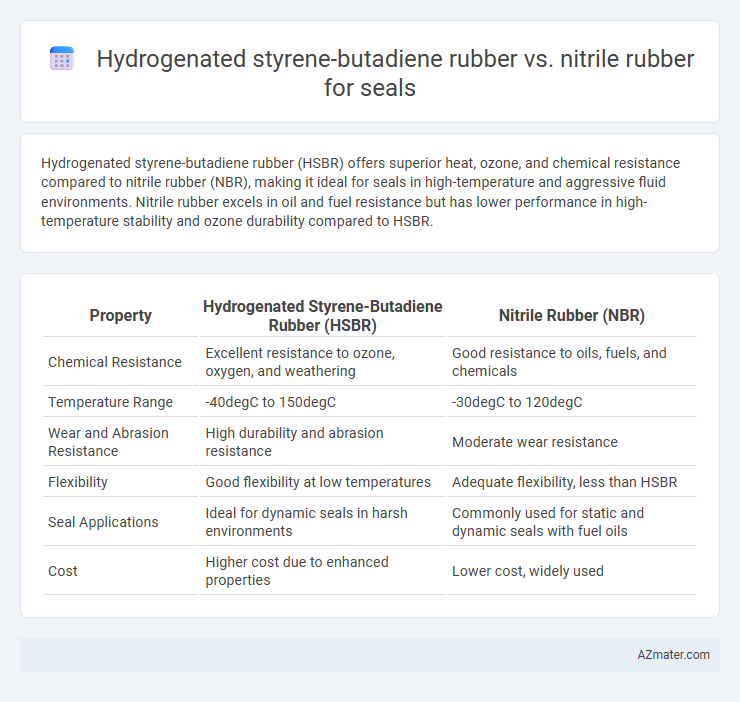
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for seals in high-temperature and aggressive fluid environments. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance but has lower performance in high-temperature stability and ozone durability compared to HSBR.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, oxygen, and weathering | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -30degC to 120degC |
| Wear and Abrasion Resistance | High durability and abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Adequate flexibility, less than HSBR |
| Seal Applications | Ideal for dynamic seals in harsh environments | Commonly used for static and dynamic seals with fuel oils |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to Seal Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior chemical resistance and enhanced thermal stability, making it highly suitable for seals exposed to aggressive environments and high temperatures. Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits excellent oil and fuel resistance alongside good mechanical properties, which makes it a preferred choice for seals in automotive and industrial hydraulic applications. Both materials are widely used in sealing solutions, with HSBR favored in demanding chemical and oxidative conditions, whereas NBR is optimal for applications requiring resistance to petroleum-based fluids.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation, making it highly suitable for sealing applications in harsh environments. Its hydrogenation process saturates the polymer backbone, significantly improving aging stability compared to conventional Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and providing enhanced mechanical properties such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance. HSBR seals offer superior performance in high-temperature and chemically aggressive conditions, positioning them as an advanced alternative to Nitrile Rubber (NBR) in applications requiring extended durability and reliability.
Key Properties of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) boasts superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance compared to Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR), making it ideal for seals in harsh environments. Its excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance enhance durability under mechanical stress and dynamic conditions. Additionally, NBR's wide temperature range from -40degC to 120degC ensures effective sealing performance across diverse industrial applications.
Chemical Resistance: HSBR vs NBR
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), particularly against ozone, oxygen, and heat degradation, making HSBR ideal for seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. NBR, while effective against oils, fuels, and many hydrocarbons, shows limited resistance to ozone, weathering, and certain solvents, resulting in faster degradation in aggressive chemical environments. For applications requiring durable seals with excellent resistance to chemicals like aromatic hydrocarbons and oxidative agents, HSBR provides enhanced longevity and reliability over NBR.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance, maintaining stability and flexibility typically up to 150degC, while nitrile rubber (NBR) performs well in moderate temperatures up to around 120degC but can degrade faster under prolonged heat exposure. HSBR's enhanced saturation of the butadiene segments reduces unsaturation, increasing thermal stability and oxidation resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature seal applications. NBR provides excellent oil resistance but may harden and lose elasticity at elevated temperatures where HSBR remains more durable and resilient.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it highly effective in sealing applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and chemical resistance but generally exhibits lower durability under high mechanical stress and prolonged thermal exposure. The hydrogenation process in HSBR improves its resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation, resulting in longer service life and greater durability for seals in demanding industrial environments.
Compatibility with Industrial Fluids
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits excellent resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels, making it highly compatible with a wide range of industrial fluids, especially in harsh chemical environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and solvents but shows limited performance against aromatic and oxygenated fluids compared to HSBR. For seals exposed to diverse industrial fluids, HSBR provides enhanced chemical stability and longer service life, whereas NBR delivers cost-effective and reliable sealing in mineral oil applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability, making it more suitable for high-performance seals, though it comes at a higher cost compared to nitrile rubber (NBR). Nitrile rubber remains the most cost-efficient choice due to its widespread availability and excellent resistance to oils and fuels, ideal for general sealing applications. The global supply chain for NBR is robust, ensuring lower lead times and prices, whereas HSBR's more complex production and limited suppliers often result in higher procurement costs.
Typical Applications in Sealing
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) is widely used in sealing applications requiring excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive and industrial seals exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance, commonly employed in fuel system seals, gaskets, and hydraulic seals where contact with petroleum products is frequent. Both rubbers provide durable sealing solutions, but HSBR is preferred for high-temperature and outdoor applications, while NBR is favored for chemical and oil exposure.
Which Rubber is Better for Your Seal?
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature and dynamic sealing applications, while nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, suited for automotive and industrial seals exposed to petroleum-based fluids. NBR's excellent tensile strength and resistance to swelling in hydrocarbons often make it the preferred choice for seals in oil and gas industries. Selecting between HSBR and NBR depends primarily on the operational environment, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands of the sealing application.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com