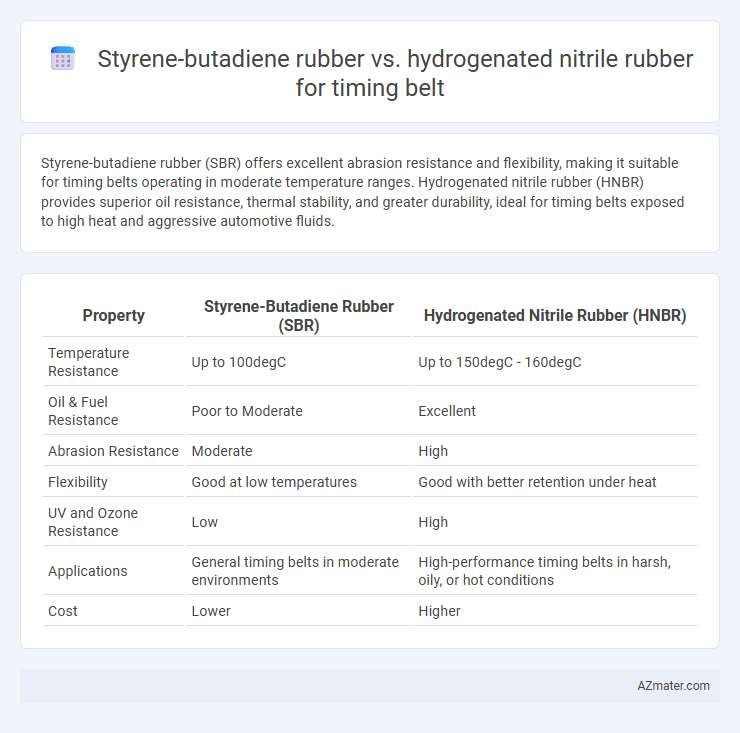
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for timing belts operating in moderate temperature ranges. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior oil resistance, thermal stability, and greater durability, ideal for timing belts exposed to high heat and aggressive automotive fluids.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 150degC - 160degC |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures | Good with better retention under heat |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Low | High |
| Applications | General timing belts in moderate environments | High-performance timing belts in harsh, oily, or hot conditions |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Timing Belts and Material Selection
Timing belts require materials with high wear resistance, thermal stability, and flexibility to ensure precise power transmission and durability. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for moderate temperature ranges and general-purpose timing belts. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance, heat tolerance up to 150degC, and enhanced mechanical properties, making it preferable for high-performance timing belts exposed to harsh environments.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance, aging stability, and good tensile strength, making it suitable for timing belt applications where durability and wear resistance are critical. SBR offers cost-effective performance with moderate thermal stability and flexibility but has lower oil and chemical resistance compared to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR). Its balanced mechanical properties make SBR ideal for timing belts in moderate temperature and load environments, whereas HNBR is preferred for more demanding conditions involving higher heat and exposure to oils.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for timing belts operating in harsh automotive environments. HNBR maintains excellent mechanical properties and dimensional stability at temperatures up to 150degC, extending timing belt lifespan in engines. Its enhanced abrasion resistance and low compression set ensure reliable performance and durability under continuous stress and exposure to automotive fluids.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good tensile strength, making it suitable for timing belts requiring moderate mechanical durability and flexibility. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, increased tensile strength up to 25 MPa, and enhanced resistance to oils and chemicals, resulting in longer service life under high-temperature and harsh oil-exposure conditions. For timing belt applications demanding elevated mechanical performance and chemical resilience, HNBR outperforms SBR in maintaining dimensional stability and tensile integrity over time.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate heat resistance and is generally less resistant to oils and chemicals, making it less suitable for high-temperature timing belt applications exposed to aggressive fluids. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat resistance up to 150degC and enhanced chemical stability against oils, fuels, and oxidizing agents, ensuring increased durability and longevity in demanding engine environments. The higher resilience of HNBR to thermal degradation and chemical exposure makes it the preferred material for timing belts requiring reliable performance under harsh automotive conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but falls short in oil and heat resistance, limiting durability in high-temperature automotive timing belt applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, ensuring enhanced longevity and reliability under harsh engine conditions. For timing belts exposed to oil, heat, and mechanical stress, HNBR outperforms SBR by providing extended service life and reduced maintenance intervals.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers lower initial costs and good abrasion resistance, making it a budget-friendly choice for timing belts in standard automotive applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) delivers superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance expenses despite higher upfront costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, HNBR can provide better long-term value through enhanced durability and reliability under extreme operating conditions.
Environmental Performance and Aging Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate environmental resistance but exhibits faster degradation under thermal and ozone exposure, making it less suitable for long-term aging resistance in timing belts. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior environmental performance with outstanding resistance to heat, oil, ozone, and chemicals, ensuring enhanced durability and longevity in harsh operating conditions. The enhanced cross-linking and hydrogenation in HNBR provide significantly improved aging resistance compared to SBR, extending the service life of timing belts in demanding automotive applications.
Industry Standards and Certification Requirements
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) for timing belts are evaluated under industry standards such as ASTM D2000 and ISO 1629 for material classification and performance criteria. HNBR offers superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance, meeting the stringent certification requirements of automotive OEMs like ISO/TS 16949 and SAE J200 for enhanced durability in high-temperature engine environments. SBR complies with general purpose standards but is limited in high-performance certification scopes due to lower thermal stability and oil resistance compared to HNBR.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Rubber for Timing Belts
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for general timing belt applications, while hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, ideal for demanding environments. HNBR's enhanced durability under high temperatures and exposure to automotive fluids often results in longer belt life and reduced maintenance. Selecting the best rubber depends on the specific operational conditions, where HNBR is preferred for high-performance engines and harsh conditions, and SBR fits standard applications with moderate demands.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Timing belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com