Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for tire inner liners. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and traction, enhancing tire durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
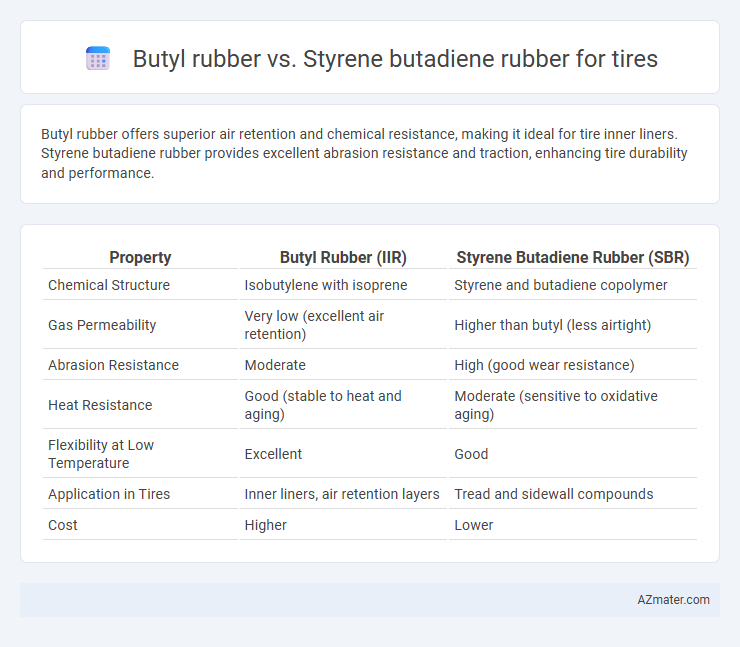
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Isobutylene with isoprene | Styrene and butadiene copolymer |
| Gas Permeability | Very low (excellent air retention) | Higher than butyl (less airtight) |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High (good wear resistance) |
| Heat Resistance | Good (stable to heat and aging) | Moderate (sensitive to oxidative aging) |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Excellent | Good |
| Application in Tires | Inner liners, air retention layers | Tread and sidewall compounds |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Butyl Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer derived from isobutylene and isoprene, is renowned for its excellent air impermeability and resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for inner liners of tires to maintain air pressure. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, offers superior abrasion resistance and good aging stability, commonly used in tire treads for enhanced durability and traction. The combination of butyl rubber's impermeability and SBR's mechanical strength is fundamental in tire manufacturing to balance performance and longevity.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Butyl rubber consists of a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, offering excellent impermeability to gases due to its saturated hydrocarbon backbone. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, featuring both saturated and unsaturated segments that provide enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability. The chemical differences in saturation and monomer composition directly influence their performance in tire applications, with butyl rubber excelling in air retention and SBR offering superior wear resistance.
Key Physical Properties: Butyl vs. SBR
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner linings in tires to maintain air pressure. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides higher abrasion resistance and better wet traction, which enhances tire tread performance and durability. The key physical differences include butyl's lower tensile strength and higher elongation compared to SBR's greater resilience and wear resistance under dynamic loads.
Air Retention Capabilities in Tire Applications
Butyl rubber exhibits superior air retention capabilities due to its low gas permeability, making it the preferred material for tire inner liners and tubes. In contrast, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers lower air barrier properties, which can lead to increased air loss over time. Utilizing butyl rubber significantly enhances tire longevity and maintains consistent inflation pressure, critical for performance and safety in automotive applications.
Abrasion Resistance and Tread Longevity
Butyl rubber offers superior abrasion resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), enhancing tire durability under harsh conditions. SBR provides balanced tread longevity but wears faster on rough surfaces due to lower abrasion resistance. Tires with butyl rubber compound exhibit extended tread life, making them ideal for heavy-duty and long-lasting tire applications.
Heat and Weather Resistance Differences
Butyl rubber exhibits superior heat resistance with a higher tolerance to thermal degradation compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it more durable under prolonged high-temperature conditions in tires. In terms of weather resistance, butyl rubber outperforms SBR due to its excellent impermeability to gases and superior resilience against ozone and UV radiation, which prevents cracking and extends tire life. SBR, while commonly used for its good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, typically shows reduced aging performance and faster degradation when exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Impact on Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and flexibility, which reduces rolling resistance and enhances fuel efficiency in tires compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR provides better abrasion resistance and traction but typically results in higher rolling resistance, negatively affecting fuel economy. Optimizing tire compounds with butyl rubber minimizes energy loss during rotation, leading to improved fuel savings and lower carbon emissions.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner liners in tires, while styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides enhanced abrasion resistance and better traction due to its higher tensile strength. In terms of cost efficiency, SBR is generally more affordable and widely used for tread compounds, contributing to lower overall tire production costs. Manufacturing processes for butyl rubber require more specialized mixing and curing techniques, increasing complexity and expense compared to the simpler processing of SBR in mass production.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and chemical resistance, contributing to longer tire life and reduced environmental impact through less frequent replacements. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), commonly used in tire treads, is derived predominantly from petroleum but can incorporate recycled content, slightly mitigating its carbon footprint. Both materials pose challenges in biodegradability, yet ongoing innovations in bio-based SBR and improved recycling processes aim to enhance sustainability in tire manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Rubber for Tires
When selecting the best rubber for tires, Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes and applications requiring airtight properties. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and traction, enhancing tire durability and performance on various road conditions. For a balanced tire compound, combining SBR's wear resistance with Butyl's impermeability optimizes overall tire longevity and safety.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com