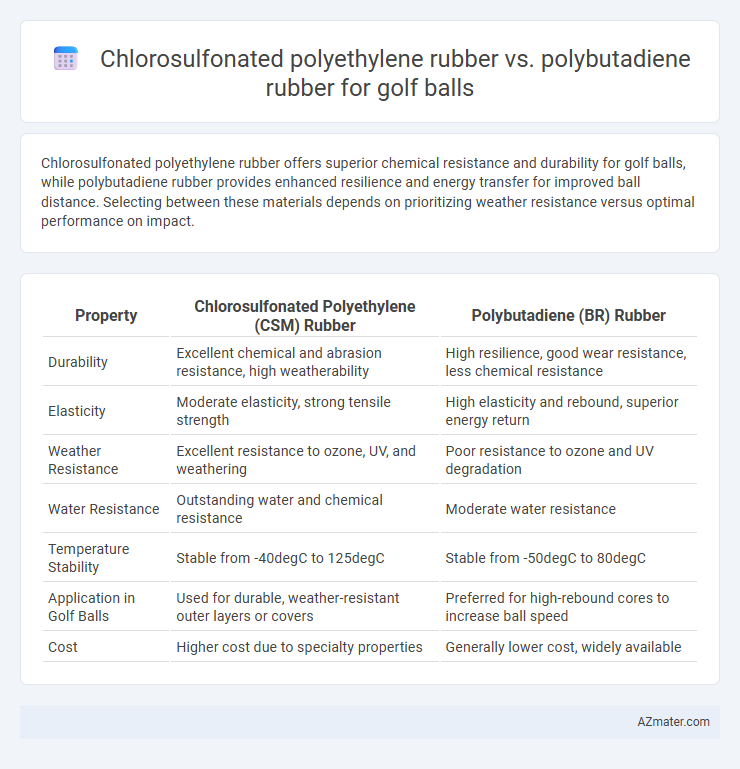
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability for golf balls, while polybutadiene rubber provides enhanced resilience and energy transfer for improved ball distance. Selecting between these materials depends on prioritizing weather resistance versus optimal performance on impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber | Polybutadiene (BR) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance, high weatherability | High resilience, good wear resistance, less chemical resistance |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, strong tensile strength | High elasticity and rebound, superior energy return |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Poor resistance to ozone and UV degradation |
| Water Resistance | Outstanding water and chemical resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Temperature Stability | Stable from -40degC to 125degC | Stable from -50degC to 80degC |
| Application in Golf Balls | Used for durable, weather-resistant outer layers or covers | Preferred for high-rebound cores to increase ball speed |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Generally lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Golf Ball Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior weather resistance and chemical stability, making it a durable choice for golf ball covers and cores exposed to harsh playing conditions. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent resilience and high energy return, contributing significantly to the golf ball's distance and performance. Selecting between CSM and BR depends on balancing durability with elasticity to optimize overall ball characteristics for various levels of play.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is a synthetic elastomer characterized by exceptional weather resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it suitable for harsh environments. In golf ball manufacturing, CSM enhances cover toughness and abrasion resistance while maintaining flexibility and resilience, crucial for consistent ball performance. Compared to polybutadiene rubber, which excels in energy restitution and core elasticity, CSM offers superior resistance to oxidative degradation and chemical attack, improving the longevity of golf ball covers.
Overview of Polybutadiene Rubber (BR)
Polybutadiene rubber (BR) is prized in golf ball manufacturing for its exceptional resilience and high rebound properties, which contribute to increased ball distance. Its molecular structure provides superior abrasion resistance and low heat buildup, enhancing durability and performance under repeated impacts. Compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber, BR offers improved elasticity and energy return, making it the preferred choice for core and mantle layers in premium golf balls.
Physical Properties Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, enhanced UV stability, and higher tensile strength compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), making it ideal for golf ball covers exposed to varying environmental conditions. Polybutadiene rubber offers excellent resilience and lower compression, contributing to improved energy return and longer ball flight distance but falls short in resistance to abrasion and oxidation. The choice between CSM and BR hinges on balancing durability and performance, where CSM excels in physical robustness while BR prioritizes elasticity and impact resistance.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), making it ideal for golf ball covers that endure repetitive impacts and abrasion. CSM's chemical structure provides excellent resistance to oxidation, UV degradation, and harsh environmental conditions, extending the lifespan of golf balls in outdoor play. Polybutadiene rubber, while offering high resilience and impact absorption, tends to wear faster and degrades more quickly under prolonged exposure to stresses and elements.
Performance Impact on Golf Ball Flight
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber provides superior weather resistance and UV stability, enhancing the durability and consistent elasticity of golf balls during flight. Polybutadiene rubber excels in high resilience and energy return, promoting greater initial velocity and longer carry distances. The choice between CSPE and polybutadiene significantly influences ball spin control, distance, and overall flight performance under variable environmental conditions.
Weather and Chemical Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior weather resistance and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for golf ball covers exposed to UV radiation, ozone, and harsh environmental conditions. Polybutadiene rubber, while providing high resilience and impact resistance, exhibits lower resistance to oxidation and chemical degradation, leading to faster deterioration under prolonged exposure. CSPE's improved durability enhances golf ball performance by maintaining material integrity and surface properties over extended outdoor use.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), but it generally incurs higher material costs and requires more complex manufacturing processes due to its specialized curing methods. Polybutadiene rubber is favored in golf ball production for its lower cost and excellent resilience, enabling high energy return for longer shots while simplifying manufacturing with established, cost-effective compounding and molding techniques. Manufacturing facilities often choose polybutadiene rubber to balance performance and economical production, whereas CSM rubber is selected for premium golf balls emphasizing durability despite increased production expenses.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weatherability, leading to longer golf ball durability and reducing waste compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), which degrades faster under UV exposure and oxidation. CSM's resistance to water and chemicals minimizes environmental contamination during production and end-of-life disposal, whereas BR manufacturing involves higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and petroleum-derived raw materials. Sustainable golf ball design increasingly favors CSM due to its lower environmental impact, extended service life, and potential for improved recyclability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Golf Balls
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior weather resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it ideal for golf balls exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Polybutadiene rubber provides excellent resilience and high energy return, which enhances ball distance and performance. Choosing the right rubber depends on prioritizing either weather resistance and longevity with chlorosulfonated polyethylene or maximizing distance and elasticity with polybutadiene.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Golf ball
 azmater.com
azmater.com