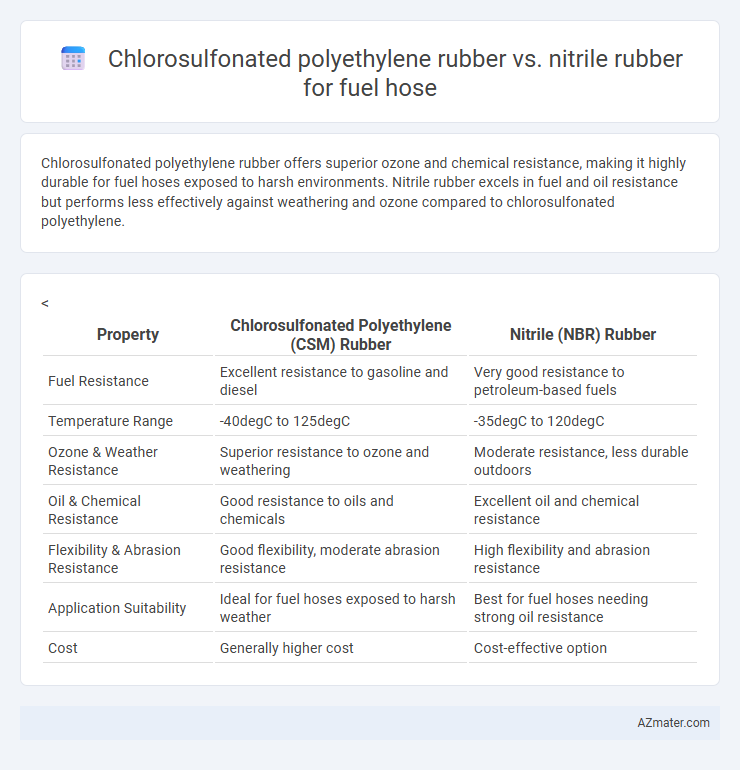
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior ozone and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel and oil resistance but performs less effectively against weathering and ozone compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber | Nitrile (NBR) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent resistance to gasoline and diesel | Very good resistance to petroleum-based fuels |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -35degC to 120degC |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Superior resistance to ozone and weathering | Moderate resistance, less durable outdoors |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent oil and chemical resistance |
| Flexibility & Abrasion Resistance | Good flexibility, moderate abrasion resistance | High flexibility and abrasion resistance |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh weather | Best for fuel hoses needing strong oil resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective option |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Material Selection
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, ozone protection, and durability, making it suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environments and aggressive fuels. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases, ensuring reliable performance in standard fuel hose conditions. Selecting the appropriate fuel hose material depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range, flexibility, and environmental exposure to optimize longevity and safety.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, ozone, weathering, and heat, making it a durable choice for fuel hose applications. Its chemical structure combines chlorine and sulfonyl groups bonded to polyethylene, resulting in superior impermeability and enhanced mechanical strength compared to nitrile rubber. CSM's excellent fuel resistance, along with its flexibility and abrasion resistance, ensures reliable performance in harsh automotive and industrial environments.
Understanding Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Properties
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits exceptional resistance to petroleum-based fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hose applications where chemical compatibility is critical. Its excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance provide durability under harsh working conditions, while its wide temperature tolerance (-40degC to 120degC) ensures reliable performance in varying environments. Compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber, NBR offers superior impermeability to hydrocarbons, enhancing fuel hose longevity and safety.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: CSM vs NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) exhibits superior chemical resistance to a wide range of fuels, oils, and solvents compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), especially in aggressive environments involving aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. NBR performs well against petroleum-based fuels and oils but degrades faster in the presence of ozone, weathering, and certain fuels containing oxygenates or polar solvents. For fuel hoses, CSM's enhanced resistance to fuel permeation and chemical attack extends service life and reliability under harsh chemical exposure conditions.
Fuel Permeability and Barrier Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior fuel permeability resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced chemical stability and cross-linked polymer structure, which significantly reduces hydrocarbon diffusion. The barrier performance of CSM is notably higher, enabling it to withstand aggressive fuels and additives without degradation, making it ideal for high-performance fuel hose applications. NBR, while cost-effective and widely used, generally demonstrates higher fuel permeability rates and lower resistance to aromatic fuels and solvents, limiting its service life in demanding environments.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining performance in continuous temperatures up to 135degC and intermittent exposure up to 150degC, outperforming nitrile rubber (NBR), which typically withstands continuous temperatures up to 100degC with limited thermal stability beyond 120degC. Thermal stability of CSM fuel hoses offers enhanced resistance to heat aging, oxidation, and ozone degradation, ensuring longer service life in high-temperature environments compared to NBR hoses. Nitrile rubber, while effective against petroleum-based fuels and oils, demonstrates reduced durability at elevated temperatures due to its lower thermal decomposition point and susceptibility to thermal hardening.
Mechanical Properties: Flexibility and Durability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior durability and excellent flexibility, making it highly resistant to fuel, weathering, and ozone exposure, which extends the lifespan of fuel hoses in harsh environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides strong resistance to oil and fuel but tends to have lower flexibility and less resistance to ozone and weathering compared to CSM. For fuel hoses requiring enhanced mechanical performance, CSM's balanced flexibility and durability often outperform NBR, especially in demanding outdoor conditions.
Cost Analysis: CSM vs NBR for Fuel Hoses
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber generally incurs higher initial material costs compared to Nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced chemical resistance and durability in fuel hose applications. NBR offers a cost-effective solution with lower price points, making it suitable for standard fuel hoses where moderate resistance to fuels and oils is sufficient. The long-term cost benefits of CSM emerge from its extended service life and reduced maintenance needs, offsetting the upfront expense in demanding operational environments.
Industry Applications and Standards Compliance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hoses in harsh industrial environments such as automotive and petrochemical sectors, meeting standards like SAE J30 and ISO 15540. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in fuel and oil resistance, widely used for fuel hose applications requiring compatibility with gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuels, complying with standards including SAE J30 Type A and D and ASTM D2000. Both materials ensure durability and safety in fuel hose manufacturing, with CSPE preferred for outdoor exposure and NBR favored for its superior fuel resistance and flexibility.
Conclusion: Optimal Rubber Choice for Fuel Hoses
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance, ozone resistance, and durability in fuel hose applications compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), which is more susceptible to fuel permeation and degradation over time. The enhanced resistance of CSM to a wide range of fuels, oils, and environmental factors makes it the optimal material for fuel hoses used in demanding automotive and industrial settings. Selecting CSM rubber ensures longer service life, reduced maintenance, and improved safety performance in fuel hose systems.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com