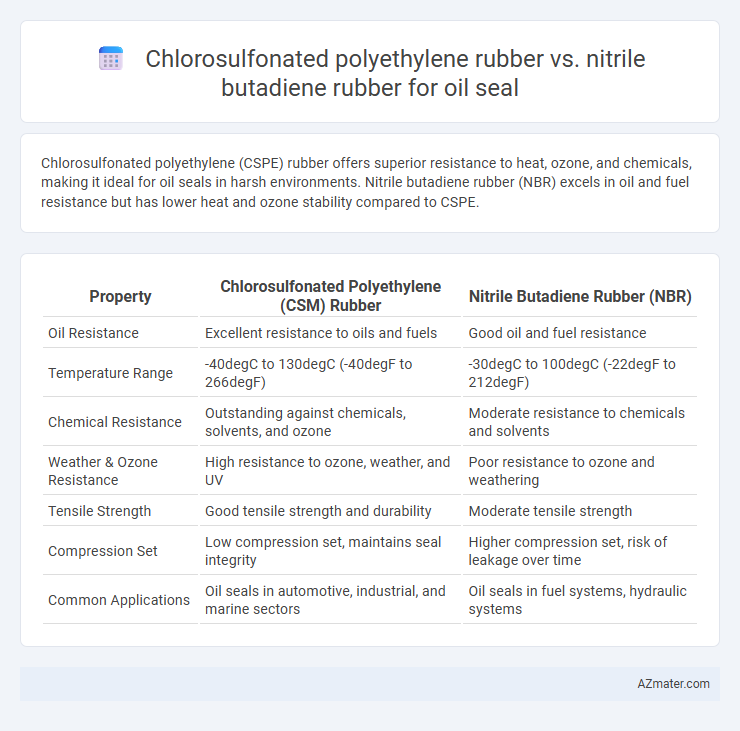
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for oil seals in harsh environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance but has lower heat and ozone stability compared to CSPE.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and fuels | Good oil and fuel resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 130degC (-40degF to 266degF) | -30degC to 100degC (-22degF to 212degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding against chemicals, solvents, and ozone | Moderate resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | High resistance to ozone, weather, and UV | Poor resistance to ozone and weathering |
| Tensile Strength | Good tensile strength and durability | Moderate tensile strength |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains seal integrity | Higher compression set, risk of leakage over time |
| Common Applications | Oil seals in automotive, industrial, and marine sectors | Oil seals in fuel systems, hydraulic systems |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) are commonly used materials for oil seals due to their excellent resistance properties. CSM offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. NBR exhibits excellent oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, providing reliable sealing performance in automotive and industrial applications.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional resistance to oil, weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for oil seal applications in harsh environments. Its unique molecular structure provides enhanced durability and flexibility at a wide temperature range from -40degC to 120degC. Compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), CSM exhibits superior UV stability and resistance to aromatic and aliphatic oils, ensuring longer seal life and reduced maintenance in industrial settings.
Overview of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and other chemicals, making it highly suitable for oil seal applications. It offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and low-temperature flexibility compared to Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) rubber. NBR's ability to maintain performance under dynamic sealing conditions and exposure to petroleum-based fluids highlights its widespread use in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents, making it highly effective for oil seals exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases but shows limited resistance to ozone, weathering, and certain chemicals like ketones and chlorinated hydrocarbons. For oil seals requiring prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals beyond hydrocarbons, CSM provides enhanced chemical stability and durability compared to NBR.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining stability in ranges from -40degC to 125degC, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to fluctuating thermal conditions. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers excellent oil resistance but typically operates effectively between -30degC and 100degC, limiting its use in higher temperature environments. CSM's enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering provides longer service life and reliable sealing performance in demanding oil seal applications.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, exceptional tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it more suitable for oil seal applications exposed to harsh environments. NBR offers good oil and fuel resistance with moderate mechanical properties but generally falls short in durability under extreme temperature and chemical conditions relative to CSM. The enhanced durability and mechanical robustness of CSM contribute to longer service life and better performance in sealing applications involving aggressive oils and solvents.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent resistance to a wide range of oils, fuels, and chemicals, maintaining flexibility and durability in harsh environments, making it suitable for oil seal applications exposed to gasoline, diesel, and hydraulic fluids. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) also provides strong oil and fuel compatibility, especially with petroleum-based fluids, but tends to degrade faster when exposed to aromatic hydrocarbons and certain synthetic oils compared to CSM. The superior chemical inertness and weather resistance of CSM rubber generally result in longer service life for oil seals in aggressive oil and fuel conditions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber generally incurs higher material costs than nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced chemical resistance and weathering durability, making it less cost-effective for standard oil seal applications. NBR offers superior availability as it is widely produced and preferred for oil seals in automotive and industrial markets, contributing to lower lead times and bulk pricing advantages. Cost efficiency favors NBR for large-scale deployments, while CSM is selected for specialized environments demanding increased resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone.
Typical Applications in Oil Seals
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is widely used in oil seals for applications requiring excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for automotive and industrial machinery oil seals operating in harsh environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) is preferred for oil seals in fuel systems, hydraulic systems, and engines due to its superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and lubricants. Both elastomers provide reliable sealing performance, but CSM offers enhanced durability in extreme weather conditions, while NBR excels in oil and fuel resistance for standard sealing applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Oil Seals
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, weathering, and ozone, making it suitable for oil seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, with enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Selecting between CSM and NBR for oil seals depends on specific operating environments, chemical exposure, and temperature ranges, with NBR preferred for high oil compatibility and CSM favored for extreme weather durability.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Nitrile butadiene rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com