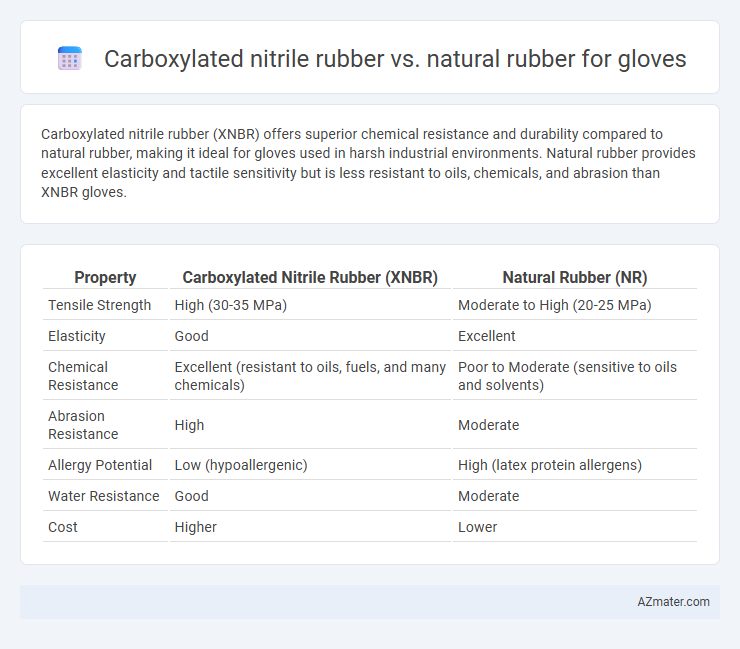
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for gloves used in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity but is less resistant to oils, chemicals, and abrasion than XNBR gloves.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (30-35 MPa) | Moderate to High (20-25 MPa) |
| Elasticity | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to oils, fuels, and many chemicals) | Poor to Moderate (sensitive to oils and solvents) |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Allergy Potential | Low (hypoallergenic) | High (latex protein allergens) |
| Water Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Glove Materials: NBR and Natural Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and tensile strength compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for industrial and medical gloves requiring superior durability. Natural rubber excels in elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, preferred for tasks demanding high dexterity and touch sensitivity. Both materials serve critical roles in glove manufacturing, with XNBR often chosen for chemical resistance and natural rubber favored for flexibility and biodegradability.
Chemical Composition: Carboxylated Nitrile vs Natural Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains nitrile groups with carboxyl functional groups (-COOH) that enhance oil resistance, chemical stability, and tensile strength in gloves. Natural rubber (NR) is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, providing excellent elasticity and flexibility but lower chemical and oil resistance compared to XNBR. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR facilitates cross-linking and improves mechanical properties, making it superior for gloves exposed to harsh chemicals.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength and durability compared to natural rubber gloves due to enhanced cross-linking and resistance to abrasion, punctures, and oils. The carboxyl groups in XNBR improve tensile strength and elongation at break, resulting in gloves that maintain integrity under rigorous use. Natural rubber gloves, while flexible and comfortable, tend to degrade faster when exposed to chemicals and mechanical stress, limiting their lifespan in industrial applications.
Chemical Resistance: Solvents, Oils, and Acids
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and acids compared to natural rubber, due to its enhanced cross-linking and polar carboxyl groups that improve barrier properties and durability. Natural rubber tends to degrade quickly when exposed to petroleum-based solvents and strong acids, limiting its effectiveness in harsh chemical environments. XNBR gloves provide extended protection and longevity in industrial applications where exposure to aggressive chemicals is frequent.
Comfort, Fit, and Skin Sensitivity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves offer superior comfort and fit due to their enhanced elasticity and resilience, reducing hand fatigue during prolonged use compared to natural rubber gloves. These gloves provide excellent skin sensitivity, allowing precise tactile feedback and dexterity critical for medical and laboratory tasks. Natural rubber gloves may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, whereas carboxylated nitrile rubber significantly lowers the risk of latex allergies, making them a safer option for sensitive skin.
Allergic Reactions: Latex vs Latex-Free Gloves
Carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves offer a latex-free alternative that significantly reduces the risk of allergic reactions associated with natural rubber latex gloves, which contain proteins that can trigger hypersensitivity in sensitive individuals. These synthetic gloves provide comparable durability and protection without the potential for Type I latex allergies, making them ideal for healthcare and industrial use where frequent glove changes occur. Choosing carboxylated nitrile rubber helps prevent both immediate and delayed allergic responses, ensuring safer handling for users with latex sensitivities.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior cost efficiency compared to natural rubber due to its enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion, reducing replacement frequency in industrial glove applications. Manufacturing processes for XNBR gloves involve complex polymerization and vulcanization techniques that increase initial production costs but yield higher durability and performance. Natural rubber gloves benefit from lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, yet they lack chemical resistance and have a shorter lifespan, impacting long-term cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves offer superior chemical resistance but have a higher environmental impact due to their synthetic origin and slower biodegradability compared to natural rubber gloves. Natural rubber gloves are derived from renewable latex sap and exhibit better biodegradability, breaking down more rapidly in soil and compost environments. Selecting natural rubber reduces reliance on petrochemicals and lowers long-term waste accumulation in landfills.
Industry Applications: Medical, Laboratory, and Industrial Use
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves offer superior chemical resistance, durability, and puncture resistance compared to natural rubber, making them ideal for industrial applications where exposure to oils, solvents, and harsh chemicals is common. In medical and laboratory settings, XNBR gloves provide enhanced protection against bloodborne pathogens and chemical contaminants, ensuring safety without sacrificing tactile sensitivity. Natural rubber gloves, while highly elastic and comfortable, may cause allergic reactions and have limited chemical resistance, restricting their use primarily to general medical examinations and light laboratory tasks.
Choosing the Best Glove Material for Your Needs
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves offer superior chemical resistance, puncture protection, and durability compared to natural rubber, making them ideal for industrial and chemical handling applications. Natural rubber gloves provide excellent elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, suited for medical and general-use tasks requiring dexterity. Selecting between XNBR and natural rubber gloves depends on exposure risks, flexibility needs, and allergy considerations to ensure optimal safety and performance.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Natural rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com