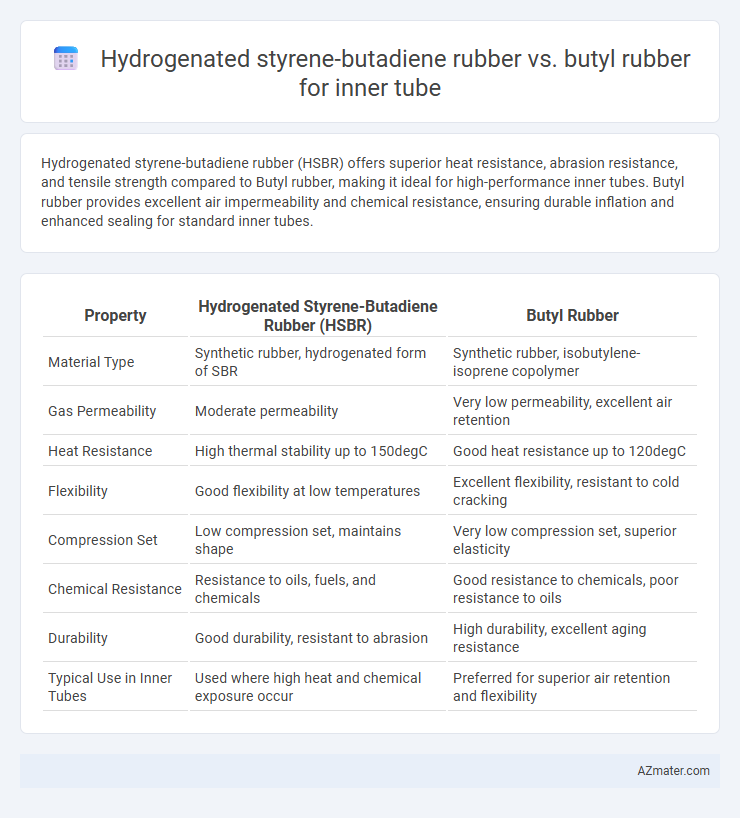
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength compared to Butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-performance inner tubes. Butyl rubber provides excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, ensuring durable inflation and enhanced sealing for standard inner tubes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber, hydrogenated form of SBR | Synthetic rubber, isobutylene-isoprene copolymer |
| Gas Permeability | Moderate permeability | Very low permeability, excellent air retention |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability up to 150degC | Good heat resistance up to 120degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent flexibility, resistant to cold cracking |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains shape | Very low compression set, superior elasticity |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to chemicals, poor resistance to oils |
| Durability | Good durability, resistant to abrasion | High durability, excellent aging resistance |
| Typical Use in Inner Tubes | Used where high heat and chemical exposure occur | Preferred for superior air retention and flexibility |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to traditional styrene-butadiene rubber, making it suitable for high-performance inner tube applications. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, remains the industry standard for inner tubes requiring superior airtightness and durability. Selecting between HSBR and butyl rubber depends on performance priorities such as flexibility, air retention, and resistance to environmental degradation in inner tube manufacturing.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and aging compared to traditional styrene-butadiene rubber, making it highly durable for inner tube applications. Its improved chemical stability and low gas permeability contribute to prolonged tire life and safety. HSBR's mechanical strength and flexibility balance maintain performance under various operating conditions, outperforming Butyl rubber in high-temperature environments.
Properties of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber (IIR) exhibits excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for inner tube applications where air retention is crucial. It has superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals compared to hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR), enhancing durability and longevity under harsh conditions. Its low permeability and high resilience ensure reliable performance and extended service life in tires and inner tubes.
Air Retention Performance Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior air retention compared to butyl rubber when used in inner tubes due to its enhanced gas impermeability and resistance to oxidative degradation. HSBR's tighter polymer network reduces helium and nitrogen diffusion rates, resulting in prolonged inflation intervals and improved tire pressure stability. While butyl rubber offers good overall air retention and cost efficiency, HSBR provides a technologically advanced solution for applications demanding extended air retention and durability.
Durability and Aging Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior aging resistance and enhanced durability compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. HSBR exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, heat, and oxidative degradation, thereby extending the lifespan of inner tubes and reducing maintenance needs. While butyl rubber provides good air retention and chemical resistance, HSBR's improved mechanical strength and longevity deliver better performance in demanding applications.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance compared to butyl rubber, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for high-heat inner tube applications. Chemically, HSBR exhibits enhanced resistance to oils, fuels, and oxidation due to hydrogenation, providing greater durability in harsh environments. In contrast, butyl rubber excels in gas impermeability but has lower heat resistance, typically up to 100degC, and moderate chemical resistance, limiting its use where elevated temperatures and aggressive chemicals are present.
Ride Comfort and Flexibility
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior flexibility and resilience compared to butyl rubber, enhancing ride comfort by better absorbing road vibrations. HSBR's molecular structure provides excellent elasticity, allowing inner tubes to maintain shape under varying pressure without compromising flexibility. Butyl rubber, while highly impermeable and durable, tends to be stiffer, which can result in a less cushioned ride experience.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat stability compared to butyl rubber, but its higher raw material and processing costs affect overall expenditure for inner tube manufacturing. Butyl rubber's lower cost and simpler production process provide economic advantages, making it a common choice for mass-produced inner tubes despite its lower durability. Manufacturers balance cost-effectiveness and performance, often selecting butyl rubber for budget-sensitive applications and HSBR when enhanced wear resistance justifies the premium price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers improved resistance to oxidative degradation, extending inner tube lifespan and reducing waste generation compared to traditional butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, while effective for impermeability and flexibility, is derived predominantly from petroleum-based sources, contributing to higher carbon emissions during production. Both materials present challenges in recyclability; however, recent advances in HSBR recycling technologies suggest a potential for enhanced circularity and lower environmental impact in inner tube applications.
Conclusion: HSBR vs Butyl Rubber for Inner Tubes
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and better heat aging properties compared to butyl rubber, making it suitable for high-performance inner tubes requiring enhanced durability. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, remains the preferred choice for inner tubes where airtightness and flexibility are critical. Selecting HSBR versus butyl rubber depends on balancing the need for longevity and mechanical strength versus cost-effectiveness and superior air retention in inner tube applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com