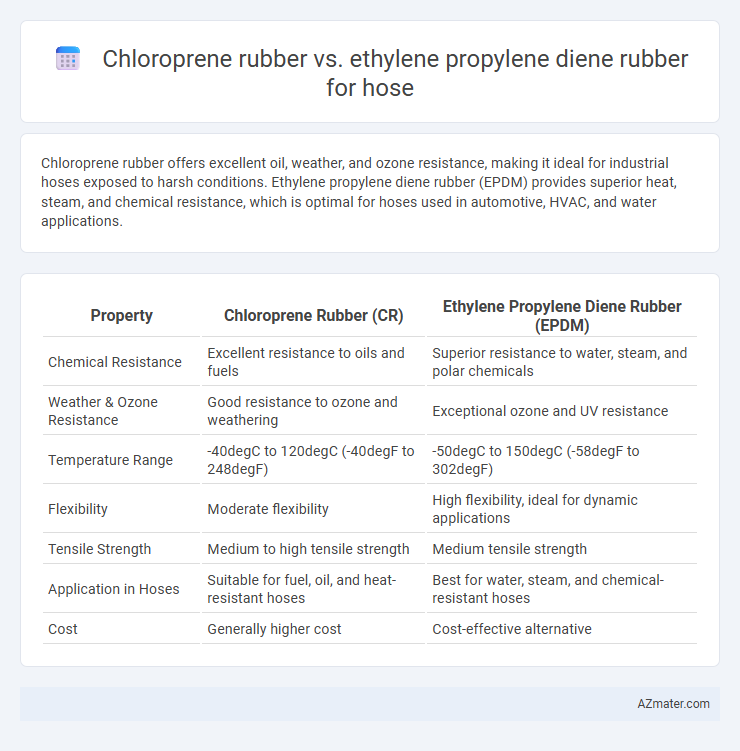
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent oil, weather, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to harsh conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior heat, steam, and chemical resistance, which is optimal for hoses used in automotive, HVAC, and water applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and fuels | Superior resistance to water, steam, and polar chemicals |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Good resistance to ozone and weathering | Exceptional ozone and UV resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility, ideal for dynamic applications |
| Tensile Strength | Medium to high tensile strength | Medium tensile strength |
| Application in Hoses | Suitable for fuel, oil, and heat-resistant hoses | Best for water, steam, and chemical-resistant hoses |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective alternative |
Introduction to Chloroprene and Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits excellent oil resistance, weathering stability, and moderate flexibility, making it ideal for hoses exposed to various environmental stresses and chemicals. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, known for superior heat, ozone, and abrasion resistance, offers excellent performance in high-temperature and outdoor hose applications. Both materials provide diverse mechanical properties tailored to hose manufacturing, with CR preferred for chemical resistance and EPDM favored for thermal endurance.
Chemical Structure Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) contains chlorine atoms attached to its polymer backbone derived from chloroprene monomers, providing enhanced chemical resistance and flame retardancy. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) consists of ethylene and propylene units with a diene component for crosslinking, offering excellent weather and ozone resistance but lower resistance to oils and solvents. The presence of chlorine in CR's molecular structure results in superior durability for chemical hose applications, while the saturated hydrocarbon backbone of EPDM provides outstanding flexibility and environmental resistance.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior ozone resistance, good tensile strength (typically around 15-25 MPa), and excellent oil and weather resistance, making it ideal for industrial hose applications exposed to harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits outstanding heat resistance up to 150degC, excellent flexibility at low temperatures, and superior resistance to water, steam, and alkalis, with tensile strength ranging from 10-20 MPa. Both materials provide good abrasion resistance, but CR excels in solvent resistance while EPDM is preferred for applications requiring superior weatherability and steam resistance.
Weather and Ozone Resistance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) demonstrates excellent weather and ozone resistance due to its inherent chlorine content, making it highly durable for outdoor hose applications exposed to UV radiation and ozone-rich environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to ozone and weathering as well, especially in extreme temperature ranges, often outperforming Chloroprene in long-term exposure scenarios. Both materials are suitable for hoses requiring environmental resilience, but EPDM is typically preferred for superior ozone and aging resistance in harsh climatic conditions.
Temperature Tolerance for Hose Applications
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits a temperature tolerance range from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature hose applications requiring oil and weather resistance. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) withstands a broader temperature spectrum, typically from -50degC to 150degC, offering superior heat, ozone, and steam resistance for hose systems exposed to extreme conditions. EPDM is preferred in high-temperature hose applications due to its enhanced thermal stability and resistance to aging under continuous heat exposure.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Performance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior oil resistance due to its enhanced polarity and chlorine content, making it highly effective against petroleum-based oils and fuels commonly encountered in hose applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) demonstrates excellent resistance to polar solvents, acids, and alkalis but shows limited performance against hydrocarbon oils and fuels, which can cause swelling and degradation. For hose systems exposed to diverse chemical environments with significant oil exposure, CR offers more reliable durability and chemical resistance than EPDM.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior mechanical strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly durable for hose applications exposed to harsh conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides exceptional flexibility and outstanding resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat, ideal for hoses requiring prolonged elasticity and environmental resilience. EPDM generally outperforms CR in flexibility, while CR excels in tensile strength and mechanical toughness.
Typical Applications in Hose Manufacturing
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is widely used for hoses requiring excellent oil, weather, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for automotive fuel and hydraulic hoses, as well as industrial and chemical transport applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior heat, steam, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for hot water hoses, steam hoses, and those used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Both elastomers provide flexibility and durability, but CR excels in oil-based environments, while EPDM is preferred for heat and weather resistance in hose manufacturing.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) generally offers a moderate cost with good availability, making it a popular choice for hose applications requiring oil resistance and weather durability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) often has a lower base cost but can fluctuate due to raw material supply, impacting overall pricing and availability for industrial hose manufacturing. Both materials are widely available, but CR might incur higher costs in specialized blends, whereas EPDM benefits from stable supply chains, especially in larger volume demands.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Hose Needs
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oil exposure, making it ideal for industrial and outdoor hoses requiring durability and flexibility. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in high-temperature resistance, superior steam, water, and chemical compatibility, suitable for hoses in automotive, HVAC, and chemical processing applications. Selecting the right rubber involves evaluating environmental exposure, temperature range, and chemical contact to ensure optimal hose performance and longevity.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com