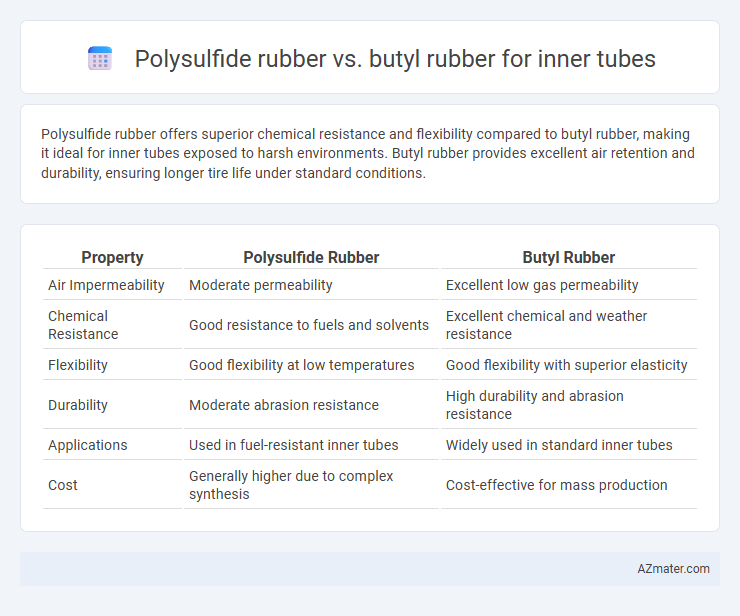
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber provides excellent air retention and durability, ensuring longer tire life under standard conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Air Impermeability | Moderate permeability | Excellent low gas permeability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to fuels and solvents | Excellent chemical and weather resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility with superior elasticity |
| Durability | Moderate abrasion resistance | High durability and abrasion resistance |
| Applications | Used in fuel-resistant inner tubes | Widely used in standard inner tubes |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complex synthesis | Cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Polysulfide rubber and butyl rubber are key materials used in the manufacture of inner tubes, each offering distinct properties that influence performance. Polysulfide rubber excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to fuels and oils. Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and elasticity, ensuring longer-lasting inner tubes with excellent impermeability to gases.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it suitable for inner tube applications requiring high resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents. Its unique polysulfide bonds provide excellent impermeability to gases, which helps maintain inner tube pressure and extends tire life. Compared to butyl rubber, polysulfide rubber offers superior resistance to ozone and weathering but typically has a stiffer feel and higher production cost.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases, making it an ideal material for inner tubes in tires. It offers superior air retention compared to polysulfide rubber, enhancing tire longevity and performance. Its resistance to heat, ozone, and aging further ensures durability under various driving conditions.
Key Properties Comparison
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh environments and fuels. Butyl rubber excels in air retention and impermeability, providing superior airtightness and durability for inner tubes in automotive and bicycle applications. Both materials exhibit strong elasticity, but butyl rubber's low permeability to gases ensures longer-lasting inflation.
Air Retention Capabilities
Polysulfide rubber offers moderate air retention due to its chemical resistance but is often less effective than butyl rubber for maintaining internal pressure over time. Butyl rubber exhibits superior air impermeability, making it the preferred choice for inner tubes where prolonged air retention is critical. Its low gas permeability significantly reduces air loss, enhancing tire durability and performance.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Polysulfide rubber offers superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and oils, making it ideal for inner tubes used in harsh environments where exposure to petroleum products and solvents is common. Butyl rubber provides excellent impermeability and good resistance to water and air but is generally less effective against oils and aggressive chemicals compared to polysulfide rubber. Selecting polysulfide rubber enhances durability and longevity of inner tubes in chemically demanding applications.
Durability and Puncture Resistance
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior puncture resistance due to its enhanced cross-linking density, making it highly durable for inner tubes subjected to rough terrain and debris. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air retention and chemical stability, offers good durability but is comparatively less resistant to punctures under harsh conditions. Choosing polysulfide rubber increases lifespan and minimizes puncture incidents, while butyl rubber provides a balance of flexibility and airtightness for standard inner tube applications.
Temperature Performance
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and mechanical strength in a range from -40degC to 150degC, making it suitable for high-temperature applications in inner tubes. Butyl rubber, while offering excellent air retention and chemical resistance, typically performs well within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 120degC, with reduced elasticity at elevated temperatures. For inner tubes requiring enhanced thermal stability and prolonged durability under extreme heat, polysulfide rubber is the preferred material.
Cost and Availability
Polysulfide rubber typically offers lower raw material costs compared to butyl rubber, making it a more budget-friendly choice for inner tube manufacturing. Butyl rubber, however, is more widely available in the market due to its extensive use in automotive and bicycle tires, leading to better supply stability. Cost-efficiency and availability must be balanced with performance requirements when selecting between polysulfide and butyl rubber for inner tubes.
Which Rubber is Best for Inner Tubes?
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions, while Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and flexibility, ensuring longer-lasting inflation and optimal performance. Butyl rubber is generally considered the best choice for inner tubes due to its low permeability to gases, which reduces air leakage and extends tire life. For most inner tube applications, Butyl rubber's combination of impermeability, resilience, and ease of repair outperforms polysulfide rubber in maintaining consistent tire pressure.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com