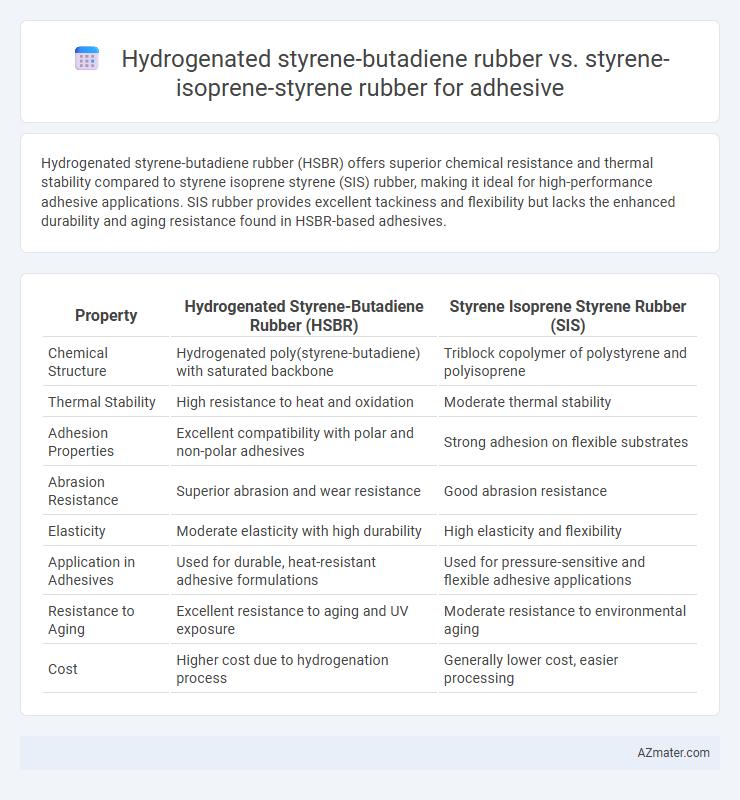
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber, making it ideal for high-performance adhesive applications. SIS rubber provides excellent tackiness and flexibility but lacks the enhanced durability and aging resistance found in HSBR-based adhesives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Styrene Isoprene Styrene Rubber (SIS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Hydrogenated poly(styrene-butadiene) with saturated backbone | Triblock copolymer of polystyrene and polyisoprene |
| Thermal Stability | High resistance to heat and oxidation | Moderate thermal stability |
| Adhesion Properties | Excellent compatibility with polar and non-polar adhesives | Strong adhesion on flexible substrates |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion and wear resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity with high durability | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Application in Adhesives | Used for durable, heat-resistant adhesive formulations | Used for pressure-sensitive and flexible adhesive applications |
| Resistance to Aging | Excellent resistance to aging and UV exposure | Moderate resistance to environmental aging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to hydrogenation process | Generally lower cost, easier processing |
Introduction to Adhesive Polymers
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) rubber, making HSBR ideal for high-performance adhesive applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. SIS rubber provides excellent elasticity and tackiness, resulting in strong initial bond strength and flexibility in pressure-sensitive adhesives. These intrinsic polymer properties influence adhesive formulation choices, with HSBR favored for structural adhesives and SIS preferred for flexible, removable adhesives.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its enhanced chemical resistance, improved thermal stability, and excellent aging properties due to hydrogenation of the polybutadiene segment. Compared to Styrene Isoprene Styrene (SIS) rubber, HSBR offers superior resistance to oils, solvents, and ozone, making it highly suitable for adhesive formulations requiring durability under harsh conditions. The hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation, resulting in lower gas permeability and improved mechanical strength, which enhances adhesive performance in automotive and industrial applications.
Overview of Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Rubber (SIS)
Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene (SIS) rubber is a block copolymer known for its excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior resistance to aging and UV exposure, making it ideal for adhesive applications requiring flexibility and durability. Compared to Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR), SIS offers enhanced tackiness and improved low-temperature performance, which contribute to stronger bonding and consistent adhesive properties. Its thermoplastic elastomer nature allows for easier processing and recycling, providing significant advantages in pressure-sensitive adhesives and sealants.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) consists of a saturated polybutadiene backbone with styrene end blocks, featuring enhanced thermal and chemical stability due to hydrogenation. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) rubber is a block copolymer with polystyrene end blocks and a polyisoprene mid-block, providing a balance of elasticity and tackiness from the unsaturated isoprene segments. The hydrogenation in HSBR reduces double bonds, improving oxidative resistance, while SIS retains unsaturation, contributing to superior adhesive properties but lower thermal stability.
Adhesion Properties: HSBR vs SIS
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior oxidation and thermal stability compared to styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber, enhancing long-term adhesion performance in demanding environments. HSBR's saturated polymer backbone provides better resistance to chemical degradation, resulting in stronger and more durable adhesive bonds on various substrates. Conversely, SIS exhibits higher tackiness and flexibility but lower resistance to heat and aging, making HSBR the preferred choice for applications requiring robust adhesion under harsh conditions.
Thermal and Oxidative Stability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior thermal and oxidative stability compared to styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber, making HSBR more suitable for adhesive applications exposed to high temperatures and oxidative environments. The saturation of double bonds in HSBR's polymer backbone enhances resistance to thermal degradation and oxidation, prolonging adhesive performance under harsh conditions. In contrast, SIS contains unsaturated isoprene segments prone to oxidation, resulting in reduced durability and shorter adhesive lifespan when exposed to heat and oxygen.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior mechanical strength due to its enhanced resistance to heat and chemical degradation, making it ideal for adhesives requiring durability under stress. Styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber exhibits greater flexibility and elasticity owing to its block copolymer structure, enabling adhesives to maintain strong bonds under dynamic movement and deformation. For applications demanding a balance of mechanical strength and flexibility, HSBR provides robustness, while SIS excels in elasticity for flexible adhesive formulations.
Processing and Compatibility with Formulations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior thermal and oxidative stability compared to styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) rubber, enhancing its processing consistency in adhesive formulations. HSBR exhibits better compatibility with polar solvents and crosslinking agents due to its saturated polymer backbone, facilitating more uniform curing and improved adhesive strength. SIS rubber provides excellent tack and flexibility but may require specialized processing conditions and additives to achieve optimal formulation stability and performance.
Typical Applications in Adhesive Industries
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) is widely used in adhesives requiring enhanced chemical resistance, weatherability, and thermal stability, making it ideal for automotive and construction sealants. Styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber excels in pressure-sensitive adhesives due to its superior tackiness, flexibility, and elastomeric properties, commonly applied in tapes, labels, and medical adhesives. Both polymers are selected based on performance demands, with HSBR favored for durable, high-performance bonding and SIS chosen for removable or repositionable adhesive solutions in packaging and hygiene products.
Sustainability and Cost Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical and oxidative resistance, increasing the durability and lifespan of adhesives, which contributes to sustainability by reducing frequent replacements and waste. Styrene isoprene styrene (SIS) rubber, while providing excellent flexibility and tack, tends to have higher raw material costs and lower thermal stability, impacting overall cost-effectiveness. HSBR's longer service life and lower volatility align better with eco-friendly adhesive formulations aiming to minimize environmental impact and optimize long-term cost savings.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Styrene isoprene styrene rubber for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com