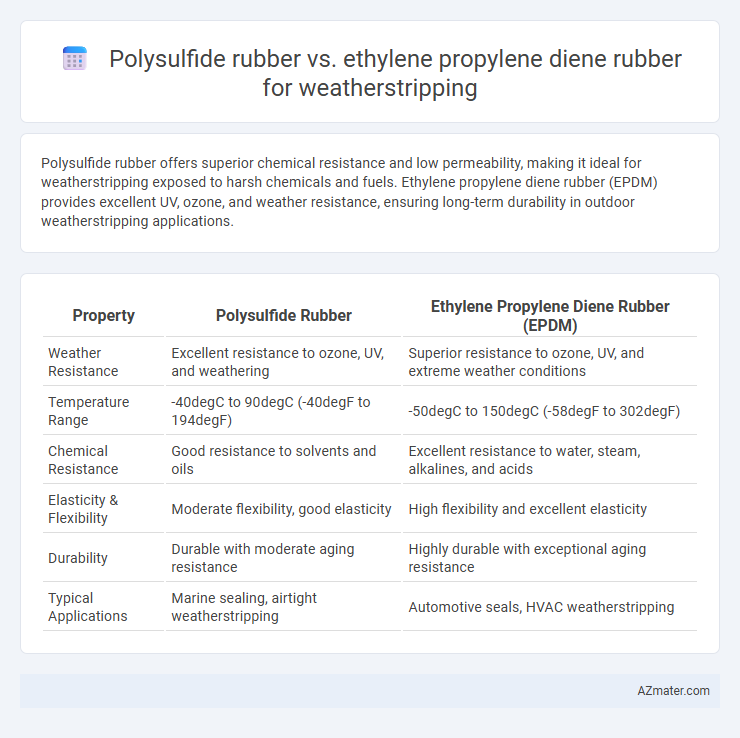
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and low permeability, making it ideal for weatherstripping exposed to harsh chemicals and fuels. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides excellent UV, ozone, and weather resistance, ensuring long-term durability in outdoor weatherstripping applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Superior resistance to ozone, UV, and extreme weather conditions |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 90degC (-40degF to 194degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and oils | Excellent resistance to water, steam, alkalines, and acids |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, good elasticity | High flexibility and excellent elasticity |
| Durability | Durable with moderate aging resistance | Highly durable with exceptional aging resistance |
| Typical Applications | Marine sealing, airtight weatherstripping | Automotive seals, HVAC weatherstripping |
Introduction to Weatherstripping Materials
Polysulfide rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber are widely used materials in weatherstripping applications due to their distinct chemical properties and performance characteristics. Polysulfide rubber offers excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it suitable for sealing in harsh chemical environments, while EPDM rubber excels in ultraviolet radiation, ozone, and extreme temperature resistance, providing durable protection in outdoor settings. Selection between these materials hinges on specific application needs such as environmental exposure, flexibility, and longevity essential for effective weather sealing solutions.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is renowned for its excellent chemical resistance, low permeability to gases and moisture, and superior durability under harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications requiring long-term performance. It exhibits strong resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and temperature extremes ranging from -40degC to 150degC, ensuring effective sealing and flexibility over time. Compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), polysulfide offers enhanced solvent resistance and longevity, particularly in industrial or marine environments prone to exposure from fuels, oils, and solvents.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer widely used in weatherstripping due to its exceptional resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, ranging from -40degC to 150degC. Its excellent waterproofing properties and flexibility make it ideal for sealing applications in automotive, construction, and industrial environments. Compared to Polysulfide rubber, EPDM offers superior durability against environmental aging and is more cost-effective for large-scale weatherstripping solutions.
Weather Resistance Comparison
Polysulfide rubber offers superior weather resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, particularly in resisting ozone, UV rays, and moisture degradation, making it ideal for prolonged outdoor weatherstripping applications. EPDM provides excellent resistance to heat and aging but tends to degrade faster under constant exposure to hydrocarbons and certain solvents, limiting its longevity in harsh weather environments. For weatherstripping requiring high durability against extreme weather conditions, polysulfide rubber outperforms EPDM in maintaining flexibility and sealing integrity over time.
Durability and Longevity
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent resistance to ozone and UV degradation, making it highly durable for weatherstripping applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) also provides excellent weather resistance, particularly against heat, ozone, and moisture, with notable elasticity that maintains a tight seal over long periods. Polysulfide tends to have better longevity in environments with exposure to fuels and solvents, while EPDM excels in sustained outdoor use due to its resilience to temperature fluctuations and aging.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance and moderate flexibility, making it effective for weatherstripping in harsh environments but with limited elasticity over prolonged stretching. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent flexibility and high elasticity, allowing it to maintain a tight seal under varying temperatures and repeated compressions essential for weatherstripping applications. EPDM's ability to recover quickly from deformation enhances its performance in dynamic sealing conditions compared to the more rigid Polysulfide rubber.
Chemical and UV Resistance
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent chemical resistance, particularly against fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for weatherstripping in harsh chemical environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior UV and ozone resistance, ensuring long-lasting durability in outdoor applications exposed to sunlight. Both materials provide distinct advantages for weatherstripping, with polysulfide excelling in chemical resistance and EPDM in UV stability.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it easier to install in irregular gaps for weatherstripping applications, though it requires longer curing times compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM rubber is favored for its UV and ozone resistance, allowing quicker installation with strong adhesion to most surfaces, reducing initial labor costs. Maintenance for polysulfide seals generally demands less frequent replacement due to chemical durability, whereas EPDM may require more regular inspection and replacement in harsh chemical environments.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polysulfide rubber offers superior resistance to weathering and chemicals, resulting in longer service life for weatherstripping applications, which can lower replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) generally provides a lower initial cost and excellent UV and ozone resistance, making it a cost-effective option for moderate exposure environments. Considering total lifecycle costs, polysulfide may be more economically viable for harsh conditions, while EPDM suits budget-conscious projects with less extreme environmental demands.
Best Applications for Each Material
Polysulfide rubber excels in weatherstripping applications requiring superior chemical resistance and long-term durability against solvents, oils, and fuels, making it ideal for industrial and marine environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is best suited for outdoor weatherstripping exposed to extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and ozone due to its excellent weather resistance and flexibility. Selecting polysulfide is advantageous for sealing joints in chemical plants or fuel systems, while EPDM performs optimally in automotive, roofing, and window seals exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weatherstripping
 azmater.com
azmater.com