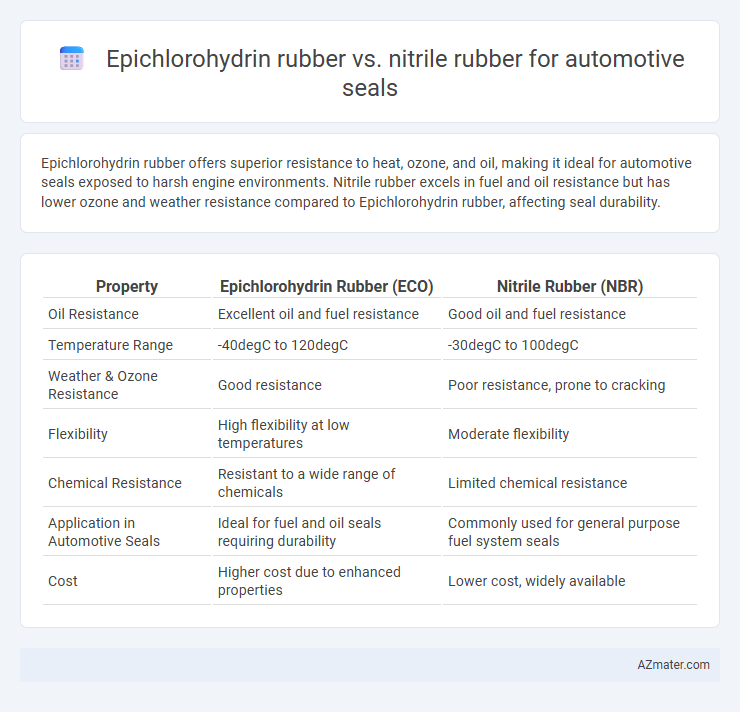
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oil, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel and oil resistance but has lower ozone and weather resistance compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, affecting seal durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Good oil and fuel resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Good resistance | Poor resistance, prone to cracking |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to a wide range of chemicals | Limited chemical resistance |
| Application in Automotive Seals | Ideal for fuel and oil seals requiring durability | Commonly used for general purpose fuel system seals |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance, providing durable sealing solutions in engine compartments and fuel systems. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the specific automotive application requirements, including chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and oil, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh environments. Its low permeability to gases and good flexibility at low temperatures provide superior sealing performance compared to nitrile rubber in coolant and transmission applications. Unlike nitrile rubber, ECO exhibits improved resistance to weathering and chemical degradation, enhancing durability in engine and transmission systems.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in automotive seals due to its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons, making it ideal for harsh engine environments. Compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, NBR offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance but has lower resistance to ozone and weathering. This balance of chemical resistance and mechanical performance positions nitrile rubber as a preferred material for fuel system seals, gaskets, and O-rings in modern vehicles.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECH) exhibits superior oil resistance and excellent gas permeability compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to fuel and coolant fluids. Nitrile rubber offers higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, supporting durability under mechanical stress in dynamic sealing applications. Both materials provide good compression set resistance, but ECH typically outperforms NBR in low-temperature flexibility, enhancing seal performance in extreme environments.
Chemical Resistance: Epichlorohydrin vs Nitrile Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents, making it highly effective for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber demonstrates excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and non-polar solvents but performs poorly against ozone and weathering compared to epichlorohydrin. The balanced chemical resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced durability and longevity in automotive sealing applications where both oil and weather resistance are critical.
Temperature Performance in Automotive Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to low temperatures down to -40degC, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to cold climates, whereas Nitrile rubber (NBR) typically performs well up to 100degC but becomes brittle below -30degC. ECO exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, heat aging, and automotive fluids, maintaining flexibility and sealing integrity from -40degC to 120degC, outperforming NBR in sustained high-temperature environments. Nitrile rubber is favored for its fuel and oil resistance but has limited temperature resilience compared to Epichlorohydrin in demanding automotive sealing applications.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to ozone cracking and prolonged ultraviolet exposure, ensuring longer seal life and reliability. Nitrile rubber, while effective against oils and fuels, is less resistant to ozone and weathering, limiting its durability in outdoor auto applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate cost and good chemical resistance but is less commonly available than nitrile rubber, which is widely used in automotive seals due to its lower price and broad accessibility. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil and fuel resistance at a more competitive cost, making it a preferred choice for large-scale automotive manufacturing. Availability of nitrile rubber in various hardness grades and formulations supports cost-effective production and ensures consistent supply for automotive sealing applications.
Typical Automotive Seal Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber excels in automotive seal applications requiring excellent oil resistance, low gas permeability, and superior heat resistance, making it ideal for coolant system hoses, transmission seals, and vapor recovery systems. Nitrile rubber is commonly used in fuel system seals, engine gaskets, and oil seals due to its outstanding resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. Both materials are selected based on the specific chemical exposure and temperature ranges encountered in automotive sealing environments.
Final Recommendation: Choosing Between Epichlorohydrin and Nitrile Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and fuels, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environments and variable temperatures. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance but may degrade faster under prolonged ozone exposure and extreme weather conditions. For automotive seals requiring durability in fuel-rich, high-temperature environments with frequent ozone exposure, epichlorohydrin rubber is the preferred choice, while nitrile rubber suits applications prioritizing cost-effectiveness and oil resistance.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com