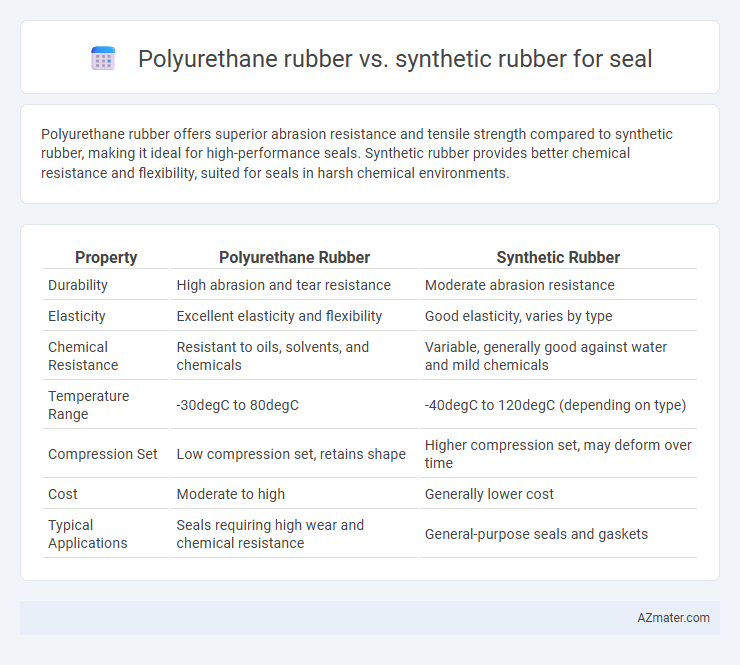
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for high-performance seals. Synthetic rubber provides better chemical resistance and flexibility, suited for seals in harsh chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Excellent elasticity and flexibility | Good elasticity, varies by type |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Variable, generally good against water and mild chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC (depending on type) |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, retains shape | Higher compression set, may deform over time |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower cost |
| Typical Applications | Seals requiring high wear and chemical resistance | General-purpose seals and gaskets |
Introduction to Seal Material Choices
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for high-performance seals in heavy-duty applications. Synthetic rubber varieties such as nitrile, EPDM, and silicone provide excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, catering to diverse sealing environments involving oils, weathering, and extreme temperatures. Selecting the appropriate seal material requires balancing factors like durability, chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and longevity in specific industrial conditions.
Defining Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its exceptional abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent load-bearing capabilities, making it a prime choice for seals in demanding industrial applications. Unlike synthetic rubbers such as nitrile or EPDM, polyurethane offers superior resistance to oil, solvents, and mechanical wear, which extends the lifespan of seals under dynamic conditions. Its unique molecular structure provides unmatched elasticity and durability, ensuring reliable sealing performance in environments subjected to high pressure and friction.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber Types
Synthetic rubber types commonly used for seals include Nitrile (NBR), EPDM, Silicone, and Neoprene, each offering unique properties such as oil resistance, heat tolerance, and chemical stability. Polyurethane rubber stands out for its superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Selecting the appropriate synthetic rubber type depends on the specific environmental conditions and performance requirements of the seal.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength ranging from 20 to 50 MPa, and excellent tear resistance compared to synthetic rubbers such as nitrile or EPDM, which typically have tensile strengths between 10 to 25 MPa. Polyurethane seals exhibit lower compression set values (around 10-15%), enhancing long-term sealing performance under dynamic stress, whereas synthetic rubbers usually show higher compression set percentages, impacting their durability. Temperature resistance varies with polyurethane maintaining flexibility from -30degC up to 80degC, while certain synthetic rubbers like fluorosilicone tolerate broader ranges (-60degC to 200degC) but may compromise on mechanical resilience.
Chemical Resistance: Polyurethane vs Synthetic Rubber
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against oils, fuels, and abrasion, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh industrial chemicals. Synthetic rubber, such as Nitrile (NBR) or EPDM, offers varied chemical resistance depending on the type but generally performs well against water, alcohols, and certain acids. Choosing between polyurethane and synthetic rubber seals depends on specific chemical exposure, temperature ranges, and mechanical stresses for optimal durability.
Durability and Lifespan in Sealing Applications
Polyurethane rubber offers superior durability and abrasion resistance compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for sealing applications exposed to mechanical wear and aggressive environments. Its lifespan in sealing applications often exceeds that of synthetic rubber due to enhanced resistance to oil, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Synthetic rubber variants like NBR or EPDM provide good flexibility and chemical resistance but typically have shorter operational lifespans under heavy mechanical stress or harsh conditions.
Temperature Tolerance and Flexibility
Polyurethane rubber offers superior temperature tolerance, operating effectively between -40degC to 80degC, with some formulations enduring up to 120degC, while synthetic rubber variants like neoprene and nitrile typically perform well within -30degC to 100degC. Polyurethane maintains excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications where movement occurs. Synthetic rubber seals provide good elasticity and resilience but generally exhibit reduced flexibility at extreme temperatures compared to polyurethane.
Cost Efficiency and Value Analysis
Polyurethane rubber offers superior cost efficiency for seals due to its exceptional abrasion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Synthetic rubber, while generally cheaper initially, tends to wear out faster under harsh conditions, increasing overall lifecycle costs. Evaluating value, polyurethane's durability and performance in sealing applications justify its higher upfront price, delivering better ROI compared to conventional synthetic rubber options.
Application Suitability: Industry Use Cases
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capabilities, making it ideal for heavy-duty seals in automotive, industrial machinery, and hydraulic systems. Synthetic rubbers such as Nitrile (NBR) and EPDM excel in chemical resistance and temperature versatility, suited for seals in oil and gas, chemical processing, and food-grade applications. Both materials cater to specific industry needs: polyurethane is preferred for high-wear environments, while synthetic rubber is favored for exposure to oils, fuels, and extreme temperatures.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Seal Needs
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for seals subjected to heavy wear and dynamic stress. Synthetic rubber, such as Nitrile (NBR) or EPDM, provides better chemical resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for seals in moderate mechanical environments and exposure to oils or weathering. Choosing the right rubber depends on the seal's operational conditions, including temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com