Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in belt applications. TPV's enhanced durability and thermal stability provide longer belt lifespan and improved performance under dynamic stress.
Table of Comparison
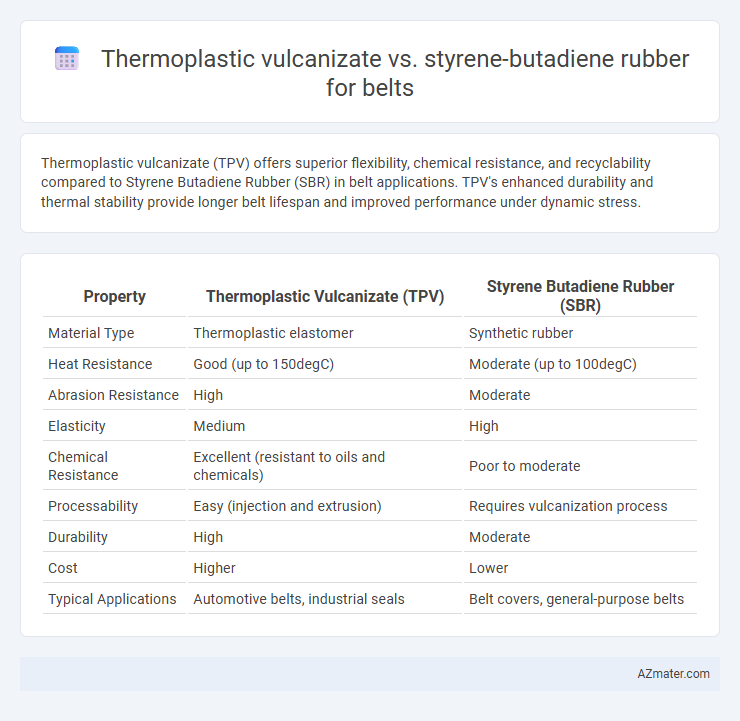
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Synthetic rubber |
| Heat Resistance | Good (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 100degC) |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Elasticity | Medium | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to oils and chemicals) | Poor to moderate |
| Processability | Easy (injection and extrusion) | Requires vulcanization process |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | Automotive belts, industrial seals | Belt covers, general-purpose belts |
Introduction to Thermoplastic Vulcanizate and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) is a class of thermoplastic elastomers combining the elastic properties of vulcanized rubber with the processing advantages of thermoplastics, offering excellent durability and flexibility for belt applications. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its good abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in conveyor belts and mechanical belts. TPV stands out for its superior weather resistance and thermal stability, while SBR remains a preferred choice for applications requiring high wear resistance and moderate flexibility.
Key Properties of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) for Belt Applications
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) for belts offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, ensuring long-lasting durability under dynamic stress conditions. Its enhanced chemical resistance and thermal stability outperform Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), allowing TPV belts to maintain performance in harsher environments. TPV's ability to be processed like a thermoplastic enables precision molding for complex belt designs, improving overall operational efficiency.
Essential Characteristics of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Belt Manufacturing
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in belt manufacturing offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it ideal for high-wear environments. Its inherent flexibility and resilience contribute to enhanced belt durability and reduced maintenance requirements compared to thermoplastic vulcanizates. Additionally, SBR's cost-effectiveness and ability to maintain mechanical properties under varying temperatures make it a preferred choice for industrial belt applications.
Comparative Mechanical Performance: TPV vs SBR in Belts
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) exhibit superior abrasion resistance and flexibility compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making them highly durable for belt applications under dynamic stress. TPVs demonstrate better compression set and tensile strength retention over a wide temperature range, enhancing belt longevity in harsh environments. In contrast, SBR offers excellent tear resistance and resilience but tends to degrade faster when exposed to oils and UV radiation, limiting its performance in industrial belt systems.
Chemical Resistance: Thermoplastic Vulcanizate vs Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), especially against oils, solvents, and acids commonly encountered in industrial belt applications. TPV's cross-linked thermoplastic structure provides enhanced durability and resistance to swelling or degradation when exposed to hydrocarbons and chemical agents. In contrast, SBR shows moderate chemical resistance but tends to absorb oils and degrade faster under harsh chemical environments, reducing belt lifespan and performance.
Flexibility and Durability: Which Offers Better Service Life?
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) exhibit superior flexibility compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), maintaining elasticity at varying temperatures which enhances belt performance in dynamic applications. TPVs also offer improved durability through enhanced resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical degradation, extending the service life of belts in harsh operational environments. Although SBR provides decent wear resistance, TPV's combination of thermoplastic processing advantages and vulcanizate strength results in longer-lasting belt solutions with optimized flexibility and toughness.
Temperature Resistance: TPV vs SBR Under Varying Conditions
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), maintaining stability and flexibility up to approximately 150degC, whereas SBR typically withstands temperatures only up to around 100degC before degradation occurs. TPV's enhanced thermal performance makes it suitable for belts operating under continuous high-heat conditions, providing better durability and reduced risk of cracking or hardening. In contrast, SBR is more prone to thermal aging and deformation under elevated temperatures, limiting its application in high-temperature belt environments.
Processing and Fabrication Differences in Belt Production
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers easier processing for belt production due to its ability to be injection molded and extruded like thermoplastics, reducing cycle times and enabling complex shapes with high dimensional stability. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) requires traditional vulcanization processes involving heat and sulfur curing, which extend fabrication time and limit design flexibility. TPV belts benefit from recyclability and faster turnaround, whereas SBR belts provide superior abrasion resistance but demand more labor-intensive processing techniques.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability: TPV vs SBR
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior cost-effectiveness compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) for belt applications due to its recyclability and ability to be reprocessed, reducing material waste and production costs. TPV's consistent performance under thermal and mechanical stress extends belt lifespan, lowering replacement frequency and overall operational expenses. SBR, while offering good abrasion resistance, often involves higher environmental impact due to its non-recyclable nature and reliance on petrochemical feedstocks, making TPV a more sustainable choice in long-term industrial use.
Choosing the Right Material: TPV or SBR for Belt Applications
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for belts exposed to harsh chemicals and fluctuating temperatures. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for heavy-duty belt applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Selecting TPV or SBR depends on specific operational environments, with TPV favored for flexibility and chemical exposure, while SBR excels in high-stress, abrasion-intensive conditions.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com