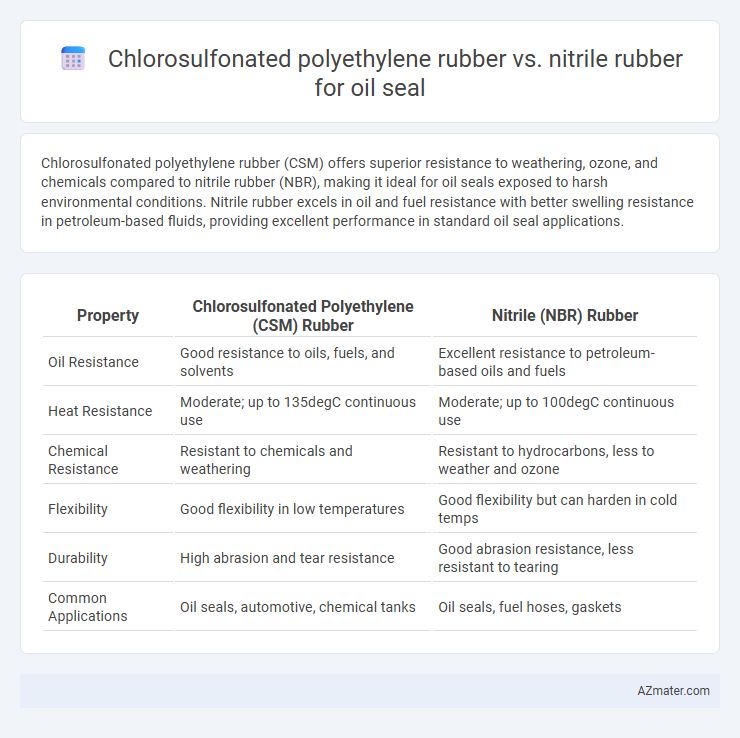
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for oil seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance with better swelling resistance in petroleum-based fluids, providing excellent performance in standard oil seal applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber | Nitrile (NBR) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate; up to 135degC continuous use | Moderate; up to 100degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to chemicals and weathering | Resistant to hydrocarbons, less to weather and ozone |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility in low temperatures | Good flexibility but can harden in cold temps |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good abrasion resistance, less resistant to tearing |
| Common Applications | Oil seals, automotive, chemical tanks | Oil seals, fuel hoses, gaskets |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, making it a durable option for oil seals exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, ensuring reliable sealing performance in automotive and industrial applications. Selecting the appropriate oil seal material depends on the operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands of the sealing environment.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits exceptional resistance to chemicals, ozone, weathering, and oxidation, making it highly durable for oil seal applications. Its unique molecular structure offers superior resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, and acids compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), which enhances longevity in harsh environments. CSM maintains flexibility across a wide temperature range (-40degC to 130degC) while providing excellent mechanical strength and superior sealing performance in both static and dynamic conditions.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it a preferred choice for oil seals in automotive and industrial applications. Its molecular structure provides strong barrier properties against petroleum-based fluids while maintaining flexibility across a wide temperature range of -40degC to 120degC. NBR outperforms Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber in abrasion resistance and tensile strength, ensuring reliable sealing performance in demanding oil sealing conditions.
Chemical Resistance: CSM vs NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber provides superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for oil seals exposed to aggressive chemicals. CSM maintains elasticity and durability in harsh environments with enhanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and oxidation, while NBR offers good resistance primarily to petroleum-based oils but degrades faster when exposed to heat or certain chemicals. This makes CSM a more reliable choice for oil seals in extreme conditions requiring prolonged chemical exposure and stability.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior resistance to a broad range of oils and fuels, including aromatic hydrocarbons and aggressive solvents, making it highly suitable for oil seal applications in harsh chemical environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR), known for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, performs well with aliphatic hydrocarbons but shows decreased compatibility with aromatic fuels and some synthetic oils. For oil seals exposed to diverse fuel compositions and higher chemical aggression, CSM provides enhanced durability and longer service life compared to NBR.
Temperature Stability of CSM and NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior temperature stability compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), maintaining performance in a broader temperature range from -40degC to 120degC, with some formulations tolerating up to 130degC. NBR typically operates effectively between -30degC and 100degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications in oil seals. The enhanced thermal resistance of CSM is attributed to its chlorosulfonation process, which improves oxidative and heat resistance, critical for maintaining sealing integrity under elevated temperatures.
Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior mechanical properties such as excellent tensile strength and elongation, making it highly durable in demanding oil seal applications compared to nitrile rubber (NBR). CSM rubber offers exceptional wear resistance and resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, outperforming nitrile rubber which has good oil resistance but lower durability under harsh environmental conditions. For oil seals subjected to extreme mechanical stress and abrasive wear, chlorosulfonated polyethylene provides longer service life and improved performance stability over nitrile rubber.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber generally has a higher cost than nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its complex manufacturing process and superior chemical resistance properties, making it a premium choice for oil seal applications where durability is critical. NBR offers excellent oil resistance at a more affordable price point and enjoys widespread availability, making it the preferred option for cost-sensitive projects and high-volume production. The global supply chain for nitrile rubber is well-established, ensuring consistent availability, while chlorosulfonated polyethylene may face limited supply in certain regions, impacting lead times and overall project budgeting.
Typical Applications in Oil Seals
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber is widely used in oil seals for automotive, chemical processing, and industrial machinery due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals including oils, acids, and alkalis. Nitrile rubber (NBR), favored for oil seal applications in fuel systems, hydraulic equipment, and general-purpose oil sealing, offers superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and synthetic lubricants at moderate temperatures. Both materials provide effective sealing solutions, but CSM excels in harsher chemical environments, while NBR offers better compatibility with oil and fuel.
Choosing the Right Rubber: CSM or NBR?
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and grease resistance with better mechanical properties, ensuring durability in dynamic sealing applications. Choosing the right rubber depends on the specific application requirements, with CSM preferred for outdoor and chemical exposure, while NBR is favored for oil and fuel sealing performance.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com