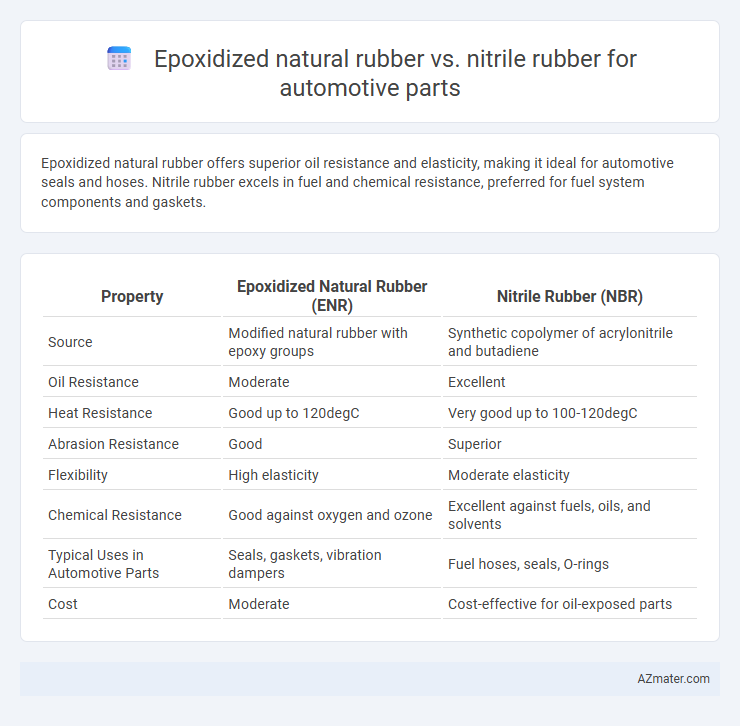
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior oil resistance and elasticity, making it ideal for automotive seals and hoses. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel and chemical resistance, preferred for fuel system components and gaskets.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Modified natural rubber with epoxy groups | Synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Oil Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Good up to 120degC | Very good up to 100-120degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Flexibility | High elasticity | Moderate elasticity |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against oxygen and ozone | Excellent against fuels, oils, and solvents |
| Typical Uses in Automotive Parts | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers | Fuel hoses, seals, O-rings |
| Cost | Moderate | Cost-effective for oil-exposed parts |
Introduction to Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) and Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is derived from natural rubber by introducing epoxy groups into its molecular structure, enhancing oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it suitable for automotive seals and hoses exposed to harsh chemicals. Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, known for excellent resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and other chemicals, widely used in automotive fuel system components and gaskets. Both ENR and NBR provide specific advantages for automotive parts, with ENR offering superior flexibility and biodegradability, while NBR excels in oil resistance and temperature stability.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) contains epoxy groups introduced into the polyisoprene backbone, enhancing its polarity and oil resistance, whereas nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene featuring nitrile groups that provide superior chemical and fuel resistance. The epoxidation degree in ENR influences its compatibility with polar substances, improving mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to unmodified natural rubber. NBR's acrylonitrile content determines its oil resistance range, making it more suitable for automotive seals and fuel system components exposed to hydrocarbons.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior elasticity and enhanced abrasion resistance, making it highly flexible and durable for automotive applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent tensile strength and outstanding resistance to oils and fuels, crucial for engine components requiring mechanical robustness. ENR provides better tear strength and resilience under dynamic stress, while NBR excels in hardness and compression set, optimizing overall mechanical performance in automotive parts.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance compared to conventional natural rubber due to its polar epoxy groups, making it suitable for automotive parts exposed to hydrocarbons. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is specifically engineered for superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and various chemicals, outperforming ENR in prolonged exposure to harsh automotive fluids. While ENR provides balanced performance with improved elasticity and oil resistance, NBR remains the preferred material for applications demanding maximum oil and chemical resistance in automotive seals and gaskets.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to nitrile rubber, maintaining elasticity and resistance to heat-induced degradation at temperatures up to 150degC. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent oil and fuel resistance but typically performs well only up to 100degC before thermal aging compromises its mechanical properties. For automotive parts exposed to high temperatures and requiring sustained flexibility, ENR provides enhanced temperature performance and longer service life than conventional nitrile rubber.
Aging and Weathering Resistance in Automotive Applications
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging and weathering resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced oxidation stability and resistance to ozone degradation, making it well-suited for automotive parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber offers excellent oil and fuel resistance but tends to deteriorate faster under UV exposure and prolonged heat, limiting its lifespan in external automotive applications. ENR's improved tensile strength and flexibility after weathering further enhance durability, ensuring prolonged performance in automotive seals, hoses, and gaskets subjected to UV radiation and varying temperature cycles.
Processing and Manufacturability in the Automotive Industry
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced processing flexibility with improved compatibility for mixing and molding, making it suitable for complex automotive components requiring superior elasticity and abrasion resistance. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in manufacturability due to its high resistance to oils, fuels, and heat, enabling efficient production of seals, hoses, and gaskets with consistent dimensional stability. Both materials support injection molding and extrusion processes, but the choice depends on specific part requirements such as chemical exposure and mechanical durability in automotive applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), but ENR generally comes at a higher raw material cost due to its specialized production process. NBR remains economically favorable for large-scale automotive part manufacturing because of its lower price and well-established supply chain, despite slightly lower performance in harsh chemical environments. Cost analysis reveals that while ENR can reduce long-term maintenance expenses, NBR's upfront affordability and consistent availability make it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive automotive applications.
Typical Automotive Applications: ENR vs NBR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is commonly utilized in automotive parts requiring excellent oil resistance, flexibility, and improved mechanical strength, such as hoses, seals, and gaskets. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in applications exposed to fuels, oils, and high-temperature environments, making it ideal for fuel system components, O-rings, and engine seals. ENR offers better biodegradability and elasticity, while NBR provides superior chemical resistance and durability in harsh automotive conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), as ENR is derived from renewable natural latex sources with partial epoxidation improving durability while maintaining eco-friendliness. Nitrile rubber, synthesized from petroleum-based monomers, poses greater environmental concerns due to its non-renewable origins and lower biodegradability, resulting in longer degradation periods and higher carbon emissions in automotive part lifecycle assessments. Sustainable automotive design increasingly favors ENR for its renewable sourcing, reduced environmental impact, and compatibility with circular economy principles in rubber manufacturing.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com