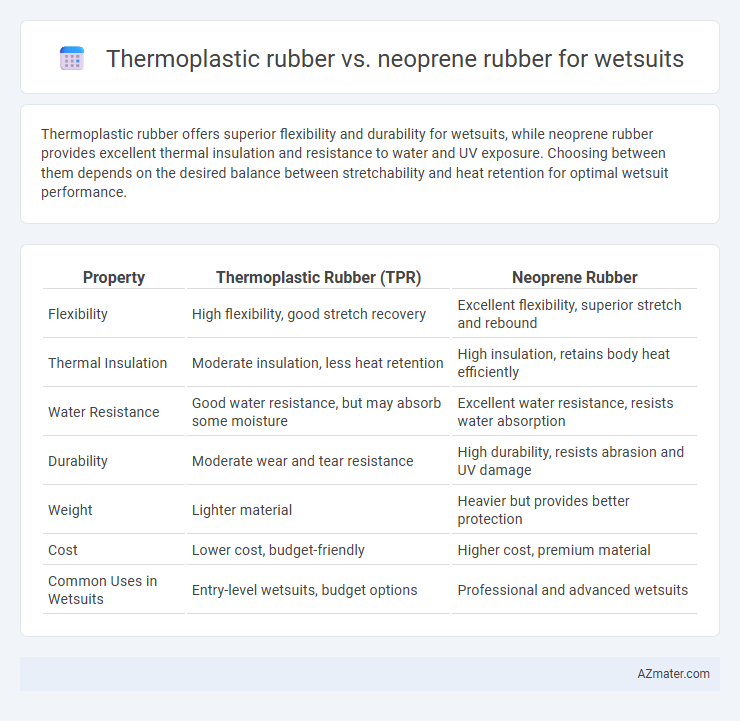
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility and durability for wetsuits, while neoprene rubber provides excellent thermal insulation and resistance to water and UV exposure. Choosing between them depends on the desired balance between stretchability and heat retention for optimal wetsuit performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good stretch recovery | Excellent flexibility, superior stretch and rebound |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation, less heat retention | High insulation, retains body heat efficiently |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance, but may absorb some moisture | Excellent water resistance, resists water absorption |
| Durability | Moderate wear and tear resistance | High durability, resists abrasion and UV damage |
| Weight | Lighter material | Heavier but provides better protection |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium material |
| Common Uses in Wetsuits | Entry-level wetsuits, budget options | Professional and advanced wetsuits |
Introduction to Wetsuit Materials
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and neoprene are common materials used in wetsuit manufacturing, each offering distinct properties important for water sports performance. Neoprene provides excellent insulation and flexibility due to its closed-cell foam structure, making it ideal for thermal protection in cold water conditions. Thermoplastic rubber, while less insulating, offers superior durability and resistance to abrasion, making it a practical choice for wetsuits designed for warmer environments and frequent use.
Overview of Thermoplastic Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers exceptional flexibility and durability, making it an effective material for wetsuit construction, especially in terms of abrasion resistance and ease of recycling. Its lightweight properties and resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation and ozone lend to prolonged wetsuit lifespan in various water conditions. Compared to neoprene rubber, TPR provides enhanced elasticity but may lack the same level of thermal insulation typically required for colder water wetsuits.
What is Neoprene Rubber?
Neoprene rubber is a synthetic elastomer commonly used in wetsuits due to its excellent insulation properties, flexibility, and resistance to water, oil, and weathering. Unlike thermoplastic rubber, neoprene is a durable and stretchy material that provides superior thermal protection by trapping a thin layer of water between the suit and the skin, which the body then heats. Its closed-cell structure enhances buoyancy and prevents water absorption, making it the preferred choice for high-performance marine and water sports gear.
Flexibility and Comfort Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior flexibility and stretch due to its elastic polymer structure, making wetsuits highly comfortable and allowing greater freedom of movement in the water. Neoprene rubber provides excellent insulation and moderate flexibility but tends to be stiffer and heavier, which can limit comfort during prolonged use. Wetsuits made from TPR deliver enhanced comfort for extended wear, while neoprene is preferred for better thermal protection in colder conditions.
Insulation and Thermal Performance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate insulation and flexibility, making it suitable for wetsuits in warmer waters, while neoprene rubber provides superior thermal performance due to its closed-cell foam structure that traps heat efficiently. Neoprene's microcellular composition minimizes heat loss and maintains body warmth in colder water conditions, outperforming the more porous TPR materials in insulation. For users prioritizing thermal protection and extended exposure in cold environments, neoprene wetsuits deliver optimal warmth and durability compared to thermoplastic alternatives.
Durability and Longevity
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it durable for prolonged wetsuit use, but it can degrade faster under UV exposure compared to neoprene. Neoprene rubber provides superior durability due to its closed-cell structure, which resists water absorption and maintains elasticity over time, enhancing wetsuit longevity. Neoprene's resistance to chemical and environmental factors gives it a longer lifespan in harsh marine conditions, outperforming standard thermoplastic rubber materials.
Water Resistance and Buoyancy
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent water resistance due to its non-porous structure, making it highly effective in preventing water absorption in wetsuit materials. Neoprene rubber, widely used in wetsuits, provides superior buoyancy as its closed-cell foam structure traps nitrogen gas, enhancing flotation and thermal insulation. While both materials resist water penetration, neoprene's buoyant properties make it the preferred choice for wetsuits designed to improve swimmer performance and warmth.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) for wetsuits offers better environmental sustainability due to its recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to neoprene rubber, which is derived from petroleum-based chloroprene and associated with higher greenhouse gas emissions. Neoprene production involves hazardous chemicals and solvent use, raising concerns about water pollution and non-biodegradability, whereas TPR materials are often designed to be more eco-friendly and recyclable. Choosing TPR wetsuits supports efforts in reducing microplastic pollution and promoting circular economy practices in the surf and dive industries.
Cost and Accessibility
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) wetsuits generally offer lower cost and greater accessibility due to mass production and easier manufacturing processes compared to neoprene rubber wetsuits. Neoprene rubber provides superior insulation and flexibility but comes at a higher price point and may require specialized suppliers. Budget-conscious consumers often choose TPR options for affordability and wider availability, while performance-focused users invest in neoprene for enhanced thermal protection.
Which Rubber is Best for Wetsuits?
Neoprene rubber is the preferred material for wetsuits due to its superior thermal insulation, flexibility, and durability in cold water conditions. Thermoplastic rubber offers more environmental resistance and ease of recycling but lacks the necessary stretch and warmth retention critical for wetsuit performance. For optimal warmth, comfort, and water resistance, neoprene remains the best choice for wetsuit construction.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Wetsuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com