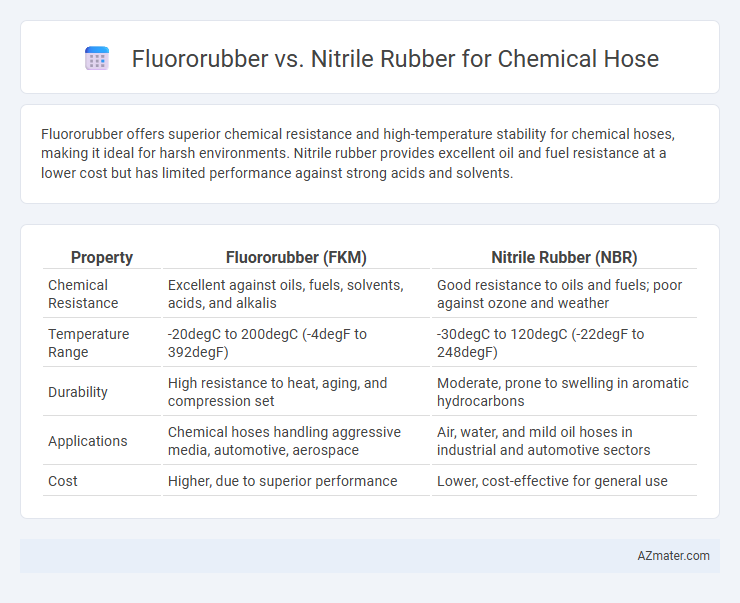
Fluororubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability for chemical hoses, making it ideal for harsh environments. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil and fuel resistance at a lower cost but has limited performance against strong acids and solvents.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluororubber (FKM) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils, fuels, solvents, acids, and alkalis | Good resistance to oils and fuels; poor against ozone and weather |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) | -30degC to 120degC (-22degF to 248degF) |
| Durability | High resistance to heat, aging, and compression set | Moderate, prone to swelling in aromatic hydrocarbons |
| Applications | Chemical hoses handling aggressive media, automotive, aerospace | Air, water, and mild oil hoses in industrial and automotive sectors |
| Cost | Higher, due to superior performance | Lower, cost-effective for general use |
Introduction to Fluororubber and Nitrile Rubber
Fluororubber, known for its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and durability, is commonly used in chemical hoses exposed to aggressive fluids and extreme environments. Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals, making it a cost-effective choice for applications requiring good mechanical strength and flexibility. Both materials provide unique advantages, with fluororubber excelling in harsh chemical resistance and nitrile rubber favored for its affordability and oil resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Fluororubber (FKM) consists primarily of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene, giving it a highly stable carbon-fluorine bond structure that provides exceptional resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, fuels, and solvents. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is composed of copolymerized acrylonitrile and butadiene, featuring polar nitrile groups that offer good resistance to hydrocarbons and oils but lower chemical resistance compared to fluororubber. The molecular structure of fluororubber's perfluorinated backbone enhances its thermal and chemical stability, making it superior for aggressive chemical hose applications, whereas nitrile rubber's less fluorinated structure limits its performance to less harsh environments.
Key Physical Properties
Fluororubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and excellent compression set performance, making it ideal for harsh chemical hose applications. Nitrile rubber offers strong resistance to oils and fuels, with a temperature range typically between -40degC to 120degC, and maintains good abrasion resistance and tensile strength. Both materials provide effective sealing but fluororubber outperforms in environments requiring prolonged chemical exposure and elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Fluororubber offers superior chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber, particularly against aggressive solvents, oils, and fuels, making it ideal for demanding chemical hose applications. Nitrile rubber performs well with petroleum-based fluids but shows vulnerability to aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and chlorinated solvents, limiting its use in highly corrosive environments. Fluororubber's resistance to a broader range of chemicals and higher temperature tolerance enhances hose durability and safety in industrial settings.
Temperature Tolerance Differences
Fluororubber exhibits exceptional temperature tolerance, withstanding continuous exposure from -26degC to 204degC, making it ideal for high-heat chemical hose applications. Nitrile rubber operates effectively within a narrower range, typically from -40degC to 120degC, but excels in oil resistance and flexibility at lower temperatures. Choosing fluororubber over nitrile rubber enhances durability in extreme thermal environments while nitrile remains suitable for moderate heat and oil-based chemical transport.
Abrasion and Wear Characteristics
Fluororubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and wear characteristics compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for chemical hoses exposed to harsh environments and aggressive chemicals. Its high resistance to swelling, heat, and oxidation ensures longer hose life, especially in applications involving oils, fuels, and solvents. Nitrile rubber offers good abrasion resistance but typically degrades faster under chemical exposure and elevated temperatures, resulting in shorter service intervals.
Flexibility and Handling in Chemical Hoses
Fluororubber exhibits superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability but tends to be less flexible than nitrile rubber, affecting ease of handling in chemical hoses. Nitrile rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience in a wide range of temperatures, making it easier to maneuver and install in dynamic applications. For chemical hoses requiring frequent bending or handling, nitrile rubber often provides better performance without compromising durability in moderate chemical environments.
Cost Considerations and Economical Use
Fluororubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature durability for chemical hoses, but its higher material and manufacturing costs make it less economical for general applications. Nitrile rubber provides a cost-effective alternative with good resistance to oils and fuels, making it suitable for less aggressive chemical environments and budget-sensitive projects. Selecting between fluororubber and nitrile rubber depends on balancing chemical compatibility requirements with overall budget constraints to optimize hose lifespan and maintenance expenses.
Common Applications in Chemical Hose Industry
Fluororubber hoses excel in handling aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and fuels, making them ideal for applications in the automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceutical industries. Nitrile rubber hoses are commonly used for petroleum-based fluids, oils, and greases, frequently found in hydraulic systems, fuel lines, and industrial machinery. The chemical hose industry selects fluororubber for superior chemical resistance and nitrile rubber for cost-effective solutions requiring good oil and abrasion resistance.
Choosing the Right Material for Chemical Hose Solutions
Fluororubber offers superior resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and oils, making it ideal for demanding chemical hose applications requiring durability and chemical inertness. Nitrile rubber provides excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it cost-effective for less aggressive chemical environments. Selecting the right material depends on the chemical composition, temperature range, and pressure conditions of the hose application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Fluororubber vs Nitrile rubber for Chemical hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com