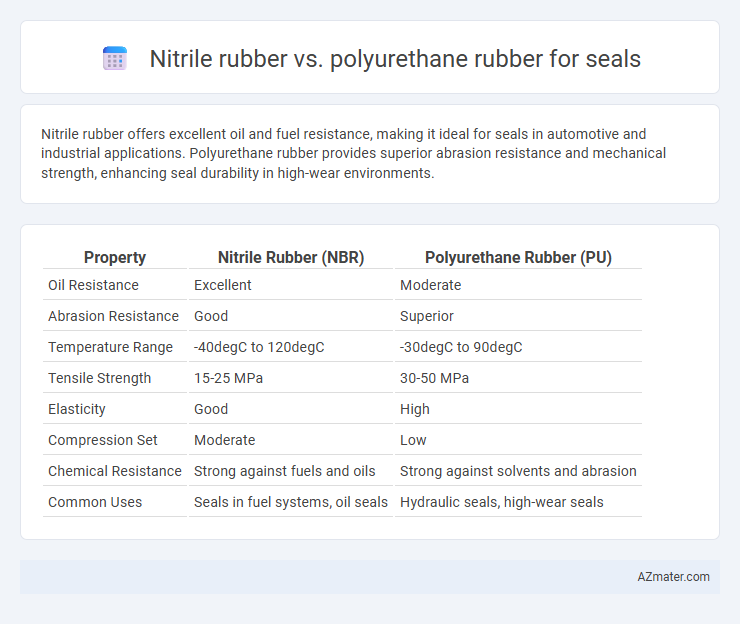
Nitrile rubber offers excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial applications. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, enhancing seal durability in high-wear environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 90degC |
| Tensile Strength | 15-25 MPa | 30-50 MPa |
| Elasticity | Good | High |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Strong against fuels and oils | Strong against solvents and abrasion |
| Common Uses | Seals in fuel systems, oil seals | Hydraulic seals, high-wear seals |
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber and Polyurethane Rubber
Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, is widely used in seals for automotive and industrial applications due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent tear resistance, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh mechanical stress and dynamic conditions. Both materials provide distinct advantages depending on the sealing environment, with nitrile rubber favoring chemical resistance and polyurethane excelling in mechanical performance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by its polar nitrile groups that provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. Polyurethane rubber (PU) consists of segmented polymers formed from polyols and diisocyanates, featuring hard and soft segments that deliver superior abrasion resistance and elasticity. The chemical structure of NBR favors oil and fuel sealing applications, while PU's urethane linkages offer enhanced mechanical strength in dynamic sealing environments.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits excellent tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making it highly durable for seals in oil and fuel applications, while maintaining moderate flexibility. Polyurethane rubber offers superior tensile strength and exceptional elasticity combined with higher tear resistance, which enhances its lifespan and performance under dynamic mechanical stress. For sealing applications requiring a balance of high mechanical strength and flexibility, polyurethane rubber typically outperforms nitrile rubber, especially in heavy-duty or high-wear environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to a wide range of oils, fuels, and many chemicals, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial applications. Polyurethane rubber (PU) provides superior abrasion and tear resistance but has limited chemical resistance, especially to petroleum-based oils and solvents. When selecting seals for chemical and oil exposure, nitrile rubber is generally preferred due to its balanced durability and chemical compatibility.
Temperature Resistance and Performance
Nitrile rubber exhibits excellent resistance to temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making it highly effective for seals exposed to moderate thermal conditions and oil-based fluids. Polyurethane rubber outperforms nitrile in high-performance sealing applications with a broader temperature range from -30degC to 130degC, offering superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength. Choosing between nitrile and polyurethane seals depends on specific temperature requirements and the need for durability in harsh environments.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and wear durability, making it ideal for seals exposed to oils, fuels, and mechanical stress. Polyurethane rubber (PU) surpasses nitrile in wear resistance, providing superior toughness and resilience against tearing and mechanical abrasion in dynamic sealing applications. Selecting polyurethane seals enhances longevity and performance in high-abrasion environments, while nitrile remains cost-effective for moderate wear conditions.
Longevity and Durability in Seal Applications
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it exceptionally durable in harsh seal applications where exposure to petroleum-based fluids is common. Polyurethane rubber provides outstanding abrasion resistance and tensile strength, resulting in extended longevity under mechanical stress and in dynamic sealing environments. The choice between nitrile and polyurethane seals depends on the specific operating conditions, with nitrile excelling in chemical compatibility and polyurethane favoring wear resistance and mechanical durability.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability, making it the preferred choice for seals in many industrial applications due to its competitive pricing and robust supply chain. Polyurethane rubber, while generally more expensive, provides superior abrasion resistance and durability, which can justify the higher upfront cost through extended seal lifespan and reduced maintenance. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals nitrile is suitable for budget-sensitive projects, whereas polyurethane is beneficial when longevity and performance outweigh initial expenses.
Typical Applications in Sealing Industries
Nitrile rubber is extensively used in sealing applications involving oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based substances and moderate temperature range of -40degC to 120degC. Polyurethane rubber is favored in dynamic sealing environments such as hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic systems for its superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and elasticity, functioning effectively between -30degC and 80degC. Both materials serve critical roles in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery seals, with nitrile prioritized for fluid compatibility and polyurethane for mechanical durability.
Choosing the Right Material: Nitrile vs Polyurethane for Seals
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, making it a preferred choice for seals in automotive and industrial applications requiring strong chemical compatibility. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and elasticity, ideal for dynamic seals subject to heavy wear and mechanical stress. When selecting seals, prioritize nitrile for fluid compatibility and polyurethane for durability and mechanical performance to ensure optimal seal longevity and effectiveness.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com