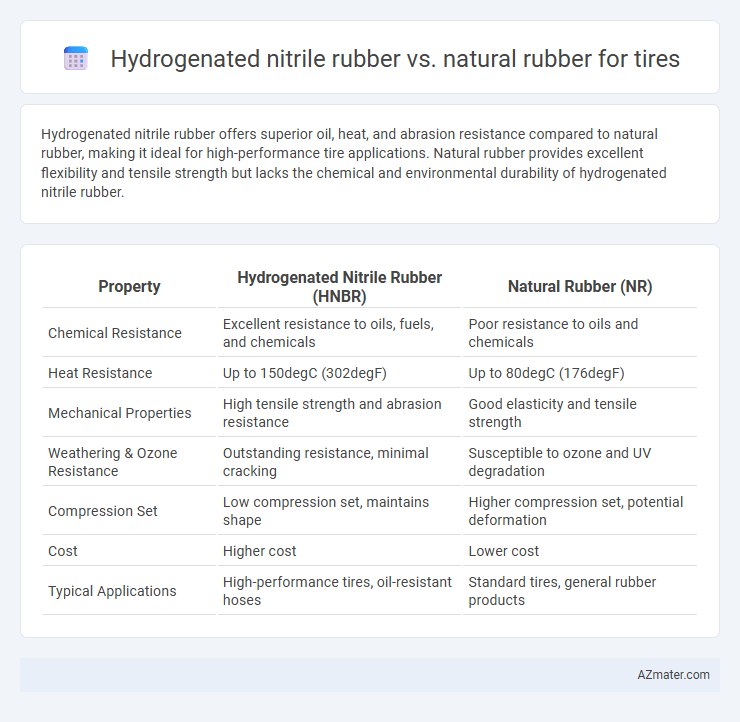
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber offers superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and tensile strength but lacks the chemical and environmental durability of hydrogenated nitrile rubber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Good elasticity and tensile strength |
| Weathering & Ozone Resistance | Outstanding resistance, minimal cracking | Susceptible to ozone and UV degradation |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains shape | Higher compression set, potential deformation |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Typical Applications | High-performance tires, oil-resistant hoses | Standard tires, general rubber products |
Introduction to Tire Rubber Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and abrasion durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications. Natural rubber excels in elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, providing excellent grip and flexibility essential for standard tire tread and sidewall components. Selecting between HNBR and natural rubber depends on specific tire performance requirements, including temperature ranges, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance, heat tolerance up to 150degC, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for tire manufacturing in demanding environments. Compared to natural rubber, HNBR offers enhanced durability against oil, fuel, and oxidative degradation, significantly extending tire lifespan. Its ability to maintain mechanical properties under extreme temperatures provides improved performance and reliability in automotive and industrial tire applications.
Characteristics of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber offers exceptional elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, making it highly effective for tire applications requiring superior grip and durability under varied road conditions. Its excellent resistance to fatigue and ability to maintain flexibility across a wide temperature range contribute to enhanced performance and safety. Unlike hydrogenated nitrile rubber, natural rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and natural wear characteristics essential for long-lasting tire tread life.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and heat aging properties compared to natural rubber, making it highly suitable for high-performance tire applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tear resistance but suffers from lower ozone and chemical resistance, leading to faster degradation under harsh conditions. The mechanical advantage of HNBR in maintaining durability and flexibility at elevated temperatures ensures enhanced tire longevity and performance under demanding operating environments.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, maintaining performance at temperatures up to 150degC, compared to natural rubber, which typically degrades above 80degC. HNBR also exhibits enhanced chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for tires exposed to harsh environments. Natural rubber, while flexible and having good elasticity, lacks the durability needed for high-temperature and chemical exposure in demanding tire applications.
Wear and Aging Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior wear resistance and aging stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. HNBR's enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation extends tire lifespan by maintaining elasticity and physical properties over time. Natural rubber, while offering excellent flexibility and grip, tends to degrade faster due to susceptibility to environmental factors, resulting in reduced wear resistance and shorter aging performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and ozone compared to natural rubber, reducing tire degradation and extending tire lifespan, which contributes to lower environmental waste. Natural rubber, derived from rubber tree plantations, is renewable and biodegradable, but its cultivation involves significant land use and deforestation concerns. The environmental impact of HNBR depends on synthetic production from petrochemicals, whereas natural rubber's sustainability relies on responsible agricultural practices and biodiversity conservation.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it cost-effective for high-performance tire applications despite higher raw material expenses. Manufacturing with HNBR requires specialized compounding and curing processes that can increase production complexity and initial investment. Natural rubber remains more economical due to lower material costs and simpler processing, but its susceptibility to degradation often results in shorter tire lifespan and higher replacement frequency.
Typical Applications in Tire Production
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is widely used in tire production for its superior resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemicals, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads and sidewalls. Natural rubber remains essential in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, primarily used in passenger car tires and truck tire carcasses. The combination of HNBR and natural rubber enhances tire durability, fuel efficiency, and wear resistance across various tire types.
Future Trends in Tire Material Development
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance compared to natural rubber, making it increasingly favored for performance tire manufacturing. Future trends emphasize the integration of HNBR in tire compounds to enhance durability, fuel efficiency, and environmental sustainability through improved wear resistance and reduced rolling resistance. Advancements in polymer blending and catalyst technology are expected to optimize HNBR's mechanical properties, positioning it as a key material in the evolving tire industry.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com